Online Masters in STEM Education
Master’s in STEM education online offers a flexible and accessible path to advanced learning. This program provides a comprehensive curriculum, catering to various specializations within the STEM field. It equips graduates with the knowledge and skills necessary for a successful career in this rapidly evolving sector.
The program’s structure typically involves a blend of theoretical coursework and practical applications. Students can expect to delve into various STEM disciplines, from mathematics and engineering to computer science and the natural sciences. Furthermore, the program acknowledges the importance of technology integration in modern education and includes the use of various learning management systems and online resources. This structured approach allows students to master crucial STEM skills, such as critical thinking and problem-solving, while working around their schedules.
Introduction to Online Master’s in STEM Education
Source: bestkidstuff.com
Online Master’s programs in STEM education provide a flexible and accessible pathway for individuals to deepen their understanding of teaching and learning within science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. These programs are designed to equip educators with advanced pedagogical knowledge, research skills, and specialized subject matter expertise, fostering a new generation of effective STEM educators. They offer a unique blend of theoretical frameworks and practical applications, often incorporating real-world case studies and interactive learning experiences.
These programs typically follow a structured curriculum that combines coursework in educational theory, research methodologies, and specialized STEM content. The learning experience is often enhanced by virtual collaboration and interactive online tools. Flexibility is a key benefit, allowing learners to fit their studies around existing commitments and geographical limitations.
<h3>Curriculum Structure</h3>
The curriculum in online STEM education master’s programs typically comprises core courses in educational psychology, curriculum design, and assessment strategies. These courses lay the foundation for understanding how students learn and how to effectively teach STEM concepts. Students also take specialized courses focusing on specific STEM disciplines, allowing them to develop subject matter expertise and teaching skills in areas like physics, biology, or computer science. The program may also incorporate practicum experiences, enabling students to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world settings, even if remotely.
<h3>Specializations</h3>
Online Master’s programs in STEM education often offer diverse specializations to cater to varied interests and career goals. Some common specializations include:
- STEM Curriculum Development: This specialization focuses on the creation and implementation of engaging and effective STEM curricula, aligning them with educational standards and best practices.
- STEM Teacher Leadership: This area prepares educators to lead and mentor colleagues, fostering a collaborative and innovative learning environment within their schools or institutions.
- STEM Assessment and Evaluation: This specialization emphasizes the development and use of diverse assessment methods to evaluate student learning and understanding in STEM subjects.
- Technology Integration in STEM Education: This focus emphasizes the effective integration of technology to enhance STEM instruction, utilizing digital tools and resources to engage students.
<h3>Career Paths</h3>
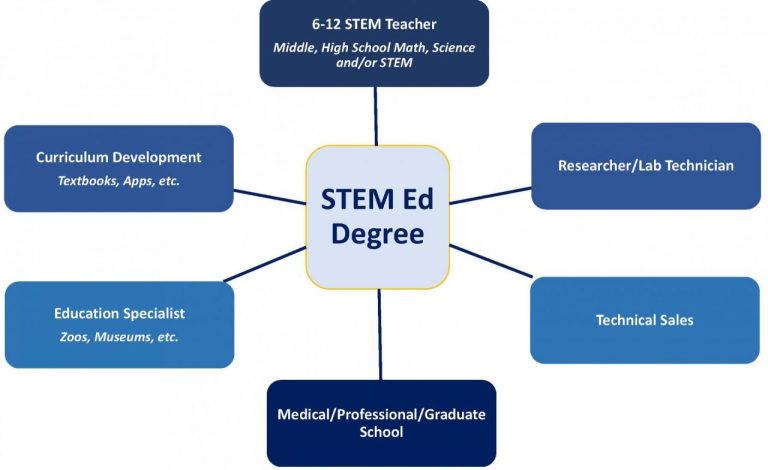
Graduates of online STEM education master’s programs can pursue various fulfilling career paths. These include roles like STEM teacher educators, curriculum developers, STEM program coordinators, instructional designers, and educational researchers. Many graduates also use their expertise to design and implement STEM programs within organizations or educational institutions. Some may transition into leadership roles within school districts or other educational settings.
<h3>Comparison of Online and In-Person Programs</h3>
| Feature | Online Program | In-Person Program |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Anywhere with internet access | Specific campus location |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Cost | Potentially lower | Potentially higher |
| Time Commitment | Variable | Fixed |
| Interaction | Often virtual (e.g., online discussions, video conferencing) | Often in-person (e.g., classroom discussions, group projects) |
Curriculum and Coursework
The coursework in online STEM education master’s programs frequently includes a range of courses focusing on diverse aspects of STEM teaching. These courses aim to provide a holistic understanding of pedagogy, subject matter knowledge, and technology integration in the classroom.
- Educational Psychology and Learning Theories: This course explores various learning theories and their application to STEM education, equipping educators with strategies to cater to diverse learning styles and needs.
- STEM Pedagogy and Curriculum Design: This course delves into the principles and practices of effective STEM curriculum development and design. It helps educators create engaging and enriching STEM learning experiences for their students.
- Assessment and Evaluation in STEM Education: This course covers various assessment methods, including formative and summative assessments, and their importance in evaluating student learning and understanding in STEM subjects.
- Technology Integration in STEM Education: This course focuses on utilizing technology effectively to enhance STEM instruction, promote student engagement, and create innovative learning environments.
- Research Methods in STEM Education: This course provides students with the skills to conduct research and analyze data related to STEM education practices.
- Specific STEM Subjects (e.g., Biology, Physics, Computer Science): Courses are tailored to provide in-depth subject knowledge, enabling educators to effectively teach these subjects.
<h3>Core Competencies and Skills, Master’s inSTEMm education online</h3>
Successful completion of a master’s program in STEM education fosters the development of crucial competencies and skills in educators. These include not only subject matter knowledge but also the ability to design engaging lessons, assess student learning, and integrate technology effectively.
- Subject Matter Knowledge: A strong foundation in STEM subjects is essential for educators to teach these disciplines effectively.
- Pedagogical Expertise: Understanding various learning theories and applying appropriate teaching strategies for diverse learners is critical.
- Curriculum Development Skills: Creating engaging and relevant STEM curriculum is a core competency that is emphasized.
- Assessment and Evaluation Expertise: Developing and implementing effective assessment strategies to gauge student understanding is a vital skill.
- Technology Integration Skills: Utilizing technology to enhance STEM instruction and promote student engagement is a crucial element.
- Communication and Collaboration Skills: Effective communication and collaboration with students, colleagues, and parents are essential for success.
<h3>Project-Based Learning Approaches</h3>
Project-based learning (PBL) is a widely used pedagogical approach in online STEM education. PBL encourages students to engage in hands-on activities, solve real-world problems, and develop critical thinking skills.
- Example 1: A project on designing and building a miniature solar-powered car. This project encourages students to apply physics concepts, engineering principles, and problem-solving skills.
- Example 2: A project on creating a computer program to simulate a natural phenomenon, such as the movement of planets. This project allows students to apply computational thinking and develop programming skills.
<h3>Technology Integration</h3>
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing STEM education. Online programs often incorporate interactive simulations, virtual labs, and digital resources to create engaging learning experiences for students.
- Importance: Technology integration in STEM education fosters active learning, promotes creativity, and enhances student understanding of complex concepts.
- Examples: Virtual labs allow students to conduct experiments without the limitations of physical resources, while online simulations provide opportunities to explore abstract concepts.
<h3>Sample Courses</h3>
| Course Name | Course Description | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction to STEM Education | Examines the fundamental principles and practices of STEM education. | 3 |
| Curriculum Design for STEM | Develops strategies for creating engaging and effective STEM curricula. | 3 |
| Technology Integration in STEM | Explores the use of technology to enhance STEM instruction. | 3 |
<h3>Program Delivery and Technology</h3>
Our program utilizes a user-friendly learning management system (LMS) to manage course materials, assignments, and communication. This platform provides a centralized hub for all course-related activities. Specific features include interactive modules, secure file sharing, and a grading system. The LMS chosen is designed to be accessible and intuitive, catering to diverse learning styles and technical proficiencies.
<h3>Online Tools and Resources</h3>
A wide array of online tools and resources enhances the course experience. These resources extend beyond the core curriculum, offering supplementary learning opportunities. Examples include interactive simulations, virtual laboratories, and online libraries of relevant research papers. This diverse collection of materials caters to the various learning preferences and needs of our students.
<h3>Online Discussion Forums and Collaborative Projects</h3>
Online discussion forums are integral to fostering a sense of community and facilitating peer-to-peer learning. These forums provide a platform for students to ask questions, share insights, and engage in constructive discussions. Furthermore, collaborative projects allow students to work together on complex tasks, encouraging teamwork and critical thinking. These elements enhance the learning experience, creating an environment of mutual support and knowledge sharing.
<h3>Virtual Labs and Simulations</h3>
Virtual labs and simulations are used extensively to complement traditional laboratory experiences. These tools offer safe and accessible environments for students to conduct experiments, analyze data, and explore complex scientific concepts. Examples include virtual dissections, molecular modeling, and engineering simulations, providing a hands-on learning experience without the limitations of physical space or resources.
<h3>Communication and Collaboration Tools</h3>
A variety of tools facilitate communication and collaboration among students and faculty. These tools are integrated into the learning management system to maintain seamless interaction.
| Tool | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Video Conferencing (e.g., Zoom, Google Meet) | Facilitates real-time interactions for lectures, discussions, and one-on-one meetings. | Live lectures, virtual office hours, and group project meetings. |
| Provides a platform for communication outside of scheduled interactions. | General inquiries, announcements, and follow-up communications. | |
| Chat (e.g., integrated chat within LMS) | Allows for quick and informal communication among participants. | Quick questions, clarifying doubts during discussions. |
| Collaborative Document Editors (e.g., Google Docs) | Enables simultaneous editing and revision of documents by multiple users. | Group projects, writing assignments, research papers. |
<h3>Learning Styles and Support</h3>
Source: store-assets.com
Online STEM education programs strive to cater to diverse learning styles and provide comprehensive support to ensure student success. Recognizing that learners absorb information in various ways is crucial for effective online instruction. This section details the support structures and resources available to facilitate a positive and productive learning experience for all students.
<h3>Different Learning Styles Accommodated</h3>
Online STEM education programs often employ a variety of pedagogical approaches to address different learning preferences. Visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners are all considered, and resources are designed to accommodate diverse needs. Interactive simulations, videos, and multimedia presentations cater to visual learners. Audio lectures and discussions provide avenues for auditory learners, while hands-on projects and laboratory exercises support kinesthetic learning.
<h3>Support Services Provided to Online Students</h3>
Students enrolled in online STEM programs benefit from a range of support services designed to address the unique challenges and opportunities of online learning. These services typically include access to online forums, dedicated email support, and virtual office hours with instructors. Many programs offer technical assistance to help students navigate online platforms and troubleshoot technological issues.
<h3>Role of Mentors and Advisors</h3>
Faculty mentors and advisors play a critical role in guiding online students through their academic journey. They provide personalized guidance, support, and encouragement to help students stay on track and achieve their educational goals. Mentors often offer advice on course selection, research opportunities, and career development. Advisors provide comprehensive support, assisting students with registration, academic planning, and program completion.
<h3>Importance of Online Communities for Students</h3>
Online STEM education programs often foster vibrant online communities where students can connect with peers and instructors. These communities provide opportunities for collaboration, knowledge sharing, and peer support. Discussion forums, virtual study groups, and online project teams facilitate interactions and build a sense of belonging.
<h3>Support Mechanisms Available to Online Students</h3>
Various support mechanisms are implemented to ensure a smooth and effective learning experience. These include:
- Dedicated Technical Support: Assistance with online platforms and technology issues.
- 24/7 Online Help Desk: Addressing technical and academic concerns outside of regular office hours.
- Virtual Office Hours: Scheduled meetings with instructors and support staff for personalized guidance.
- Student Success Coaches: Personalized support and guidance for academic planning and goal setting.
- Online Forums and Discussion Boards: Opportunities for students to connect with peers and instructors and share knowledge.
<h3>Key Aspects of Student Support</h3>
“Students receive individualized support from faculty mentors and advisors, enabling them to achieve their academic goals effectively.”
Final Review: Master’s In Stem Education Online
In summary, an online Master’s in STEM education provides a compelling alternative to traditional programs. The flexibility and accessibility of online learning are crucial advantages, allowing students to pursue advanced education while maintaining a balance with personal and professional commitments. The curriculum is designed to equip graduates with the skills and knowledge necessary for impactful careers in the dynamic STEM sector. The program’s emphasis on technology integration and student support further solidifies its value proposition.