ISO 27001 Accreditation Bodies A Comprehensive Guide
ISO 27001 accreditation bodies play a crucial role in ensuring organizations meet stringent information security standards. Choosing the right accreditation body is vital for successful certification, and this guide explores the critical factors to consider. Understanding the accreditation process, the different bodies available, and their respective strengths and weaknesses is key to navigating this complex landscape.
This comprehensive overview delves into the intricacies of ISO 27001 accreditation. From the fundamental principles of ISO 27001 and the importance of accreditation to the practical considerations for selecting a suitable body, we’ll cover all the essential aspects of the process. We’ll examine the responsibilities of accreditation bodies, the selection criteria, the accreditation process itself, and the benefits and risks associated with different options. Finally, we’ll explore the maintenance of accreditation and provide actionable steps for organizations seeking to achieve and maintain this vital certification.
Introduction to ISO 27001 Accreditation Bodies

Source: medium.com
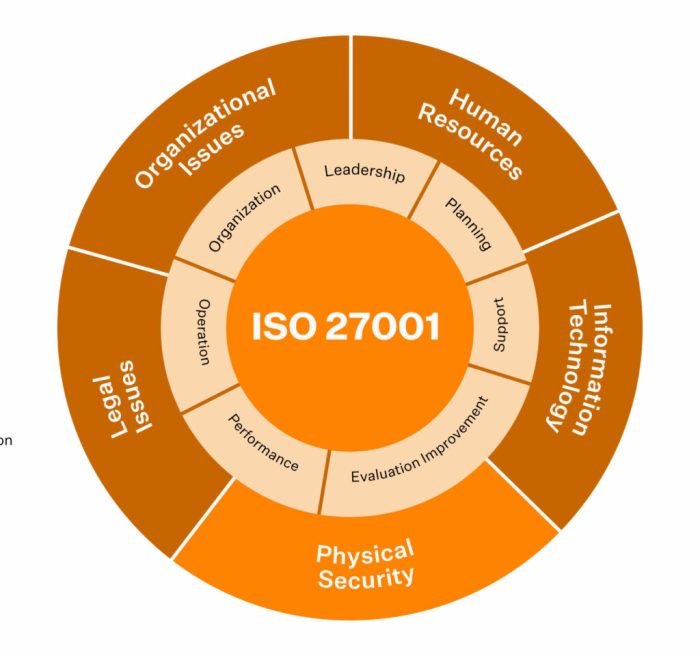
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and improve their information security practices. Adherence to this standard demonstrates a commitment to protecting sensitive data and assets and helps organizations mitigate potential risks.
The importance of accreditation in ISO 27001 certification stems from its role in ensuring the impartiality and competence of the certification bodies. Accreditation validates the certification body’s capability to conduct rigorous assessments and issue accurate certifications, fostering trust and confidence among stakeholders. This, in turn, enhances the credibility and value of the ISO 27001 certification.
Role of Accreditation Bodies
Accreditation bodies play a crucial role in the ISO 27001 certification process. They act as independent third-party entities that evaluate and accredit certification bodies. This oversight mechanism ensures that the certification bodies meet predefined standards of competence, impartiality, and consistency. This fosters confidence in the certification process.
Responsibilities of an ISO 27001 Accreditation Body
Accreditation bodies have several key responsibilities. These responsibilities ensure the integrity and reliability of the ISO 27001 certification process.
| Responsibility | Description | Example | Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| Establishing and Maintaining Standards | Accreditation bodies define and maintain the criteria against which certification bodies are assessed. | Developing and updating assessment criteria for ISO 27001 certification bodies. | Ensuring consistent and reliable evaluation across different certification bodies. |
| Evaluating Certification Bodies | Accreditation bodies assess certification bodies to confirm their compliance with the established standards. | Conducting audits of certification bodies’ processes and procedures. | Verifying that certification bodies are competent to perform assessments and issue certifications. |
| Accrediting Certification Bodies | Based on a successful evaluation, accreditation bodies grant accreditation to competent certification bodies. | Issuing accreditation certificates to qualified certification bodies. | Recognizing and validating certification bodies’ ability to conduct ISO 27001 assessments. |
| Monitoring and Surveillance | Accreditation bodies periodically monitor and oversee accredited certification bodies to maintain compliance and competence. | Conducting follow-up audits to ensure ongoing adherence to standards. | Maintaining a system of continuous improvement for the certification process. |
Certification vs. Accreditation
Certification is the process by which an organization demonstrates compliance with a standard. Accreditation, on the other hand, is the process by which an organization, in this case a certification body, is recognized as competent to perform the certification process. Accreditation is a higher level of validation, ensuring that the certification process itself is trustworthy. Certification bodies are accredited by an accreditation body, which is itself accredited by a higher-level body. This creates a chain of trust.
Identifying Accreditation Bodies
Selecting a reputable ISO 27001 accreditation body is crucial for organizations seeking to demonstrate their commitment to information security. A well-recognized and rigorously audited accreditation body fosters trust and confidence among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors. This section articulates the process of identifying suitable accreditation bodies, focusing on globally recognized entities.
Globally Recognized ISO 27001 Accreditation Bodies
Several organizations worldwide offer ISO 27001 accreditation services. These bodies adhere to strict standards and guidelines to ensure impartiality and competence. A selection of globally recognized bodies includes:
- TÜV Rheinland: A renowned global testing, inspection, and certification group, offering ISO 27001 accreditation services across numerous industries.
- DNV GL: A leading provider of assurance and certification services, supporting organizations in achieving and maintaining ISO 27001 certification.
- Bureau Veritas: A global leader in testing, inspection, and certification, offering ISO 27001 accreditation services to a diverse range of organizations.
- Intertek: A global provider of quality and safety solutions, with extensive experience in ISO 27001 accreditation and certification.
- SGS: A globally recognized inspection, verification, testing, and certification company, providing ISO 27001 accreditation services.
Criteria for Selecting Reputable Accreditation Bodies, Iso 27001 accreditation bodies
Several factors contribute to the selection of a reputable accreditation body. These factors include:
- Accreditation Standards Adherence: The body must rigorously adhere to established accreditation standards, ensuring impartiality and competence in the certification process.
- Industry Recognition and Reputation: A long-standing history of providing high-quality services and a positive reputation within the industry contribute to the selection process.
- Transparency and Communication: Clear communication and transparency in the accreditation process, including clear procedures and readily accessible information, are essential factors.
- Geographic Reach: The geographic reach of the accreditation body should align with the organization’s global operations, if applicable.
- Expert Staff and Resources: The accreditation body should employ qualified and experienced personnel with expertise in information security and the ISO 27001 standard.
Comparative Analysis of Accreditation Bodies
The table below provides a comparative analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of different accreditation bodies, offering insights into their capabilities and limitations.
| Accreditation Body | Strengths | Weaknesses | Geographic Reach |
|---|---|---|---|
| TÜV Rheinland | Extensive experience, global presence, strong reputation, and diverse range of services. | Potentially higher costs compared to some smaller organizations. | Global |
| DNV GL | Strong industry expertise, recognized for quality assurance, comprehensive certification offerings. | Potential bureaucratic processes might have less local presence in some regions. | Global |
| Bureau Veritas | Extensive global presence, broad range of industries served, well-established track record. | Potentially slower response times in certain regions compared to competitors. | Global |
| Intertek | Wide array of testing and certification services, strong focus on quality and safety. | Might have less specialization in specific information security aspects compared to dedicated players. | Global |
| SGS | Global network, broad range of services, well-recognized brand name. | Potential for standardization across different sectors, leading to less specialization. | Global |
Method for Researching Accreditation Bodies
A structured approach to researching accreditation bodies is vital. This approach should involve:
- Defining Specific Needs: Clearly identifying the organization’s specific requirements and the scope of the accreditation process is the initial step.
- Online Research: Utilizing online resources, such as the accreditation body’s website, industry reviews, and case studies, can provide valuable insights.
- Direct Communication: Contacting the accreditation body directly to inquire about their services, processes, and fees is crucial for gaining a deeper understanding.
- Referencing and Verification: Gathering information from reputable sources and verifying the accreditation body’s legitimacy through official channels is essential.
Accreditation Process Overview
The ISO 27001 accreditation process is a rigorous evaluation of an organization’s Information Security Management System (ISMS). Successful completion leads to a recognized certification, demonstrating a commitment to robust information security practices and meeting international standards. This process typically involves a series of steps, culminating in a formal audit conducted by a qualified accreditation body.
The accreditation process aims to ensure that organizations have implemented and maintain an ISMS that effectively addresses the risks to their information assets. This process requires meticulous documentation, a comprehensive understanding of the standard, and a dedication to ongoing improvement.
Steps Involved in the ISO 27001 Accreditation Process
The ISO 27001 accreditation journey involves several key steps. Understanding each stage is critical for organizations embarking on this process.
- Preparation and Documentation: Thorough planning and documentation are foundational. This includes developing a comprehensive ISMS policy, defining roles and responsibilities, establishing procedures, and creating a detailed risk assessment. This is critical to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s information security needs.
- Implementation and Review: The next step involves implementing the planned ISMS, including the procedures and controls identified in the risk assessment. Regular review and improvement of the system are crucial for ongoing effectiveness.
- Application to Accreditation Body: Once the ISMS is fully implemented and documented, the organization formally applies to a recognized accreditation body. This application typically requires detailed information about the organization’s ISMS, its scope, and the relevant documentation.
- Pre-Assessment/Initial Audit: The accreditation body conducts a preliminary assessment or audit. This stage evaluates the organization’s compliance with ISO 27001 standards, identifying areas for improvement and assessing the completeness of documentation. Any identified issues are documented and addressed before the formal audit.
- Formal Audit: The formal audit is the core of the process. This is a comprehensive evaluation of the organization’s ISMS performed by a team of certified auditors. The audit assesses adherence to the standard, the effectiveness of controls, and the overall maturity of the ISMS.
- Accreditation Decision: Based on the findings of the audit, the accreditation body makes a decision on whether to grant accreditation. This decision considers the extent of compliance with ISO 27001 and the adequacy of the implemented controls. If approved, the organization receives accreditation, typically for a specific period.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Accreditation is not a one-time event. Organizations must maintain compliance with the standard and the accreditation requirements through regular internal audits, updates to the ISMS, and ongoing training.
Required Documentation and Procedures
A comprehensive set of documents is essential throughout the accreditation process. These documents demonstrate the organization’s commitment to information security and provide evidence of compliance. This documentation should be meticulously maintained and updated.
- ISMS Policy: The organization’s commitment to information security.
- Risk Assessment: Identifies and evaluates potential threats and vulnerabilities to information assets.
- Control Procedures: Detail the measures taken to mitigate identified risks.
- Documented Procedures: Formal procedures governing the implementation and maintenance of the ISMS.
- Records of Internal Audits: Demonstrate the effectiveness of the ISMS through ongoing assessment.
- Records of Staff Training: Ensure personnel are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills.
Role of Audits in the Accreditation Process
Audits play a critical role in verifying compliance with ISO 27001. These evaluations assess the effectiveness of implemented controls and identify areas requiring improvement. This continuous evaluation ensures that the ISMS remains robust and capable of adapting to evolving threats.
| Stage | Description | Documents Required | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Assessment | Initial evaluation by the accreditation body | ISMS documentation, risk assessment, control procedures | Variable, depends on the complexity of the ISMS |
| Formal Audit | Comprehensive evaluation of the ISMS | All documented procedures, internal audit reports, staff training records | Variable, often several days |
| Accreditation Decision | The accreditation body’s decision is based on audit findings | Audit report, evidence of compliance | Variable; can take weeks or months |
Benefits and Risks of Choosing Specific Accreditation Bodies

Source: qfscerts.com
Selecting the right accreditation body is crucial for organizations seeking ISO 27001 certification. A well-chosen body can streamline the process, enhance credibility, and, ultimately, foster a robust information security management system. Conversely, an unsuitable choice might lead to unnecessary delays, cost overruns, or even a compromised certification outcome.
Choosing an accreditation body involves careful consideration of several factors. This includes evaluating the body’s reputation, expertise, and track record. The geographical location of the body and its familiarity with the industry standards can also influence the decision-making process.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Accreditation Body
Accreditation bodies vary in their approach, resources, and expertise. Organizations should assess these factors to make an informed decision. Consider the body’s experience in handling similar certifications, its reputation for fairness and transparency, and its geographical reach. A body with a strong understanding of a specific industry or sector might offer a tailored and more efficient certification process. Ultimately, choosing an accreditation body should align with the organization’s specific needs and priorities.
Accreditation Body Comparison
This table provides a comparative overview of potential benefits, risks, and cost implications associated with different accreditation bodies. Understanding these aspects will aid in making an informed decision.
| Accreditation Body | Benefits | Risks | Cost Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accreditation Body A | Known for its swift turnaround times and streamlined procedures. Excellent track record in handling complex certifications. | Potentially higher fees compared to other bodies. It may have less accessibility for smaller organizations. | Generally higher than average due to expertise and streamlined processes. |
| Accreditation Body B | Offers a wider range of support services, including training and guidance. Strong reputation for transparent communication. | Potential for longer processing times, especially during peak seasons. | Typically moderate in cost, offering a balance between efficiency and comprehensive support. |
| Accreditation Body C | Highly recognized for its specialized expertise in the financial sector. Often results in higher perceived credibility within that industry. | Limited reach in other sectors; potential for lack of familiarity with certain organizational structures. | Cost is often moderate but may be higher if the organization’s sector isn’t a specialization of the body. |
| Accreditation Body D | Strong reputation for fair and unbiased assessments. Well-established network across multiple regions. | It may have less tailored services for specific industries. Turnaround times may be slightly longer than other options. | Usually, this is the most cost-effective option, although it is not always the fastest. |
Cost and Timeline Considerations
The cost of accreditation varies significantly depending on the body and the complexity of the organization’s system. Factors like the size of the organization, the scope of the certification, and the required resources impact the overall cost. Furthermore, processing timelines can also vary. Some bodies offer expedited services at a premium, while others prioritize thorough assessments. It’s important to request detailed cost breakdowns and timelines from prospective accreditation bodies. Consider not only the initial fees but also potential ongoing maintenance costs. For example, ongoing support for audits can be a factor. Comparing the total cost of ownership is essential.
Accreditation Body Requirements and Standards

Accreditation bodies play a crucial role in ensuring the credibility and competence of organizations seeking ISO 27001 certification. Their adherence to rigorous standards and requirements is paramount to maintaining the integrity of the certification process. This section details the specific standards and criteria for evaluating such bodies.
Accreditation bodies are governed by a framework of specific requirements designed to uphold the quality and consistency of their operations. These requirements encompass the technical competence of the staff, the impartiality of their decision-making processes, and the effective management of their resources.
Specific Requirements and Standards for Accreditation Bodies
Accreditation bodies must adhere to internationally recognized standards, often based on ISO/IEC 17011. These standards articulate the procedures for conducting assessments, ensuring impartiality, and maintaining the overall competence of the accreditation body. Crucially, the standards emphasize the importance of transparency, objectivity, and accountability in all stages of the accreditation process. The standards also mandate procedures for handling complaints and resolving disputes.
Critical Criteria for Evaluating Accreditation Bodies
Evaluating accreditation bodies involves assessing several critical criteria. These include, but are not limited to, their experience and expertise in the specific area of certification, the qualifications of their personnel, their demonstrated commitment to impartiality, and the effectiveness of their quality management system. Thorough examination of these elements is essential for making informed decisions regarding the choice of an accreditation body.
- Experience and ExpertiseAccreditation bodies should possess a proven track record in assessing organizations against relevant standards, such as ISO 27001. This expertise demonstrates their ability to evaluate accurately the strengths and weaknesses of the systems being audited.
- Personnel Qualifications: The staff conducting audits should have the necessary qualifications and training to effectively assess compliance with the ISO 27001 standard. This includes knowledge of the standard itself and relevant industry best practices.
- Impartiality and Objectivity: Accreditation bodies must maintain complete impartiality in their assessment processes. Bias or conflicts of interest must be avoided, ensuring fair and objective evaluations.
- Quality Management System: The accreditation body’s quality management system should be robust and effective, covering all aspects of their operations, from audit procedures to complaint resolution.
Common Compliance Issues Encountered by Accreditation Bodies
Unfortunately, some accreditation bodies face challenges in maintaining compliance with the required standards. Common issues include inadequate training for assessors, conflicts of interest, or inconsistencies in audit procedures. These shortcomings can undermine the credibility of the entire certification process.
- Inadequate Assessor Training: Assessors lacking sufficient training may not accurately assess the effectiveness of an organization’s security controls. This can lead to inaccurate or inconsistent certifications.
- Conflicts of Interest: Potential conflicts of interest, such as existing relationships with organizations being assessed, can compromise the impartiality of the accreditation body.
- Inconsistent Audit Procedures: Variances in audit procedures across different assessments can lead to inconsistencies in the application of the standard, potentially affecting the reliability of the certification.
Essential Requirements for Accreditation Bodies
A clear understanding of the essential requirements for accreditation bodies is crucial for selecting a reputable organization.
| Requirement Category | Requirement Description | Examples | Supporting Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Governance and Structure | Clearly defined organizational structure, management responsibilities, and procedures for decision-making. | Formal policies, charters, and documented procedures. | ISO/IEC 17011, Accreditation body’s internal documents. |
| Competence of Personnel | Demonstrated competence and qualifications of personnel involved in the accreditation process, including assessors and auditors. | Relevant certifications, professional licenses, and training records. | Relevant professional certifications and training records. |
| Impartiality and Objectivity | Clear procedures to ensure impartiality and objectivity in all assessment and decision-making processes. | Conflict of interest declarations, transparent assessment procedures. | Policies and procedures regarding conflict of interest. |
| Quality Management System | Effective quality management system encompassing procedures for audit planning, execution, reporting, and continuous improvement. | Documented audit procedures, review mechanisms, and corrective actions. | Quality management system documentation. |
Determining Legitimacy of an Accreditation Body
Verifying the legitimacy of an accreditation body is essential. This involves checking for recognition by relevant national or international accreditation organizations, reviewing their accreditation status, and examining their published policies and procedures. Crucially, an organization should check for compliance with ISO/IEC 17011.
Maintaining Accreditation
Maintaining ISO 27001 accreditation requires a proactive and ongoing commitment to upholding the required security controls. This involves a continuous improvement process, actively monitoring and adapting to evolving threats and best practices. The onus is on the certified organization to demonstrate its continued adherence to the standard’s requirements.
Accreditation isn’t a one-time achievement; it’s a journey that demands sustained effort and meticulous record-keeping. Organizations must diligently address any identified gaps, proactively update their controls, and demonstrate their commitment to security through ongoing activities and audits.
Accreditation Maintenance Procedures
Organizations must establish a formal process for maintaining their ISO 27001 accreditation. This typically includes regular internal audits, documented reviews of security controls, and periodic external audits conducted by the accreditation body. Effective communication and collaboration between the organization’s management, security team, and the accreditation body are vital for a smooth and successful maintenance process.
Actions for ISO 27001 Compliance Post-Accreditation
Maintaining compliance with ISO 27001 standards after accreditation involves a multifaceted approach. Key actions include regularly reviewing and updating the documented information security system (ISMS), addressing any identified risks or vulnerabilities, and ensuring all personnel are appropriately trained. Training must be consistently delivered and updated to reflect current threats and emerging best practices. Additionally, maintaining effective communication channels for reporting incidents and near misses is critical.
Importance of Ongoing Audits and Updates
Ongoing internal and external audits are fundamental to maintaining ISO 27001 accreditation. Internal audits allow organizations to assess their compliance with the standard, identify areas for improvement, and proactively address potential issues. External audits, conducted by the accreditation body, provide an independent verification of the organization’s adherence to the standard. These audits contribute to maintaining the organization’s credibility and demonstrating its ongoing commitment to security. Regular updates to security policies, procedures, and controls are crucial to address evolving threats and risks and ensure the ISMS remains effective and relevant.
Summary of Key Activities for Maintaining Accreditation
| Activity | Description | Frequency | Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Audits | Periodic assessments of security controls and processes within the organization. | Regular, e.g., quarterly or semi-annually | Audit reports, corrective action plans, evidence of control implementation |
| Review and Update of ISMS | Assessing the ISMS’s effectiveness and making necessary modifications to reflect evolving threats and risks. | Ongoing, e.g., annually or as needed | Updated policies, procedures, documentation, risk assessments |
| Corrective Action Implementation | Addressing any identified gaps or deficiencies in security controls. | As required, based on audit findings | Documented corrective action plans, evidence of remediation |
| External Audits | Independent assessments conducted by the accreditation body to verify ongoing compliance. | Periodic, e.g., annually or as per the accreditation body’s schedule | Audit reports, certificates of compliance, evidence of corrective actions |
Identifying and Addressing Potential Issues
Identifying and promptly addressing potential issues related to accreditation is crucial. This includes proactive risk assessments, regular security awareness training for personnel, and a robust incident response plan. Regular reviews of security controls, monitoring for emerging threats, and staying updated on best practices are critical for identifying and mitigating potential problems before they impact accreditation. A proactive approach to identifying and resolving potential issues helps maintain a strong security posture and ensures continued compliance.
Practical Considerations for Selecting an Accreditation Body

Selecting the right ISO 27001 accreditation body is crucial for a successful implementation and maintenance of a robust information security management system (ISMS). Choosing a body that aligns with your organization’s specific needs and objectives is paramount to achieving the desired outcomes and demonstrating commitment to information security. This involves careful consideration of several factors beyond the accreditation process itself.
Evaluating Accreditation Bodies
TA’s thorough evaluation of potential accreditation bodies involves examining their reputation, experience, and procedures. A strong track record and demonstrable expertise in assessing ISMSs are essential indicators of their competence. Look for accreditation bodies that have a proven history of successful audits and certifications, evidenced through case studies, testimonials, or publications. Furthermore, their transparency in processes and communication should be assessed. This includes their communication channels, responsiveness, and the clarity of their documentation.
Understanding Reputation and Experience
Accreditation bodies’ reputation and experience significantly impact their credibility and ability to effectively evaluate ISMSs. A reputable body is likely to have established procedures and qualified personnel, leading to a more robust and objective assessment. Organizations should research the accreditation body’s past performance, examining its handling of previous audits and certifications. Reviewing independent reviews, industry reports, or testimonials from previous clients can offer valuable insights into the accreditation body’s standing and competence.
Geographic Location’s Impact
Geographic proximity can influence factors like travel costs, communication ease, and the accessibility of support services. However, geographic location alone should not be the primary deciding factor. The critical aspects are the accreditation body’s expertise, reputation, and the quality of their services, regardless of location. A reputable body operating in a different geographic region may still be a suitable choice if its expertise aligns with the organization’s needs. Organizations must carefully weigh the pros and cons of geographic location against other factors like reputation and experience.
Questions to Ask an Accreditation Body
To facilitate an informed decision, a list of pre-emptive questions can be invaluable. These questions should delve into the accreditation body’s specific processes, expertise, and support services.
- What is your accreditation body’s history and experience with ISO 27001 assessments?
- Can you provide case studies or examples of successful implementations you have supported?
- What is your process for auditor training and competency management?
- What support resources are available to organizations after the certification process, such as ongoing guidance or consultation?
- What are your policies regarding conflicts of interest and maintaining impartiality in assessments?
- How do you handle complaints and appeals related to audits?
- What are your communication protocols and responsiveness to queries or issues during the accreditation process?
- What is your commitment to continuous improvement, and how is this demonstrated?
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, navigating the world of ISO 27001 accreditation bodies requires careful consideration of various factors. Understanding the roles, responsibilities, and procedures involved is paramount. By thoroughly researching accreditation bodies, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses, and comprehending the accreditation process, organizations can make informed decisions and increase their chances of successful certification. The key takeaways from this guide will empower organizations to select the most suitable accreditation body, ensuring a smooth and effective certification journey.