Master of Science in STEM Education Online Your Path to Excellence
The Master of Science in STEM education online offers a flexible and accessible pathway to advanced knowledge in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics education. This program equips educators with the skills and expertise needed to teach these subjects in various settings. It encompasses a wide range of STEM fields, from biology to computer science and engineering, allowing specialization in areas of interest. The online format fosters flexibility and convenience, enabling learners to balance their studies with other commitments while gaining a competitive edge in the field.
The program’s curriculum is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of STEM pedagogy, assessment, and technology integration. Different course formats, including interactive online platforms and various learning tools, enhance the educational experience. The program’s structure also includes diverse assessment methods, mirroring real-world applications and providing a balanced approach to learning.
Introduction to Online STEM Education Master’s Programs

Source: blogspot.com
Online Master of Science programs in STEM education offer a flexible and accessible pathway for aspiring educators to deepen their knowledge and expertise in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. These programs equip educators with the theoretical frameworks and practical skills necessary to design engaging and effective STEM curricula for diverse learners.
These programs typically leverage online learning platforms, allowing students to balance their studies with other commitments. The curriculum is structured to provide a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application, preparing graduates for roles in various STEM educational settings.
Typical Program Structure and Course Content
These programs often include courses in educational psychology, curriculum development, and instructional design specifically tailored to the STEM disciplines. Students typically engage with advanced pedagogical theories and methodologies applicable to teaching science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Coursework may also encompass specific STEM content knowledge, allowing students to enhance their understanding of the subject matter.
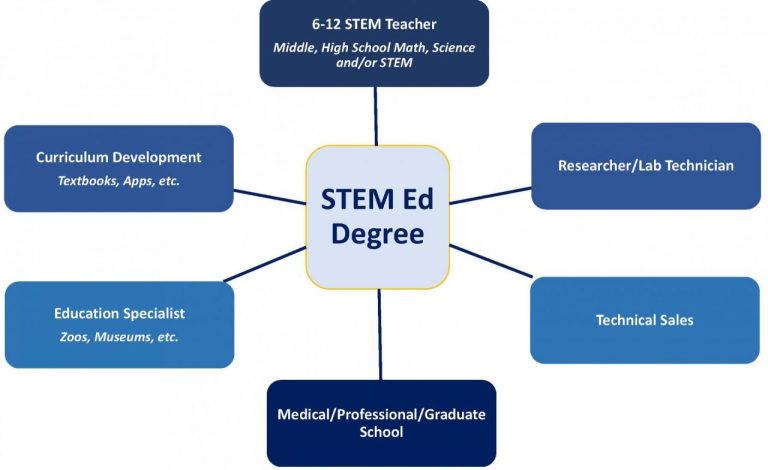
Potential Career Paths for Graduates
Graduates of these programs are well-positioned for diverse career paths in K-12 education. These include roles such as STEM curriculum developers, instructional designers, STEM teacher trainers, and educational researchers. They can also pursue leadership positions within schools or STEM organizations. Further, some graduates may transition into roles focused on outreach or community engagement within STEM fields.
STEM Fields Covered
The programs encompass a wide range of STEM fields, offering specialization options within various disciplines. These include, but are not limited to, biology, computer science, engineering, and mathematics. Programs often allow students to focus on specific areas like biotechnology, software engineering, or environmental engineering, depending on their interests and career goals.
Program Duration, Prerequisites, and Specializations
| Program Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Program Duration | Typically ranges from 1 to 2 years, depending on the specific program and the student’s pace of learning. |
| Required Prerequisites | Often includes a bachelor’s degree in a relevant STEM field or a related discipline. Some programs may require specific coursework in mathematics, science, or education. |
| Potential Specializations | Examples include:
|
Benefits and Advantages of Online STEM Education
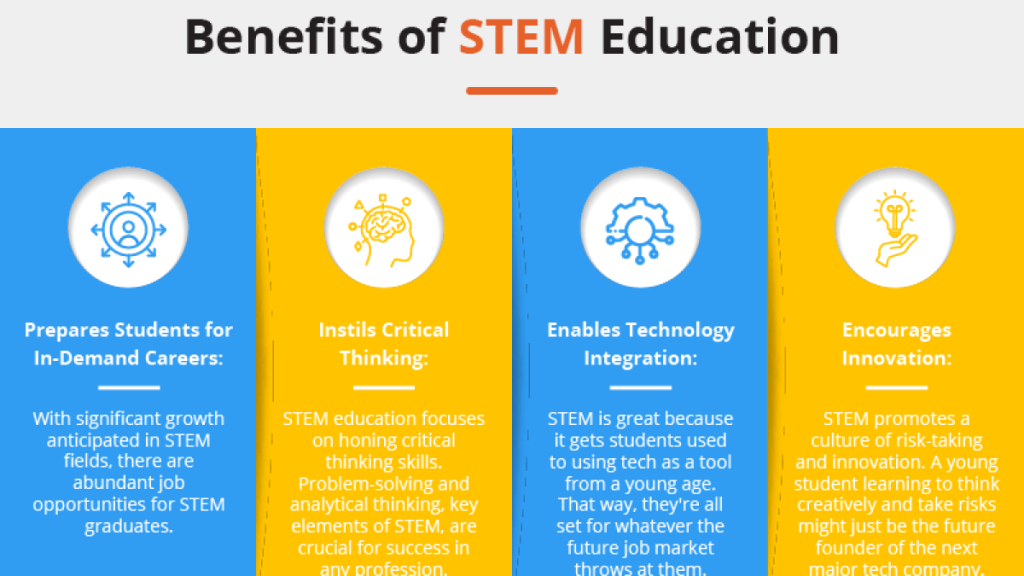
Online Master’s programs in STEM education offer a compelling alternative to traditional programs, particularly for individuals seeking flexibility and accessibility. These programs leverage the power of technology to provide a high-quality educational experience, often at a more affordable cost. This flexibility is a major draw, allowing learners to balance their studies with work, family obligations, or other commitments.
Online STEM education programs offer a unique set of advantages, including a broader reach, cost-effectiveness, and personalized learning experiences. These programs are tailored to accommodate the diverse needs of modern learners, enabling them to achieve their educational goals while maintaining a fulfilling personal and professional life.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Online learning environments offer unparalleled flexibility. Students can access course materials and participate in discussions at their convenience, accommodating diverse schedules and commitments. This contrasts sharply with traditional programs, which often require strict attendance and adherence to predetermined schedules. The geographical limitations of traditional programs are also eliminated in online learning, enabling students to study from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility is particularly valuable for individuals living in remote areas or those with mobility limitations.
Cost Comparison
Online Master’s programs often have lower tuition costs compared to their traditional counterparts. Reduced overhead expenses, such as physical facilities and commuting costs, translate into savings for students. While individual program costs may vary, online programs generally offer a more budget-friendly educational pathway. This cost-effectiveness can be a significant factor in making higher education attainable for a wider range of individuals.
Professional Development and Career Advancement
Online STEM education programs are designed to equip students with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in the field. They provide opportunities for professional development through specialized courses, workshops, and networking opportunities. These programs often incorporate industry-recognized certifications, further enhancing career prospects. Graduates are well-positioned to advance their careers in the STEM field, potentially securing higher-paying positions or leadership roles.
Potential Challenges of Online Learning
While online learning offers numerous benefits, potential challenges exist. Maintaining motivation and discipline in a self-directed learning environment can be demanding. The lack of face-to-face interaction with instructors and peers can also be a concern for some learners. Technical difficulties, unreliable internet access, and a lack of access to necessary resources are also potential obstacles. Effective time management and self-discipline are crucial for the successful completion of online programs.
Table: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Value Proposition of Online STEM Education
| Aspect | Benefits | Drawbacks | Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Study at your own pace, anytime, anywhere; accommodate work/life balance. | Requires strong self-discipline and time management skills. | Provides a highly adaptable learning experience, catering to diverse lifestyles. |
| Accessibility | Removes geographical barriers; accessible to individuals in remote areas or with mobility limitations. | May require reliable internet access and technical proficiency. | Broadens educational opportunities for a wider population. |
| Cost | Potentially lower tuition costs due to reduced overhead. | May require upfront investment in technology and resources. | Offers a more budget-friendly pathway to higher education. |
| Professional Development | Equips students with in-demand skills; fosters professional networks. | Requires proactive engagement and self-motivation to build networks. | Positions graduates for career advancement and leadership roles in STEM. |
Curriculum and Coursework in Online STEM Education Programs: Master Of Science In Stem Education Online

Source: geteducated.com
Online STEM education programs offer a flexible and accessible pathway to advanced knowledge and skills. The curriculum design typically emphasizes practical application and real-world problem-solving, often incorporating cutting-edge technologies. These programs aim to equip students with the theoretical understanding and hands-on experience necessary to excel in STEM fields.
Typical Courses Offered
The course offerings in online STEM education programs are diverse, reflecting the breadth of STEM disciplines. Commonly, these programs include courses on research methodologies, pedagogical approaches in STEM, and advanced topics in specific STEM areas. Courses often explore the latest research and developments in the field, preparing students for the evolving demands of the industry. Some examples of courses might include computational biology, data analysis for engineering, or advanced physics simulations.
Pedagogical Approaches in Online Courses
Online STEM education programs utilize a variety of pedagogical approaches to foster active learning and engagement. Interactive simulations, virtual labs, and online discussions are frequently employed to complement traditional lecture formats. The goal is to create a dynamic learning environment that mirrors the complexities and challenges of the STEM field. Many programs use project-based learning, encouraging students to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Curriculum Structure and Workload
| Course Area | Topics Covered | Estimated Workload (per course) |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamentals of STEM Education | Learning theories, instructional design, assessment strategies, classroom management, and ethical considerations in STEM | 15-20 hours per week |
| Specific STEM Disciplines (e.g., Biology, Chemistry, Physics) | Advanced concepts, research methodologies, hands-on applications, and problem-solving in the chosen area | 15-25 hours per week |
| Technology Integration in STEM | Utilizing technology for enhancing learning, creating interactive activities, and incorporating digital tools in STEM classrooms | 10-15 hours per week |
| Research and Project Management | Developing research proposals, conducting experiments, analyzing data, presenting findings, and managing projects | 20-30 hours per week |
This table provides a general overview. The workload may vary based on specific course content, program structure, and individual student needs.
Comparison of Teaching Methods
Traditional classroom settings often prioritize direct instruction and in-person interaction. Online STEM education, in contrast, leverages digital tools and asynchronous learning opportunities. Online programs encourage independent study and self-directed learning, with instructors facilitating discussion and providing support. This approach fosters flexibility and adaptability.
Technology Integration
Technology is central to online STEM education programs. Interactive simulations, virtual labs, and online collaboration tools are vital components. These resources allow students to engage with concepts in a dynamic and immersive way. For instance, virtual lab experiments can replicate real-world scientific procedures, enabling students to explore variables and observe outcomes without physical limitations.
Interactive Learning Platforms
Interactive learning platforms play a crucial role in online STEM education. These platforms often provide a centralized hub for course materials, assignments, discussions, and communication. They typically feature tools for collaborative projects, multimedia content, and personalized learning experiences. These features enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of online education.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Online STEM education programs employ diverse assessment strategies to gauge student understanding and progress effectively. These methods need to adapt to the unique characteristics of online learning environments, ensuring equitable and reliable evaluation of student knowledge and skills. The incorporation of technology plays a crucial role in facilitating this process.
Different assessment methods are utilized to cater to the various learning styles and subject matter within STEM fields. These methods, when thoughtfully designed and implemented, provide a comprehensive picture of student learning, allowing instructors to tailor their approach to better support student success.
Assessment Methods in Online STEM Education
Various assessment methods are employed in online STEM education programs to measure student understanding and knowledge application. These methods range from traditional forms like quizzes and exams to more innovative approaches like project-based learning and online simulations. This variety of assessment tools aims to cater to different learning styles and ensure a well-rounded evaluation of student skills.
- Quizzes and Exams: Online quizzes and exams are commonly used to assess factual knowledge and comprehension of concepts. These assessments can be administered in various formats, such as multiple-choice, true/false, matching, and short-answer questions. They are frequently employed to gauge immediate understanding of core topics, and the use of adaptive questioning algorithms can personalize the learning experience. This approach often involves immediate feedback, allowing students to identify areas where they need further clarification.
- Projects and Case Studies: Project-based learning and case studies are prevalent in STEM education. These activities often involve complex problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration. Students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, developing practical skills and showcasing their understanding of complex concepts. These methods often assess higher-order thinking skills, allowing for a more nuanced evaluation of student learning.
- Online Simulations and Labs: Online simulations and virtual labs are increasingly utilized to provide interactive learning experiences. Students can experiment with different variables and observe the results without the limitations of physical resources. These assessments often involve tasks that mimic real-world situations, enabling students to develop a deeper understanding of scientific principles and engineering processes. The interactive nature of these simulations promotes active learning and encourages hands-on engagement.
- Discussions and Collaborative Activities: Online discussions and collaborative activities are utilized to evaluate students’ ability to communicate their ideas, engage in critical discourse, and work effectively in teams. These methods provide insights into students’ ability to apply knowledge, articulate their reasoning, and collaborate with peers. Online forums and discussion boards are effective tools for fostering such engagement and assessment.
Technology’s Role in Online Assessments
Technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating online assessments. Learning management systems (LMS) are crucial platforms for delivering and grading assessments, while automated grading tools streamline the process. The use of these tools enhances efficiency and allows instructors to provide timely feedback to students.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): LMS platforms provide a centralized hub for delivering and tracking assessments, managing student progress, and facilitating communication. They often include features for creating and distributing quizzes, exams, and other assignments. The use of LMSs enhances the organization and efficiency of the assessment process.
- Automated Grading Tools: Automated grading tools can significantly reduce the time instructors spend on grading objective assessments. These tools automatically evaluate answers based on pre-defined criteria, freeing up valuable time for instructors to provide personalized feedback and address student needs. Tools can often provide detailed explanations and constructive suggestions to help students improve their performance.
- Interactive Assessments: Online tools enable the creation of interactive assessments that provide immediate feedback to students. These tools can dynamically adjust the difficulty level based on student performance, leading to a more personalized learning experience. This immediate feedback loop facilitates active learning and encourages continuous improvement.
Examples of Online Assessments in STEM Education
Various online assessments are employed in STEM education programs. These include quizzes on scientific principles, simulations of engineering processes, and projects involving the application of mathematical concepts. These diverse methods allow for a well-rounded assessment of students’ knowledge and skills.
- Example 1: A physics quiz on Newton’s laws of motion with interactive diagrams and questions. This allows students to visualize the concepts and immediately get feedback on their understanding.
- Example 2: A virtual lab simulation where students can conduct experiments in chemistry, like titration or reaction rates. This allows students to observe the reactions and understand the scientific concepts without the limitations of physical resources.
- Example 3: A project involving the design and simulation of a bridge using engineering software. This allows students to apply mathematical principles and design principles in a real-world context.
Criteria for Evaluating Student Performance
Several criteria are employed to evaluate student performance in online STEM courses. These criteria often include accuracy, problem-solving skills, critical thinking, collaboration, and the ability to apply knowledge to real-world scenarios. A holistic approach to evaluation is crucial in assessing student growth and development.
- Accuracy and Depth of Understanding: Correct application of concepts and thorough understanding of underlying principles are crucial. This often includes demonstrating a grasp of theoretical underpinnings.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Students’ ability to apply knowledge to solve problems is a significant factor. This involves identifying the problem, developing a solution, and evaluating its effectiveness.
- Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills: Evaluating data, drawing conclusions, and making informed judgments are key aspects of critical thinking. This involves examining different perspectives and forming reasoned arguments.
- Collaboration and Communication Skills: The ability to work effectively in teams, communicate ideas clearly, and engage in respectful discourse is essential. This is particularly important in project-based or group-oriented activities.
Comparison of Assessment Methods
| Assessment Method | Online STEM Education | Traditional STEM Education |
|---|---|---|
| Quizzes/Exams | Online platforms, automated grading | Paper-based, instructor-graded |
| Projects/Case Studies | Collaborative online platforms, submission portals | In-class presentations, physical prototypes |
| Simulations/Labs | Virtual environments, interactive software | Physical labs, hands-on experiments |
| Discussions/Collaborative Activities | Online forums, discussion boards | Classroom discussions, group work |
The Role of Technology in Online STEM Education
Online STEM education leverages technology to create dynamic and engaging learning experiences, bridging geographical barriers and expanding access to high-quality education. This approach allows for flexible learning schedules, personalized instruction, and the integration of diverse learning resources, ultimately enhancing the overall learning journey for students.
Technology plays a critical role in shaping the modern online STEM learning environment. It facilitates interactive learning, promotes collaboration, and allows for the exploration of complex concepts in innovative ways. This is especially important in STEM fields, where hands-on experience and practical application are often crucial to understanding abstract principles.
Different Technologies Used to Deliver Online STEM Education
Various technologies are employed to deliver online STEM education, each contributing unique functionalities. These include learning management systems (LMS), video conferencing platforms, interactive simulations, virtual labs, and digital libraries. The combination of these technologies creates a comprehensive and versatile learning environment.
Examples of Digital Tools and Resources
Numerous digital tools and resources enhance online STEM education. Examples include interactive simulations for physics and chemistry, virtual labs for biology and engineering, online coding platforms, and digital libraries with extensive STEM resources. These resources are often integrated into the learning management systems, allowing for seamless access and interaction.
Impact of Technology on Learning Experience
Technology significantly impacts the learning experience in online STEM programs. Interactive simulations allow students to explore complex scientific phenomena in a safe and controlled environment, providing a tangible understanding of abstract concepts. Virtual labs offer hands-on experience without the constraints of physical limitations, encouraging experimentation and problem-solving. This active engagement often leads to a deeper and more meaningful understanding of the subject matter.
Role of Online Collaboration Tools
Online collaboration tools are vital in fostering a sense of community and shared learning in online STEM programs. Platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, and Slack facilitate real-time communication, allowing students to collaborate on projects, ask questions, and share ideas with their peers and instructors. This fosters a sense of belonging and encourages peer-to-peer learning, often enhancing the learning experience.
Importance of Digital Literacy Skills
Students enrolled in online STEM programs need strong digital literacy skills. These skills encompass navigating online platforms, using various digital tools effectively, and critically evaluating online resources. Strong digital literacy is essential for successful participation in online learning environments and for future career success in the STEM field.
Table: Technologies and Applications in Online STEM Education
| Technology | Application in Online STEM Education |
|---|---|
| Learning Management Systems (LMS) | Centralized platform for course materials, assignments, communication, and grading. |
| Video Conferencing Platforms | Facilitating real-time interaction between students and instructors through virtual classroom sessions. |
| Interactive Simulations | Providing hands-on experience for exploring complex scientific concepts, simulating experiments. |
| Virtual Labs | Offering virtual environments for conducting experiments and simulations, exploring real-world applications. |
| Online Coding Platforms | Providing interactive environments for learning programming languages and practicing coding skills. |
| Digital Libraries | Providing access to a wide range of STEM resources, including articles, videos, and research papers. |
Professional Development and Career Opportunities
Graduates of online STEM education programs are well-positioned for success in a rapidly evolving job market. These programs equip students with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary for thriving in STEM careers, and the flexibility of online learning allows for concurrent professional development and career advancement.
The online format of these programs often provides a unique opportunity for professionals in STEM fields to further specialize or acquire new skills, enhancing their career prospects. This is particularly beneficial for those seeking to advance in their current roles or transition to new, more challenging positions.
Career Prospects for STEM Graduates
The STEM job market is robust and offers diverse opportunities for graduates. There is a significant demand for skilled professionals in various sectors, from technology and healthcare to environmental science and engineering. The need for innovative solutions and technological advancements is continuously driving this demand.
Potential for Career Advancement
Individuals pursuing online STEM education programs can leverage their acquired knowledge and skills to advance their careers within the STEM field. This can include promotions to leadership positions, taking on more complex projects, or moving into specialized roles that require advanced knowledge and expertise. For instance, a graduate with a Master’s in STEM Education could advance from a high school science teacher to a STEM curriculum director or educational consultant.
Emerging Trends in the STEM Job Market
The STEM job market is constantly evolving, with new technologies and industries emerging. Several notable trends are shaping the future of work in this field. Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming various sectors, creating a demand for professionals who can design, implement, and manage these technologies. There is also a growing emphasis on data analysis and interpretation in various STEM fields, increasing the demand for professionals with strong analytical skills.
Examples of Successful Graduates and Their Career Trajectories
Numerous successful graduates have leveraged their online STEM education to achieve remarkable career growth. For instance, a graduate with an online Master’s in Computer Science has transitioned from a software developer to a lead engineer in a tech startup. Another example involves a graduate in Environmental Science who used their online degree to transition from a conservationist to a sustainability consultant, helping businesses implement environmentally friendly practices.
Types of Jobs Graduates Are Qualified For
Graduates of online STEM education programs are well-suited for a wide range of job roles. Their skill sets often translate to positions in research, development, education, and consulting. They can be involved in areas like software engineering, data science, environmental science, biotechnology, and education. This is because these programs emphasize practical application and problem-solving skills, which are crucial for success in various STEM fields.
Potential Career Paths and Job Roles
| Potential Career Path | Corresponding Job Roles |
|---|---|
| Software Engineering | Software Developer, Software Engineer, Lead Engineer, QA Engineer, Systems Analyst |
| Data Science | Data Scientist, Data Analyst, Machine Learning Engineer, Business Intelligence Analyst |
| Environmental Science | Environmental Consultant, Conservationist, Environmental Scientist, Sustainability Analyst |
| Biotechnology | Biochemist, Biotechnologist, Research Scientist, Pharmaceutical Scientist |
| STEM Education | STEM Teacher, Curriculum Developer, Educational Consultant, STEM Coordinator |
Learning Environment and Community
A strong online learning environment in STEM education goes beyond simply delivering content. It fosters a sense of community, encouraging interaction and collaboration among learners, and ultimately enhances the learning experience. A supportive online community can be just as effective as a traditional classroom setting, particularly when it is well-structured and facilitated.
A thriving online STEM learning environment is built on active engagement and meaningful connections between learners and instructors. This involves more than just passively consuming information; it necessitates opportunities for interaction, discussion, and collaborative problem-solving. This environment becomes a space where diverse perspectives are valued, and learners feel comfortable sharing ideas and asking questions.
Importance of Community Building
A sense of community in online STEM education is crucial for several reasons. First, it fosters a supportive learning environment where students feel encouraged to ask questions and participate actively. Second, it promotes peer-to-peer learning, allowing students to benefit from the diverse experiences and perspectives of their classmates. Third, a strong community can enhance motivation and engagement, leading to improved learning outcomes. Finally, it prepares students for the collaborative nature of STEM fields, a crucial skill in today’s professional world.
Strategies for Fostering Community
Building a sense of community in an online STEM program requires deliberate strategies. These include creating opportunities for interaction, fostering a sense of belonging, and encouraging active participation. The following are examples of effective strategies:
- Interactive Activities: Regular online discussions, group projects, and virtual labs can facilitate interaction and create a sense of shared purpose. This could involve collaborative problem-solving, peer feedback, and knowledge-sharing activities.
- Welcome and Orientation Activities: A robust welcome and orientation module can establish clear communication channels, introduce participants to the platform and its features, and foster a welcoming atmosphere. This could include icebreaker activities, introductions, and a clear explanation of the program’s expectations.
- Personalized Communication: Regular communication from instructors, including individual feedback and personalized support, can create a sense of individual connection and encouragement. This can involve direct messaging, targeted announcements, and dedicated office hours.
- Emphasis on Inclusivity: Creating an inclusive environment where diverse perspectives and backgrounds are valued is critical. This can be achieved through promoting respectful communication, actively addressing biases, and offering resources for diverse learners.
Role of Instructors (ORs), Master of science in stem education online
Instructors play a pivotal role in creating a supportive learning environment. They are not just providers of information; they are facilitators and guides who foster interaction and create a sense of community. Their active participation in discussions, prompt responses to questions, and provision of individual feedback are essential components of a successful online learning experience. They act as mentors and guides, encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing amongst students. An instructor’s presence and engagement directly influence the overall learning experience.
Examples of Successful Online STEM Communities
Several online communities have demonstrated success in creating a supportive and engaging learning environment. These include online forums dedicated to specific STEM fields, virtual laboratories, and online communities of practice. These communities facilitate interaction and collaboration, fostering a sense of belonging and shared learning amongst participants. Examples include online astronomy communities, physics discussion boards, and dedicated coding platforms.
Use of Online Tools
Various online tools can facilitate interaction and collaboration within an online STEM program. These include forums, discussion boards, virtual meeting platforms, and collaborative document editors. These tools allow for asynchronous communication, providing learners flexibility and encouraging active participation.
| Tool | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Forums and Discussion Boards | Asynchronous Communication | Facilitating discussions on specific topics, allowing learners to engage with content and each other at their own pace. |
| Virtual Meeting Platforms | Synchronous Communication | Enabling real-time interactions, such as live Q&A sessions, webinars, and group project discussions. |
| Collaborative Document Editors | Collaborative Work | Supporting group projects, enabling multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously. |
| Virtual Labs | Interactive Learning | Providing simulations and interactive environments for hands-on STEM learning experiences. |
Illustrative Program Examples
Online Master’s programs in STEM education offer a flexible and accessible pathway for professionals seeking to advance their careers in this vital field. These programs provide a robust learning experience, often incorporating cutting-edge technologies and diverse pedagogical approaches. A key aspect of these programs is their ability to accommodate working professionals and those seeking to change careers.
Exploring hypothetical and real-world program examples allows us to better understand the strengths and weaknesses of online formats, as well as the varying approaches institutions adopt. This section will examine a sample program, comparing it to traditional models, and showcasing exemplary institutions.
Hypothetical Online Master’s Program in STEM Education
This hypothetical program focuses on integrating technology into STEM instruction for K -12 students. It emphasizes project-based learning, active learning techniques, and the development of 21st-century skills. This program seeks to provide educators with a deeper understanding of STEM content and effective instructional strategies.
Curriculum
The program’s curriculum is designed to be highly interactive and practical. It blends theoretical frameworks with real-world applications. Core courses include:
- Advanced STEM Pedagogy: This course explores contemporary teaching methodologies for diverse learners in STEM, including incorporating technology into instruction and differentiated instruction.
- Technology Integration in STEM Education: This course equips students with the technical skills needed to effectively leverage digital tools for classroom applications, encompassing software, platforms, and coding principles.
- Assessment and Evaluation in STEM: This course focuses on developing effective assessment strategies that align with learning objectives, using data to inform instruction and student growth.
- Research Methods in STEM Education: This course equips students with research skills to conduct investigations on innovative approaches in STEM education.
Assessment Methods
The program utilizes a variety of assessment methods to evaluate student learning and understanding. These include:
- Online quizzes and assignments: Regular assessments gauge understanding of course concepts and application.
- Project-based learning: Students engage in projects that integrate different aspects of the curriculum and allow for practical application of knowledge.
- Case studies and simulations: These activities expose students to real-world scenarios and challenge them to apply their learning.
- Capstone project: This culminating project requires students to synthesize their learning and apply it to a real-world problem or opportunity in STEM education.
Learning Environment
The learning environment fosters collaboration and interaction among students and instructors. It utilizes a virtual learning platform with features like discussion forums, collaborative tools, and virtual office hours. A strong emphasis is placed on building a supportive and engaging online community.
Comparison to Traditional STEM Education Programs
Traditional programs often involve in-person lectures and hands-on activities, which can be less adaptable to diverse schedules and locations. Online programs offer flexibility and accessibility, accommodating working professionals and those in remote areas.
Strengths and Weaknesses
- Strengths: Online programs offer flexibility, accessibility, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional programs. They often allow for personalized learning experiences, and they can be tailored to the specific needs of students.
- Weaknesses: Online programs may lack the same level of in-person interaction and networking opportunities as traditional programs. Students may need strong self-discipline and motivation to succeed in an online format.
Examples of Successful Institutions
Several institutions offer excellent online STEM education programs. Examples include:
- University of California, Irvine
- Arizona State University
- Columbia University
Characteristics of Online STEM Education Programs
| Institution | Specialization | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Example Institution A | K-12 STEM Teacher Training | Project-based learning, collaborative projects, virtual labs |
| Example Institution B | STEM Curriculum Development | Curriculum design workshops, lesson plan creation, assessment tools |
| Example Institution C | STEM Education Leadership | Educational leadership theories, school improvement strategies, program management |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, a Master of Science in STEM education online provides a compelling opportunity for professional development and career advancement. This comprehensive program caters to diverse learning styles and preferences, making it a suitable choice for aspiring educators seeking a flexible and enriching educational journey. The program’s emphasis on technology integration, flexible learning environments, and diverse assessment methods positions graduates for success in the evolving STEM education landscape.