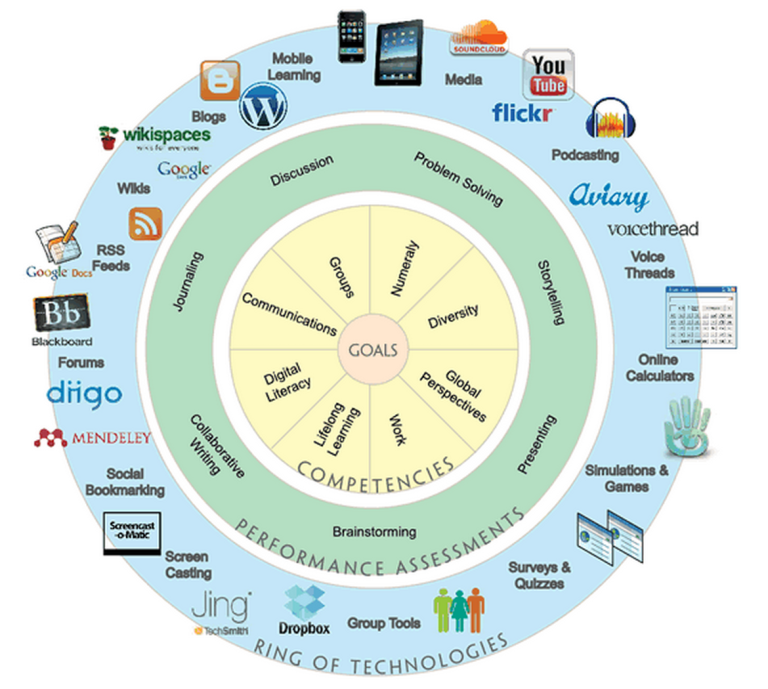
Technology Tools for Online Learning A Comprehensive Guide
Technology tools for online learning are revolutionizing education, creating dynamic and engaging learning experiences. This exploration delves into the diverse array of tools available, from video conferencing to interactive simulations, and examines their effectiveness, accessibility, and integration into existing platforms. We’ll also consider future trends and student perspectives on these powerful resources.
The various types of technology tools, ranging from learning management systems to collaborative platforms, will be meticulously categorized and examined. Their functionalities and features will be highlighted, focusing on their application in online education. This comprehensive analysis will explore the effectiveness of these tools for different learning styles and subject matters, as well as their impact on student engagement and knowledge retention. Accessibility and inclusivity are also central themes, ensuring equitable access for all learners.
Types of Technology Tools for Online Learning

A diverse range of technology tools empowers online learning experiences. These tools facilitate interaction, collaboration, and personalized learning pathways, enriching the educational journey for both students and instructors. Their effective implementation requires careful consideration of learning objectives and learner needs.
Technology Tools Categorization
Various technology tools cater to different aspects of online learning. Categorizing these tools provides a structured overview of their functionalities and applications. This organization aids in selecting appropriate tools for specific learning needs.
| Tool Name | Category | Key Features | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video Conferencing Platforms (e.g., Zoom, Google Meet) | Communication & Collaboration | Real-time audio and video communication, screen sharing, breakout rooms, chat functionalities | Facilitates synchronous interaction between instructors and students, enabling live lectures, discussions, and group work. Supports virtual classrooms and meetings. |
| Learning Management Systems (LMS) (e.g., Moodle, Canvas) | Course Management & Content Delivery | Course creation and organization, assignment submission, grading, communication tools, learning materials hosting, and progress tracking | Centralized platform for managing courses, delivering learning materials, facilitating communication, and assessing student progress. Provides a structured online learning environment. |
| Interactive Simulations & Virtual Labs (e.g., PhET Interactive Simulations, Labster) | Interactive Learning & Engagement | Interactive models, simulations, virtual experiments, data analysis tools, personalized feedback | Allow students to explore complex concepts, conduct virtual experiments, and gain hands-on experience in a safe and controlled environment. Useful for subjects like science, engineering, and medicine. |
| Online Assessment Platforms (e.g., Gradescope, Quizizz) | Assessment & Feedback | Automated grading, varied question types, instant feedback, progress tracking, and data analysis for performance improvement | Enable instructors to create and administer various types of assessments, automate grading, and provide students with timely feedback. This facilitates continuous assessment and improvement. |
| Collaborative Document Editors (e.g., Google Docs, Microsoft Office Online) | Collaboration & Content Creation | Real-time editing, version control, co-authoring capabilities, comments, and feedback features | Support simultaneous work on documents, presentations, and spreadsheets by multiple users. Fosters teamwork and collaborative learning experiences. |
| E-books and Digital Libraries (e.g., JSTOR, Project Gutenberg) | Content Access & Resources | Digital versions of books, journals, articles, and other learning materials, searchability, organization by subject | Provide accessible and organized digital resources for learning. Students can access and utilize a wide range of information materials. |
| Interactive Whiteboards (e.g., Smartboard, Activboard) | Interactive Learning & Engagement | Digital display for annotation, collaboration, presentation creation, and content display | Offer interactive tools for visual learning and presentations, facilitating active participation in learning activities. Enables real-time interaction and engagement. |
Functionalities and Applications in Online Education
Each tool listed above possesses unique functionalities that cater to distinct needs within online learning environments. Effective integration of these tools into the curriculum enhances student engagement and learning outcomes. The tools are designed to support various educational activities, including lectures, discussions, assessments, and collaborative projects.
Effectiveness and Impact
Online learning tools have demonstrably altered the landscape of education, offering unprecedented flexibility and accessibility. Their effectiveness, however, isn’t uniform. Different tools cater to varied learning styles and subject matters, impacting student engagement and knowledge retention in distinct ways. Understanding these nuances is crucial for maximizing the benefits of online learning environments.
The varying degrees of effectiveness depend heavily on the specific tool employed and how it aligns with the learner’s cognitive preferences. For example, interactive simulations might be highly effective for STEM subjects, promoting active learning and deeper comprehension. Conversely, video lectures might prove more suitable for subjects requiring a structured, linear approach, like history or literature. A critical element in evaluating tool effectiveness is the alignment of the pedagogical approach with the learning objectives.
Effectiveness for Different Learning Styles
Different learning styles respond differently to various online tools. Visual learners might find interactive diagrams and animations more engaging, while auditory learners might benefit from audio lectures and podcasts. Kinesthetic learners often thrive in environments that encourage hands-on activities and simulations. Tools that cater to a range of learning modalities are more likely to support diverse learners effectively. Understanding learner preferences is paramount for optimizing learning experiences.
Impact on Student Engagement and Knowledge Retention
The impact of different tools on student engagement and knowledge retention is multifaceted. Tools fostering active learning, such as collaborative projects and interactive exercises, often lead to higher engagement and more robust knowledge retention. Conversely, passive tools like solely relying on pre-recorded lectures can decrease engagement and hinder retention. Engaging and interactive tools facilitate active recall, which is a key component of long-term learning.
Role in Fostering Collaborative Learning Environments
Online tools play a crucial role in creating collaborative learning environments. Platforms that support real-time communication, such as video conferencing and discussion forums, allow students to interact, share ideas, and work together on projects. These tools facilitate peer-to-peer learning, where students can learn from each other’s perspectives and experiences.
Comparison of Tools for Specific Learning Objectives, Technology tools for online learning
| Tool | Learning Objective | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video lectures | Acquiring foundational knowledge | Accessible, flexible viewing, potentially broad reach | Passive learning, limited interaction, potential for disengagement |
| Interactive simulations | Developing problem-solving skills | Hands-on experience, active learning, application of knowledge | Potential complexity requires specific technical expertise |
| Collaborative platforms | Promoting teamwork and communication | Facilitates peer-to-peer learning and development of social skills | Potential for lack of participation, management challenges |
| Virtual labs | Conducting experiments and research | Safe, cost-effective access to resources not otherwise available | Requires reliable internet access, potential for technical issues |
The table above provides a concise overview. Each tool’s suitability is highly dependent on the specific learning objective. A tool deemed effective for one purpose might be less effective for another. A thorough understanding of the learning objectives and the specific needs of the learners is essential for selecting the most appropriate tools.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Technology Tools For Online Learning
Ensuring equitable access to online learning is paramount. This necessitates the incorporation of accessibility features in online learning tools, catering to diverse learning needs and backgrounds. Students with disabilities, diverse learning styles, and those facing geographical limitations all benefit from accessible educational resources. This section delves into the importance of these features, highlighting tools that support inclusivity and outlining methods for equitable access.
Accessibility in online learning environments goes beyond simply providing text alternatives for images. It encompasses a wider range of features, including adjustable font sizes, screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and alternative formats for multimedia content. These features are crucial for creating a truly inclusive learning experience where all students can participate and succeed.
Importance of Accessibility Features
Accessibility features in online learning tools are vital for fostering an inclusive environment. These features enable students with disabilities, diverse learning styles, and varying technological resources to engage fully with the learning material. They promote a more equitable learning experience, ensuring that all students can actively participate and succeed.
Tools Supporting Diverse Learning Needs
Numerous tools provide support for diverse learning needs. Examples include screen readers (like JAWS and NVDA), which convert text to speech, enabling students with visual impairments to access content. Captioning and transcription tools ensure that audio and video materials are accessible to students with hearing impairments. Furthermore, tools that offer adjustable font sizes, text-to-speech features, and alternative formats (like audio or large print) are vital for students with dyslexia, visual processing difficulties, or other learning differences. Interactive simulations and multimedia resources are often adapted for various learning styles.
Ensuring Equitable Access for All Students
Equitable access requires a multifaceted approach. This includes providing clear instructions and guidance on using accessibility features within online learning platforms. Training instructors on how to use assistive technologies can improve student support. Furthermore, creating a supportive learning environment where students feel comfortable requesting accommodations and seeking assistance is critical. Accessibility features should be integrated into the design process from the outset, not as an afterthought. This will ensure that all students can access and benefit from the learning materials and activities.
Accessibility Features of Different Learning Tools
| Learning Tool | Accessibility Features | Assistive Technology Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Canvas | Adjustable font sizes, screen reader compatibility (with extensions), alternative text for images, keyboard navigation | JAWS, NVDA, screen magnifiers |
| Google Classroom | Text-to-speech, adjustable font sizes, screen reader compatibility (with extensions), alternative formats | JAWS, NVDA, screen magnifiers |
| Zoom | Closed captioning, live transcription, adjustable font sizes, screen reader compatibility (with extensions) | JAWS, NVDA, screen magnifiers |
| Moodle | Screen reader compatibility (with extensions), alternative formats, adjustable font sizes, keyboard navigation | JAWS, NVDA, screen magnifiers |
Accessibility features should be seamlessly integrated into the learning platform, not as a separate or secondary option. This approach will ensure a unified and user-friendly experience for all students.
Integration and Implementation
Integrating technology tools effectively into online learning platforms requires careful planning and execution. A well-defined strategy, coupled with appropriate teacher training and ongoing evaluation, is crucial for successful implementation. This ensures that the tools enhance, rather than hinder, the learning experience.
Strategies for Effective Integration
A successful integration strategy considers the specific learning objectives of the course, the existing learning platform infrastructure, and the technical capabilities of the students and instructors. This tailored approach ensures the tools are seamlessly integrated into the existing framework.
- Alignment with Learning Objectives: Tools should directly support the learning outcomes of the course. For instance, a simulation tool might be ideal for a science course requiring practical application, while a collaborative platform might be best for courses fostering teamwork and communication skills.
- Platform Compatibility: Integration must consider the existing learning management system (LMS). Tools should be compatible with the platform’s functionality, avoiding the need for excessive manual workarounds or separate logins. This streamlined experience enhances user adoption.
- Student and Instructor Familiarity: Tools should be intuitive and easy to use for both students and instructors. Clear documentation, tutorials, and training materials are vital for effective adoption and minimizing technical issues.
Teacher Training and Support
Providing comprehensive training to instructors is paramount for successful integration. Training should cover both technical aspects and pedagogical approaches. Continuous support mechanisms are equally important.
- Needs Assessment: Before training, identify the specific needs and knowledge gaps of the instructors. Tailor the training to address these needs, providing relevant examples and practical exercises. This targeted approach maximizes the impact of the training.
- Hands-on Workshops: Provide opportunities for instructors to practice using the tools in a simulated classroom environment. Interactive workshops, including demonstrations, group activities, and Q&A sessions, are crucial for skill development.
- Ongoing Support Resources: Establish readily accessible resources, such as FAQs, online tutorials, and dedicated support channels (e.g., email, online forums). This continuous support network ensures that instructors feel confident and empowered to use the tools effectively.
Ongoing Evaluation and Feedback
Regular evaluation is essential to identify areas for improvement and optimize tool effectiveness. This iterative process involves gathering feedback from students and instructors.
- Data Collection: Track student engagement, participation, and performance metrics to evaluate tool effectiveness. Collect qualitative data through surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gain insights into the learning experience.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish channels for instructors and students to provide feedback on the tools’ usability, pedagogical value, and overall impact. Consider anonymous feedback mechanisms to encourage candid input.
- Iterative Improvement: Use the collected data and feedback to refine the integration strategy and make necessary adjustments to the tools and the training process. This iterative approach ensures continuous improvement in the learning experience.
Step-by-Step Guide: Integrating a Learning Tool
This example focuses on integrating a collaborative document editor into a course curriculum.
- Course Alignment: Identify specific learning objectives where collaboration is beneficial (e.g., group projects, shared research).
- Platform Compatibility: Ensure the editor is compatible with the LMS. If not, explore integrations or alternative solutions.
- Teacher Training: Provide a training session covering the tool’s functionalities, features, and integration with the LMS. Provide tutorials, sample documents, and hands-on practice exercises.
- Student Introduction: Include introductory material on the tool’s usage and guidelines for collaboration in the course syllabus. Provide initial support materials to students.
- Course Integration: Assign collaborative tasks using the tool, incorporating it into various course activities. Provide clear instructions and guidance.
- Monitoring and Feedback: Regularly monitor student participation and engagement with the tool. Collect feedback from students and instructors to identify areas for improvement.
Future Trends and Innovations
The online learning landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting pedagogical approaches. Predicting the future is inherently challenging, but examining current trends and emerging technologies provides a glimpse into the potential trajectory of online education. This section explores emerging trends, the role of AI and machine learning, and examples of innovative tools shaping the future of online learning.
Emerging Trends in Online Learning Tools
The evolution of online learning is characterized by a continual drive for personalization, enhanced accessibility, and immersive experiences. This necessitates a shift from one-size-fits-all approaches to individualized learning paths, leveraging data and technology to cater to diverse learning styles and needs. Further, the integration of augmented and virtual reality is anticipated to create more engaging and interactive learning environments.
- Personalized Learning Experiences: Adaptive learning platforms will play a crucial role in tailoring educational content and pacing to individual student needs. These platforms will analyze student performance data to identify strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences, dynamically adjusting the curriculum and providing targeted support.
- Immersive Learning Environments: Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies will offer more realistic and engaging learning experiences. For instance, students could virtually explore historical sites or conduct scientific experiments in simulated environments, leading to a deeper understanding of complex concepts.
- AI-Powered Tutoring and Support: AI tutors will provide personalized feedback, answer questions, and offer targeted support to students, thereby augmenting the role of human instructors. These systems will adapt to individual student needs and learning styles, fostering more effective and efficient learning.
Potential of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize online education, offering opportunities for personalized learning, automated assessments, and intelligent content generation. AI-powered systems can analyze student performance data to identify areas needing improvement and provide targeted interventions. Machine learning algorithms can also personalize learning pathways and adapt to individual student needs.
- Personalized Learning Pathways: AI algorithms can analyze student performance data, learning styles, and preferences to create customized learning pathways. This allows for a more efficient and effective learning experience, catering to individual needs.
- Automated Assessments: AI can automate various assessment tasks, including grading assignments and quizzes. This allows educators to focus on more nuanced aspects of student learning, providing timely feedback and support.
- Intelligent Content Generation: AI can be used to generate educational content, such as interactive exercises, simulations, and personalized study materials. This enables educators to create a more dynamic and engaging learning experience.
Examples of Innovative Tools
Several innovative tools are transforming online learning experiences. These include platforms that offer adaptive learning experiences, AI-powered tutoring systems, and virtual reality simulations. One notable example is Khan Academy’s adaptive learning platform, which dynamically adjusts the difficulty of lessons based on student performance.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: Platforms like Khan Academy leverage AI to adjust the difficulty of learning materials in real time, ensuring optimal learning for each student. The platform tailors the learning experience to each student’s pace and progress.
- AI-powered tutoring Systems: These systems provide personalized feedback, identify areas of weakness, and offer tailored support. This personalized approach ensures that students receive the right level of assistance at the right time.
- Virtual Reality Simulations: VR simulations offer immersive learning experiences, allowing students to interact with virtual environments and explore complex concepts. These interactive simulations can be used in fields like science, history, and engineering.
Practical Applications
Putting technology tools into action in online learning environments is crucial for effective and engaging experiences. This section explores diverse applications of these tools across different subjects and learning levels, showcasing real-world examples and highlighting how teachers can leverage them to create dynamic and interactive lessons. A successful implementation of a specific tool will be presented as a case study.
Applications in Different Subjects
Various technology tools cater to diverse subject areas. For instance, interactive simulations are beneficial in science classes to demonstrate complex concepts like chemical reactions or planetary movements. In history, virtual field trips to historical sites allow students to experience the past firsthand, fostering a deeper understanding of events and cultures. Mathematics can be enhanced by online graphing calculators and dynamic geometry software, enabling students to visualize and manipulate mathematical objects with ease. Language learning platforms provide opportunities for immersive communication practice, making the process more engaging and effective.
Applications Across Learning Levels
Technology tools are adaptable to various learning levels, from elementary to higher education. For younger learners, interactive games and educational apps can make learning fun and engaging. These tools can be tailored to specific learning objectives and provide customized feedback, supporting individual progress. In higher education, students can use collaborative platforms for group projects and research, fostering teamwork and critical thinking skills. Online simulations and virtual labs can provide advanced learners with opportunities to explore complex phenomena in a safe and controlled environment.
Creating Engaging Learning Experiences
Technology tools can transform online learning into dynamic and interactive experiences. Teachers can leverage tools like video conferencing to facilitate real-time discussions and Q&A sessions. Interactive whiteboards and online quizzes can enhance engagement and encourage active participation. Gamified learning platforms can motivate students and provide immediate feedback, fostering a sense of accomplishment. Tools that allow for personalized learning pathways can cater to individual student needs and preferences, leading to more effective learning outcomes.
Real-World Use Cases
Several real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of technology tools in online learning environments. A high school history class might use a virtual museum tour to study ancient civilizations, enabling students to experience the past through immersive visuals. In a university biology course, students could utilize online simulations to perform virtual experiments, exploring scientific concepts in a safe and controlled environment. A language learning program could incorporate interactive exercises and audio recordings, allowing students to practice pronunciation and improve fluency.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of Google Classroom
This case study examines the successful implementation of Google Classroom in a middle school online learning environment. The teachers used Google Classroom to streamline assignments, provide immediate feedback, and facilitate communication with students. Assignments were organized, and students had access to all relevant materials in one place. This improved student engagement and reduced the administrative burden for teachers. Regular progress updates and clear communication channels fostered a supportive learning environment.
Students reported feeling more connected to their learning and having more access to resources. Teachers also found the tool efficient for managing and delivering assignments. This enhanced communication and feedback mechanisms, leading to improved student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
Student Perspectives

Source: teachthought.com
Online learning environments are increasingly reliant on technology tools. Understanding student experiences with these tools is crucial for optimizing the learning process and ensuring their effectiveness. Student feedback provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of various platforms and applications, ultimately shaping the future of online education.
Student Experience with Technology Tools
Students interact with online learning platforms and applications in diverse ways. Their engagement with these tools often depends on the specific learning activities, the level of support provided, and the overall design of the online environment. Accessibility, usability, and the level of interactivity significantly influence the student experience. Some students thrive in the flexibility and independence online learning offers, while others might find it challenging to adapt to the new learning paradigm. This variability underscores the need for a nuanced approach to incorporating technology tools into online learning.
Student Feedback on Tool Usefulness
Student feedback reveals varying levels of satisfaction and usefulness across different technology tools. Some tools are highly praised for their ease of use, interactive features, and ability to enhance understanding. Conversely, other tools may receive criticism for their complexity, limited functionality, or lack of integration with other learning resources. This feedback highlights the importance of carefully selecting and implementing technology tools tailored to specific learning needs. A balance between functionality and simplicity is crucial for effective integration.
Areas for Tool Improvement
Students often identify areas for improvement in technology tools used for online learning. One recurring theme is the need for more intuitive interfaces and user-friendly navigation. Students also frequently request improved integration with other learning resources, including library databases, online tutorials, and other educational platforms. Personalized learning experiences and opportunities for active engagement are also commonly highlighted as areas for enhancement. Further development of tools that cater to diverse learning styles and provide more immediate feedback is a critical consideration.
Student Quotes on Technology Tools
- “The video conferencing software is great for discussions, but the recording feature could be more reliable.”
- “I love how interactive the online simulations are; they make learning so much more engaging.”
- “The platform’s interface is a bit confusing; it would be helpful if there were more clear instructions and visual guides.”
- “The online library database is a fantastic resource, but it could be easier to find specific articles.”
- “The interactive quizzes are really helpful for self-assessment, but more varied question types would be beneficial.”
These quotes represent a sample of student perspectives, emphasizing the importance of considering student feedback when designing and implementing technology tools for online learning. A comprehensive understanding of student needs and preferences can lead to more effective and engaging learning experiences.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, technology tools for online learning are transforming the educational landscape. From improving accessibility to fostering collaboration, these tools are essential for creating a richer and more effective learning environment. By understanding their effectiveness, integrating them thoughtfully, and continuously evaluating their impact, educators can leverage technology to maximize student outcomes and personalize the learning journey. Future trends, like the potential of AI and machine learning, suggest even more innovative applications in the years to come.