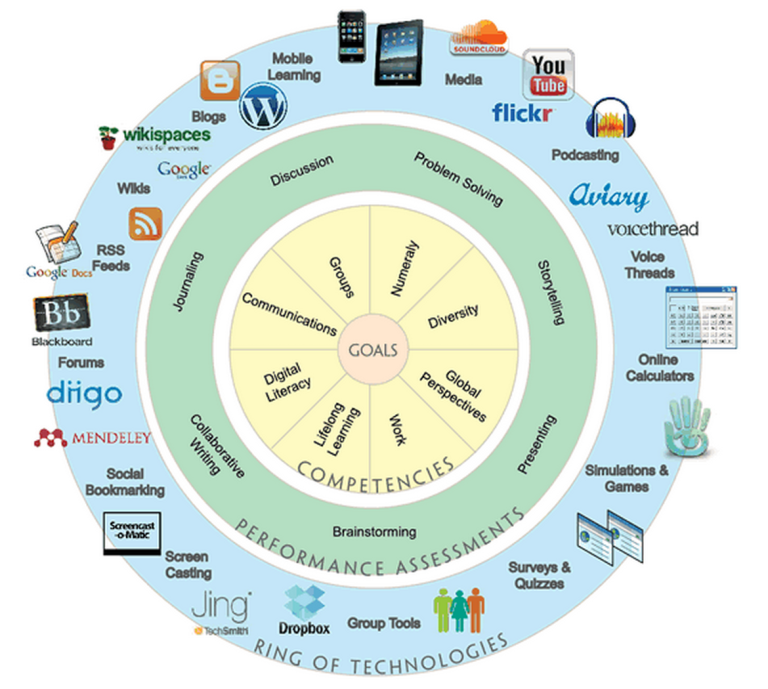
Teachers and Technology Classroom Revolution
Teachers and technology in the classroom are rapidly transforming how students learn. From innovative teaching methods to enhanced curriculum development, technology is redefining the educational landscape. This evolution brings exciting opportunities for personalized learning, increased student engagement, and the integration of digital literacy skills. However, careful consideration must be given to the equitable access, teacher training, and assessment strategies needed to fully realize the potential of technology in the classroom.
The impact of technology on teaching methods is profound, ranging from the use of interactive whiteboards to online learning platforms. Blended learning models, project-based learning, and personalized learning experiences are becoming increasingly prevalent, highlighting the versatility and adaptability of technology in diverse classroom settings. The integration of technology necessitates a thoughtful approach to curriculum development, considering both the strengths and weaknesses of different online platforms and digital tools. Moreover, fostering a culture of digital literacy is crucial for both students and teachers, equipping them with the skills needed to navigate the ever-evolving technological landscape.
The Impact of Technology on Teaching Methods
Technology has profoundly reshaped the landscape of education, impacting teaching methods across various subjects. Traditional lectures are increasingly complemented by interactive digital tools, fostering a more dynamic and engaging learning environment. This transformation is driven by the desire to cater to diverse learning styles and provide more personalized learning experiences.
Technological advancements have enabled teachers to leverage a wider array of resources and approaches. From interactive simulations to online collaboration tools, the use of technology has enriched the learning process, offering students opportunities to explore concepts in new and innovative ways. The evolution of teaching methods is also influenced by the need to prepare students for the demands of a rapidly changing world.
Alterations to Traditional Teaching Methods
Traditional teaching methods, often centered around lectures and textbooks, have been significantly modified by the integration of technology. For example, in history classes, students can now access primary source documents online, fostering a deeper understanding of historical events. Similarly, in science classes, interactive simulations allow students to experiment with complex concepts virtually, reducing the need for expensive laboratory equipment. Mathematics lessons can now incorporate dynamic software that provides immediate feedback and personalized practice. Language learning has also benefited, with online platforms offering language exchange opportunities and virtual immersion experiences.
Pedagogical Approaches Utilizing Technology
Different pedagogical approaches utilize technology in diverse ways. Blended learning models combine online and offline instruction, providing flexibility and personalized learning paths. Project-based learning, facilitated by digital tools for research and collaboration, encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Personalized learning platforms use data to tailor instruction to individual student needs, offering customized learning pathways. These methods, while promising, require careful consideration of potential disadvantages and equitable access to resources.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in the Classroom
The integration of technology in education presents a plethora of advantages. Enhanced engagement and active learning, facilitated by interactive tools and simulations, are key benefits. Students can also access a wider range of resources and learning materials online, improving accessibility. However, the use of technology also presents potential drawbacks. Unequal access to technology and reliable internet connectivity can exacerbate existing disparities among students. Furthermore, the effective integration of technology necessitates adequate teacher training and ongoing support. The digital divide, varying levels of technical proficiency, and the potential for distraction are also factors that must be considered. A balanced approach that emphasizes digital literacy, equitable access, and teacher support is crucial.
Comparison of Online Learning Platforms
| Platform | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Moodle | Highly customizable, robust features for course management, versatile for various educational levels. | The steeper learning curve for teachers can be overwhelming for some users due to complex features. |
| Canvas | Intuitive interface, strong mobile compatibility, seamless integration with other educational tools. | Limited customization options compared to Moodle, potentially less flexible for specific needs. |
| Google Classroom | User-friendly, easily integrated with existing Google tools, accessible on various devices. | Limited features for advanced course management may not be suitable for complex or large-scale courses. |
Different online learning platforms offer distinct functionalities and user experiences. Careful consideration of specific needs and resources is essential when selecting a platform for a particular course or institution. The table above provides a general overview of the key characteristics of common platforms.
Integrating Technology into Curriculum Development

Integrating technology effectively into the curriculum is crucial for preparing students for the 21st-century workplace and fostering a dynamic learning environment. It necessitates a thoughtful approach that goes beyond simply adding technology to existing methods. Instead, technology must be strategically interwoven into the curriculum’s fabric, enhancing learning outcomes and cultivating essential digital literacy skills.
This integration requires a shift in pedagogical approaches, moving away from teacher-centered models to student-centered learning environments where technology facilitates active participation, collaboration, and critical thinking. Curriculum developers must carefully consider how technology can augment and transform existing lessons, fostering deeper understanding and promoting engagement.
Strategies for Integrating Technology Across Subject Areas
Effective integration of technology requires careful planning and consideration of the subject matter. Technology can be used to supplement, enhance, or even transform the way a subject is taught. For instance, in history, interactive timelines and virtual field trips can bring historical events to life. In science, simulations can demonstrate complex processes and phenomena. In mathematics, interactive software can provide dynamic representations of abstract concepts.
Innovative Projects and Activities
Numerous innovative projects and activities leverage technology to foster student engagement and enhance learning outcomes. One example is using digital storytelling tools to allow students to explore and express their understanding of a historical event. Another example is creating interactive models in science class to explore physical principles. Collaborative projects, where students work together remotely using shared online platforms, can develop critical thinking and communication skills. A mathematics project might use online simulations to visualize geometric proofs or solve complex equations.
Incorporating Digital Literacy Skills
Digital literacy is not just about using technology; it’s about critically evaluating information, understanding ethical considerations, and using technology responsibly. Incorporating digital literacy skills into the curriculum equips students with the tools to navigate the digital world safely and effectively. Both students and teachers must develop these skills. By understanding and utilizing digital tools appropriately, students can develop crucial 21st-century skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration.
Digital Literacy Skills for Teachers
Developing teachers’ digital literacy skills is paramount for effective technology integration. These skills are essential to help teachers implement innovative teaching methods.
| Digital Literacy Skill | Description | How to Teach |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Proficiency | Understanding and effectively using various technological tools and platforms. | Provide opportunities for teachers to explore and experiment with different software and hardware. Offer workshops and professional development sessions on specific software. |
| Digital Content Creation | Creating digital resources and materials for teaching and learning. | Encourage teachers to create interactive lessons, presentations, or assessments using different tools. Provide examples and templates for various media types. |
| Assessment and Evaluation | Using technology for assessment and evaluation, such as online quizzes, rubrics, and feedback tools. | Provide opportunities to use online assessment tools and platforms. Offer training on creating effective online assessments. Show how to utilize technology for gathering feedback and giving personalized feedback. |
| Digital Safety and Security | Protecting personal information and maintaining a safe online environment. | Provide workshops and training sessions on digital citizenship and online safety. Establish clear guidelines and expectations for appropriate online behavior. |
| Critical Evaluation of Information | Evaluating the credibility and accuracy of online information. | Develop critical thinking exercises and activities focusing on identifying biases, verifying sources, and evaluating information validity. |
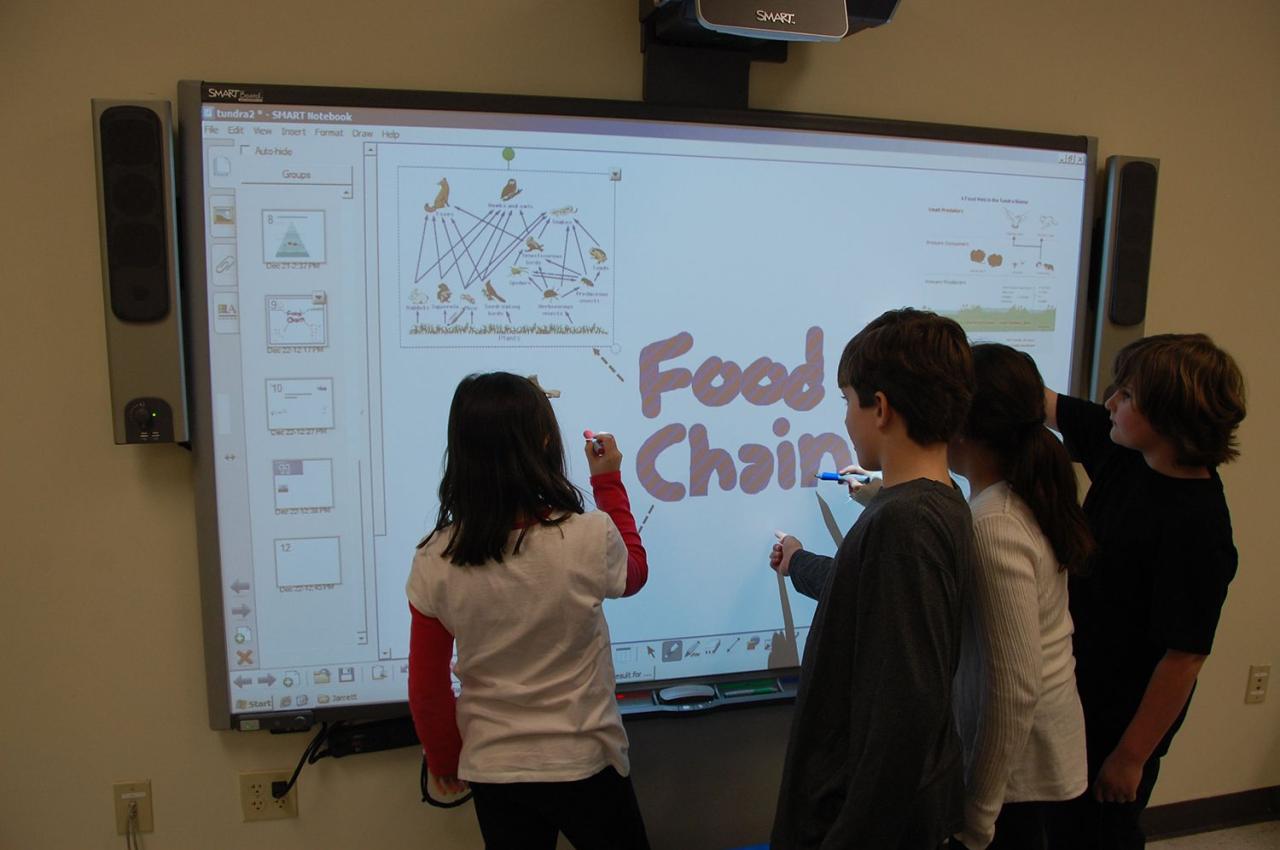
Technology and Student Engagement

Source: thoughtco.com
Technology has profoundly impacted student engagement and motivation across various learning environments. It offers exciting opportunities to personalize learning, foster collaboration, and create dynamic learning experiences that captivate students. This transformation is crucial for enhancing knowledge retention and cultivating a love for learning.
Technology’s ability to tailor educational experiences to individual student needs and learning styles is a significant factor in increased engagement. By providing interactive and adaptive learning platforms, technology can effectively cater to diverse learning preferences, thus enhancing student motivation and participation.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Technology significantly influences student motivation and engagement. Interactive simulations, virtual field trips, and gamified learning platforms make learning more exciting and relatable, leading to higher levels of student interest and participation. This heightened engagement can also foster a sense of accomplishment and ownership in the learning process, boosting intrinsic motivation.
Interactive and Dynamic Learning Experiences
Technology empowers educators to create interactive and dynamic learning experiences. For example, online simulations allow students to explore complex concepts in a safe and controlled environment, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking. Virtual field trips offer opportunities for students to experience different cultures, historical events, or scientific phenomena without geographical limitations, making learning more engaging and enriching.
Promoting Collaboration and Communication
Technology facilitates collaboration and communication among students in a variety of ways. Online collaborative platforms enable students to work together on projects, share ideas, and provide feedback, fostering teamwork and communication skills. Real-time communication tools, such as video conferencing and discussion forums, facilitate seamless interaction among students and teachers, breaking down geographical barriers and creating a more connected learning community.
Examples of Interactive Learning Tools
- Interactive Simulations: These tools allow students to manipulate variables and observe the consequences in a safe environment. Examples include simulations of chemical reactions, biological processes, or historical events. These can lead to deeper understanding and critical thinking skills by allowing students to experiment and discover relationships.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Immersive experiences provided by VR and AR technologies allow students to explore historical sites, visit different countries, or participate in scientific experiments, making learning more captivating and memorable. For instance, a VR tour of a historical museum can be far more impactful than a textbook description.
- Gamified Learning Platforms: These platforms use game mechanics to make learning more engaging and fun. Points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges can motivate students to participate actively and progress through the material. These platforms often incorporate interactive elements, making the learning process more dynamic and enjoyable.
- Online Collaborative Tools: Platforms like Google Docs, shared online spreadsheets, and project management software enable students to work together on projects in real time. This fosters teamwork and communication skills, which are crucial for success in various professional settings.
Table of Interactive Learning Tools
| Tool Type | Description | Potential Impact on Engagement |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive Simulations | Allow students to manipulate variables and observe consequences | Increased understanding, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills |
| Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) | Provide immersive learning experiences | Enhanced engagement, deeper understanding, and memorable learning experiences |
| Gamified Learning Platforms | Utilize game mechanics to make learning more engaging | Increased motivation, active participation, and a sense of accomplishment |
| Online Collaborative Tools | Enable real-time collaboration on projects | Improved teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills |
Teacher Training and Professional Development
Effective technology integration in the classroom hinges on well-prepared teachers. Comprehensive teacher training and ongoing professional development programs are crucial for equipping educators with the skills and knowledge necessary to leverage technology effectively. These programs must go beyond basic technical instruction, focusing instead on pedagogical strategies that seamlessly weave technology into existing curricula.
Teacher training programs should focus on more than just technical proficiency. A crucial aspect is helping teachers understand how technology can enhance student learning and engagement, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This includes exploring innovative teaching methods, such as project-based learning and personalized learning pathways, where technology plays a key role.
Importance of Targeted Training
Teacher training programs should be tailored to specific needs and contexts. Recognizing that different schools and districts have varying technological infrastructure and teacher experience levels is essential. Tailoring training to the specific needs of a school or district ensures that the training is relevant and practical, increasing the likelihood of successful implementation. This targeted approach will also account for the varied teaching styles and subject matter expertise within the staff.
Approaches to Ongoing Support and Resources
Providing ongoing support and resources is just as important as initial training. This involves establishing ongoing support structures that include access to online communities, mentoring programs, and readily available resources. This may include providing access to online learning platforms with interactive tutorials, downloadable materials, and downloadable templates.
Regular workshops and seminars should also be offered to provide teachers with opportunities to explore new technologies and innovative pedagogical strategies. These workshops should encourage active learning, allowing teachers to practice using new technologies and share their experiences with colleagues. Furthermore, fostering a supportive environment where teachers can freely ask questions, share best practices, and receive feedback is essential.
Encouraging Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Fostering a culture of collaboration and knowledge-sharing among teachers is vital for successful technology integration. This can be achieved by establishing online platforms where teachers can connect, share resources, and collaborate on projects. Teachers can also benefit from peer observation, where experienced teachers observe their colleagues’ classroom practices, offering feedback and guidance on technology integration.
Peer-to-peer learning groups can provide invaluable support and insights. These groups can focus on specific subject areas, offering targeted support and expertise in using technology to teach particular concepts or skills. Creating a platform for sharing successful teaching strategies, lessons learned, and innovative ideas is crucial for building a collaborative community.
Resources for Teacher Development
- Online Courses: Numerous platforms offer online courses focused on technology integration in education, covering a wide range of software and applications. These courses often provide certifications or professional development credits.
- Workshops: Local school districts, educational technology companies, and universities often conduct workshops on specific technologies or teaching strategies. These workshops provide hands-on experiences and opportunities to interact with peers.
- Articles and Blogs: Numerous educational technology blogs and journals publish articles about effective technology integration in the classroom. These resources can offer practical tips and strategies for teachers.
This structured approach to providing teachers with the necessary resources will help them feel confident and equipped to use technology in the classroom. This will lead to more effective and engaging learning experiences for students.
Assessment and Evaluation with Technology
Technology offers powerful tools to enhance student assessment, moving beyond traditional methods to create a more comprehensive and engaging learning experience. This shift allows for a more dynamic evaluation of student understanding, fostering a deeper grasp of concepts and individual learning styles.
Effective integration of technology in assessment demands a thoughtful approach. It’s not merely about replacing paper-and-pencil tests with digital versions but rather about leveraging technology’s capabilities to collect, analyze, and interpret data in new and insightful ways. This multifaceted approach provides teachers with a richer understanding of student progress and allows for more tailored instruction.
Innovative Assessment Tools and Strategies, Teachers and technology in the classroom</h3>
Technology provides a wealth of innovative assessment tools and strategies. Digital platforms facilitate the creation of interactive quizzes, simulations, and virtual labs. These tools allow students to explore complex concepts in a dynamic environment, fostering active learning and providing immediate feedback. Furthermore, adaptive learning platforms can personalize the learning experience by adjusting difficulty levels based on individual student performance.
Examples of Innovative Assessment Tools
- Interactive Simulations: Simulations of scientific processes, historical events, or economic models allow students to experiment and observe real-world phenomena in a controlled environment. For instance, a chemistry simulation allows students to conduct virtual experiments, observing reactions and collecting data without the risks associated with physical lab work.
- Online Portfolios: Digital portfolios provide a comprehensive collection of student work, demonstrating progress over time. Students can showcase projects, assignments, and reflections, providing a dynamic and visual representation of their learning journey. This allows for a deeper understanding of student growth, critical thinking skills, and self-assessment.
- Coding Platforms: Programming environments allow students to develop their computational thinking and problem-solving skills through interactive exercises and projects. Students can receive immediate feedback on their code, facilitating the iterative process of learning and development.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Implementing technology in assessment presents certain challenges. Ensuring equitable access to technology and reliable internet connectivity is crucial for all students. Moreover, concerns regarding data privacy and security need careful consideration. Students’ personal information should be handled responsibly and according to established ethical guidelines. Furthermore, appropriate training and support for teachers are necessary to ensure effective utilization of technology for assessment purposes.
Technology-Based Assessment Tools and Applications
| Type of Technology-Based Assessment Tool | Potential Applications in Various Subjects |
|---|---|
| Interactive Simulations | Science (e.g., biological processes, chemical reactions), Social Studies (e.g., historical events, economic models), Math (e.g., geometric transformations, statistical analysis) |
| Online Quizzes and Tests | All subjects (e.g., checking comprehension of concepts, assessing knowledge retention) |
| Digital Portfolios | All subjects (e.g., showcasing projects, reflecting on learning, demonstrating creativity) |
| Adaptive Learning Platforms | All subjects (e.g., personalizing learning experience, adjusting difficulty levels, providing targeted feedback) |
| Coding Platforms | Computer Science, Math, and problem-solving in other subjects (e.g., developing algorithms, building applications, visualizing data) |
Equity and Access in Technology Integration: Teachers And Technology In The Classroom
Bridging the digital divide is crucial for ensuring that all students have equal opportunities to learn and thrive in a technology-rich classroom. This involves recognizing the varying levels of access students have to technology at home and school and actively working to create equitable learning experiences for all.
Addressing the digital divide requires a multifaceted approach, going beyond simply providing devices. Schools must consider the broader context of student needs, including internet access, digital literacy support, and a supportive learning environment that leverages technology effectively.
Challenges of Equitable Access
Unequal access to technology can stem from socioeconomic factors, geographical location, and individual circumstances. Students from low-income families may lack the necessary devices or internet access at home, creating a significant learning disparity. Similarly, students in rural areas often experience limited internet bandwidth, hindering their ability to participate in online learning activities. Additionally, students with disabilities may require specialized assistive technologies, which may not be readily available or accessible to all. These factors create a complex web of challenges in ensuring equitable access to technology.
Examples of Promoting Technology Integration in Diverse Environments
Several initiatives exemplify effective technology integration in diverse learning environments. One example involves partnering with community organizations to provide internet access and digital literacy training for families in underserved communities. Another initiative is to provide loaner devices to students who lack access at home. Schools are also increasingly incorporating mobile learning solutions, such as tablets and laptops, to ensure access to technology across different locations and learning styles. These examples illustrate a range of approaches to promoting equitable access.
Strategies for Addressing the Digital Divide
Several strategies can be employed to effectively address the digital divide and ensure equitable access to technology resources. A crucial element is establishing clear school-wide policies that the expectation for all students to have access to technology and to provide appropriate support. Additionally, schools can establish clear support systems for students and families to ensure they have the resources and guidance to use technology effectively. Furthermore, developing partnerships with community organizations and local businesses can provide access to necessary technology resources.
Practical Steps for Ensuring Technology Access
Schools can take several practical steps to guarantee that all students have access to technology and support for its use in the classroom. A key step is developing a comprehensive technology access plan that articulates the resources available, procedures for obtaining them, and training for both teachers and students. Schools should also provide ongoing professional development for teachers on integrating technology effectively in diverse learning environments. Establishing clear support structures for students who may need additional assistance is essential, including dedicated staff or student mentors. Regular assessment of technology access and use can ensure that the plan remains relevant and effective.
- Inventory and Allocation: Conduct a thorough inventory of available technology resources (computers, internet access, software) and develop a plan for equitable allocation to different classrooms and learning spaces. This includes prioritizing areas with the highest need.
- Device Provisioning: Implement a device loan program for students who lack access at home. This could involve providing laptops, tablets, or other mobile devices, ensuring that they are maintained and supported. Ensure proper training for students on the use of these devices.
- Internet Connectivity: Work with internet providers to explore options for subsidized or discounted internet access for families. Consider implementing school-wide Wi-Fi networks and hot-spots to enhance connectivity.
- Professional Development: Provide comprehensive training to teachers on the effective integration of technology into their teaching methods. Focus on strategies for inclusive learning and accessibility for all students.
- Community Partnerships: Collaborate with community organizations, businesses, and local libraries to provide access to technology resources, workshops, and mentorship programs.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of technology integration initiatives, gathering feedback from students, teachers, and parents. Use this feedback to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
Future Trends in Technology Integration
The integration of technology in education is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in various fields. Predicting the future of this integration requires careful consideration of emerging technologies and their potential impact on teaching methodologies, student learning, and the role of educators. This exploration examines potential future trends, focusing on the influence of artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR) on the learning environment.
Potential Future Trends in Technology Use
The educational landscape is poised for significant transformations. A blend of factors, including evolving student needs, technological advancements, and pedagogical innovations, will shape the future of technology integration. Foremost among these is the rise of personalized learning experiences powered by AI and adaptive learning platforms. Further, the immersive potential of VR and augmented reality (AR) is expected to revolutionize classroom activities.
Impact of AI on Teaching and Learning
Artificial intelligence is rapidly changing how educators interact with students and create personalized learning paths. AI-powered tools can analyze student performance data in real time, identifying areas where students need additional support or enrichment. This data-driven approach allows for individualized instruction, catering to diverse learning styles and paces. For instance, adaptive learning platforms adjust the difficulty of questions based on student responses, ensuring optimal learning engagement. This customized approach allows for a more targeted and effective learning experience, ultimately improving student outcomes.
Impact of VR and AR on Teaching and Learning
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for immersive learning experiences. Students can explore historical events, conduct virtual field trips, and engage in interactive simulations. For example, students can visualize the human circulatory system in a 3D VR environment, fostering a deeper understanding of complex concepts. Likewise, AR can overlay digital information onto the physical world, bringing abstract concepts to life. This enhanced visualization and interaction can significantly improve comprehension and retention.
Influence on Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
The evolving role of teachers in the technology-integrated classroom requires continuous professional development. Teachers will need to shift from simply delivering content to facilitating learning experiences that leverage technology. This means becoming adept at utilizing various educational tools, designing engaging learning activities, and guiding students in their technology use. In addition, teachers will need to foster digital literacy skills in students, equipping them with the knowledge and abilities to navigate the digital world responsibly and effectively.
Mind Map: Future Trends in Technology Integration
| Category | Key Features | Examples | Potential Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Learning | AI-driven adaptive learning platforms, customized content, real-time feedback | Khan Academy, Duolingo, and personalized learning apps | Improved student engagement, tailored learning experiences, and enhanced learning outcomes |
| Immersive Learning | VR, AR, interactive simulations, virtual field trips | Virtual museums, anatomical models, historical reenactments | Enhanced comprehension, deeper understanding of complex concepts, increased motivation and engagement |
| Teacher Roles | Facilitators, designers of learning experiences, mentors in digital literacy | Creating interactive lessons, guiding students in digital tools, developing critical thinking skills | Increased demand for pedagogical innovation, enhanced student outcomes, and the need for continuous professional development. |
“The future of education is not about replacing teachers with technology, but about empowering teachers with technology to enhance the learning experience.”
Outcome Summary

Source: elearningindustry.com
In conclusion, the integration of technology in the classroom is a dynamic process, impacting teaching methods, curriculum development, and student engagement. From fostering digital literacy to ensuring equitable access, this exploration highlights the multifaceted nature of technology integration in education. The future of education, powered by emerging technologies, presents both challenges and opportunities. Ultimately, teachers and technology in the classroom are not merely tools but rather catalysts for fostering creativity, collaboration, and a lifelong love of learning. Successful implementation necessitates ongoing teacher training, robust assessment strategies, and a commitment to equity.