Get ISO 27001 Certified Your Security Roadmap
Get ISO 27001 certified to elevate your organization’s security posture. This comprehensive guide details the process, benefits, and crucial steps for achieving certification. From understanding the standard’s core principles to navigating the implementation and auditing phases, we’ll equip you with the knowledge needed for a successful certification journey. It’s a strategic move to enhance your business’s resilience and trustworthiness.
The ISO 27001 standard provides a structured framework for establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This framework helps organizations effectively manage information risks, improving operational efficiency and bolstering customer trust. By understanding the requirements and implementation procedures, you can proactively safeguard sensitive data and maintain a strong security posture. This detailed exploration encompasses everything from the initial planning phase to the crucial aspects of ongoing maintenance and auditing.
Understanding ISO 27001 Certification
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, and maintain a robust information security posture. This standard helps organizations protect sensitive data and assets, comply with regulations, and build trust with stakeholders.
Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a commitment to information security best practices. This commitment fosters a culture of security awareness, reduces risks, and ultimately enhances operational efficiency and profitability. Organizations often see a return on investment through reduced security incidents, improved customer confidence, and enhanced reputation.
Definition of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a standard that specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an information security management system (ISMS). It articulates a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security risks. This standard is designed to help organizations protect their assets and information from threats.
Purpose and Benefits of ISO 27001 Certification, Get iso 27001 certified.
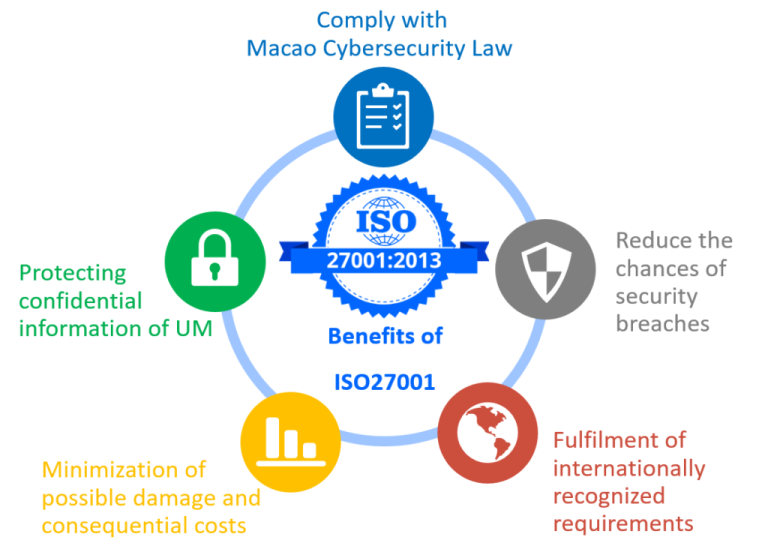
The purpose of ISO 27001 certification is to provide a framework for managing information security risks effectively. Organizations gain several key benefits, including enhanced operational efficiency, improved compliance with regulations, increased customer confidence, and reduced risk of security breaches. The benefits extend to improved stakeholder trust and enhanced reputation.
Key Principles and Concepts Behind ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is built upon several key principles, including risk management, continuous improvement, and a strong security culture. Organizations should actively identify and assess their information security risks, implement controls to mitigate those risks, and monitor the effectiveness of those controls. These principles are crucial for maintaining a robust and adaptable security posture.
Comparison of ISO 27001 with Other Standards
| Standard | Focus | Key Differences from ISO 27001 |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | Provides a comprehensive framework for information security management systems. | Focuses on the overall management system rather than specific technical controls. |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Provides a flexible and adaptable framework for managing cybersecurity risks. | Offers a more prescriptive approach, providing specific actions and activities. |
This table highlights the differing focuses of these two standards. ISO 27001 emphasizes the overarching management system, while the NIST framework offers a more specific approach to addressing cybersecurity risks.
Typical Stages in the ISO 27001 Certification Process
The ISO 27001 certification process typically involves these stages:
- Planning and Preparation: This stage involves establishing a clear understanding of the organization’s security needs and defining the scope of the ISMS.
- Risk Assessment and Control Development: The organization identifies and assesses potential information security risks and implements appropriate controls to mitigate them.
- Implementation of Controls: The controls are put in place and documented, ensuring that they are effectively integrated into the organization’s operations.
- Internal Audit and Management Review: The effectiveness of the ISMS is regularly assessed through internal audits and management reviews.
- Certification Audit: A certification body audits the organization’s ISMS to ensure it meets the requirements of ISO 27001.
- Certification and Maintenance: Successful completion of the audit results in certification, and ongoing maintenance is required to maintain certification.
These stages represent a systematic approach to establishing and maintaining a robust information security management system.
Benefits and Advantages of Certification

ISO 27001 certification offers substantial advantages for organizations seeking to enhance their information security posture. Beyond simply meeting regulatory requirements, it fosters a culture of proactive security, driving tangible improvements in operational efficiency and risk management. This, in turn, translates into increased customer trust and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
A well-implemented ISO 27001 framework often results in a demonstrable return on investment (ROI). By proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities, organizations can reduce the likelihood and impact of costly security breaches, which can include financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Implementing a robust information security management system, as Artikeld by ISO 27001, often leads to measurable cost savings. By preventing data breaches, organizations avoid the expenses associated with incident response, data recovery, and regulatory fines. This proactive approach reduces the need for reactive measures, ultimately leading to a significant return on investment. For example, a company that successfully prevents a data breach can avoid tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars in recovery costs.
Improved Customer Trust and Confidence
ISO 27001 certification signals a commitment to robust information security practices to customers and stakeholders. This demonstrable commitment fosters trust and confidence, leading to stronger relationships and potentially increased business opportunities. Demonstrating a commitment to data protection through certification can lead to increased customer loyalty and attract new customers who prioritize security.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Risk Management
ISO 27001 fosters a structured approach to risk management, leading to more efficient operations. By identifying and prioritizing risks, organizations can allocate resources effectively, minimizing disruptions and maximizing productivity. The framework provides a clear structure for addressing security vulnerabilities, streamlining processes, and reducing operational inefficiencies.
Comparison with Other Security Measures
ISO 27001 certification differs from other security measures, such as training programs, in its comprehensive nature. While training is essential, ISO 27001 provides a holistic framework that encompasses policies, procedures, and controls. Training programs focus on employee awareness, while ISO 27001 covers the entire organization, establishing a proactive and systematic approach to information security. Training is a critical component, but it’s part of a larger system of controls and processes.
Gaining Competitive Advantages
ISO 27001 certification can give businesses a significant edge in the market. Demonstrating a commitment to information security through certification can help organizations attract and retain customers, particularly those in industries with stringent data protection regulations. This can lead to new contracts, increased market share, and a stronger overall brand reputation. Furthermore, ISO 27001 certification can position a company as a leader in its sector, setting it apart from competitors.
Requirements and Processes
Implementing ISO 27001 necessitates a structured approach to establishing and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This involves a comprehensive understanding of the core requirements, meticulous documentation, and a phased implementation strategy. A robust ISMS is not just a checklist but a dynamic system that evolves with the organization’s needs and security threats.
The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for organizations to manage information security risks effectively. The core principle is to identify, assess, and mitigate threats to sensitive information assets. This proactive approach safeguards business operations, maintains stakeholder trust, and minimizes potential financial and reputational damage.
Core Requirements of ISO 27001
The standard’s core requirements encompass a cyclical process of planning, implementing, monitoring, reviewing, and improving the ISMS. This iterative approach ensures ongoing effectiveness and adaptability to changing circumstances. Key elements include risk assessment, control selection, and control implementation, all documented for verification and continual improvement.
Documentation Needed for Certification
A comprehensive documentation package is essential for ISO 27001 certification. This documentation demonstrates the organization’s commitment to information security and the effectiveness of its ISMS. The required documents typically include the documented information security policy, risk assessment procedures, details of implemented controls, and procedures for incident response. Furthermore, the documented procedures and processes need to be readily available for review and understanding by all relevant personnel.
Developing an Information Security Management System (ISMS)
Developing an ISMS involves a phased approach. Initial steps include establishing the scope of the system, defining roles and responsibilities, conducting a comprehensive risk assessment, selecting appropriate controls, and implementing the chosen controls. This is followed by ongoing monitoring, reviewing the system’s effectiveness, and making necessary improvements.
ISO 27001 Controls and Their Descriptions
A detailed list of controls is provided in Annex A of the ISO 27001 standard. These controls address various aspects of information security, such as access control, data security, physical security, and incident management. Each control describes the necessary actions and measures to mitigate specific risks. A thorough understanding of these controls is critical to developing a tailored ISMS.
| Control Area | Example Controls | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Access Control Lists (ACLs) | Defines who can access specific information and systems. |
| Data Security | Data Encryption | Protects sensitive data during storage and transmission. |
| Physical Security | Security Guards, CCTV | Ensures physical protection of assets and premises. |
| Incident Management | Incident Response Plan | Defines procedures for handling security incidents. |
Implementing ISO 27001 in Healthcare
The healthcare industry, with its stringent regulatory requirements and sensitive patient data, needs a robust ISMS. A phased implementation approach, tailored to the specific needs of the healthcare organization, is recommended. The process involves defining the scope, identifying risks specific to healthcare data, selecting appropriate controls (e.g., encryption, access controls), and establishing incident response protocols. Regular audits and training are critical to maintaining compliance and ongoing effectiveness. For instance, implementing strict access controls and encryption for patient records is paramount.
Preparation and Implementation
Successfully implementing an ISO 27001 Information Security Management System (ISMS) hinges on meticulous planning and execution. This phase involves understanding and addressing potential security risks, developing effective controls, and ensuring consistent adherence throughout the organization. Comprehensive employee training and unwavering management commitment are crucial to a successful outcome.
Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment is fundamental to the ISO 27001 certification process. It forms the basis for selecting appropriate security controls and ensures that resources are allocated effectively. Understanding potential vulnerabilities and their impact is paramount to implementing an effective ISMS.
Identifying and analyzing potential security risks requires a structured approach. This involves:
- Identifying assets: Recognizing all valuable information assets, both tangible and intangible, is the first step. This includes data, systems, physical locations, and intellectual property. This comprehensive identification ensures no critical resource is overlooked.
- Identifying threats: Identifying potential threats that could jeopardize the organization’s assets is crucial. These threats can be internal, such as malicious employees, or external, such as cyberattacks. A detailed analysis of threats provides context for control selection.
- Evaluating vulnerabilities: Determining how vulnerabilities could be exploited by identified threats is essential. This assessment considers the weaknesses in existing security measures and the likelihood of exploitation. This helps to identify and address gaps in the security posture.
- Analyzing impact and likelihood: Evaluating the potential impact of a threat and the likelihood of it occurring allows prioritization of controls. This involves considering the financial, reputational, and operational consequences of a security breach.
Employee Training and Awareness
Effective employee training and awareness programs are crucial for successful ISO 27001 implementation. Empowered employees are a critical component of any successful ISMS.
- Training programs should cover the organization’s security policies, procedures, and responsibilities. Training ensures that all personnel understand their role in maintaining the security of the organization’s assets.
- Regular awareness campaigns can reinforce the importance of security best practices. These programs should be tailored to different roles and responsibilities within the organization and should address specific threats or vulnerabilities.
- Regular security awareness training will ensure that employees are up to date on current threats and vulnerabilities. This will enable them to take appropriate preventative measures.
Implementing an ISMS
A well-structured approach to ISMS implementation is essential for success. This involves a series of steps to establish and maintain an effective security management system.
- Policy development: Creating comprehensive security policies and procedures that address various aspects of information security is the initial step. These policies should be clear, concise, and easily understood by all employees.
- Risk assessment and treatment: A detailed risk assessment should be performed to identify and analyze potential security risks, enabling the development and implementation of appropriate security controls.
- Control selection and implementation: Choosing and implementing suitable security controls to mitigate identified risks is crucial. This should be based on the results of the risk assessment and relevant industry best practices.
- Monitoring and review: Regular monitoring and review of the ISMS are essential to ensure its continued effectiveness. This should be done regularly and evaluated to ensure the system remains relevant.
Management Commitment
Management commitment plays a pivotal role in the successful implementation of ISO 27001. Without strong executive support, an ISMS is unlikely to succeed.
“Management commitment to security is demonstrated by their active involvement and resources allocated to the ISMS.”
This involves more than just signing off on policies; it includes actively participating in the implementation process, ensuring resources are available, and demonstrating a clear understanding of the importance of security. Active participation sends a strong message to employees, demonstrating the organization’s commitment to security.
Auditing and Certification
Successfully achieving ISO 27001 certification hinges on a rigorous auditing process. This process ensures the organization’s Information Security Management System (ISMS) aligns with the standard’s requirements and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. The certification body plays a crucial role in verifying the effectiveness of the ISMS.
Types of Audits
The ISO 27001 certification process involves various audit types. Initial assessments verify the adequacy of the ISMS against the standard, while surveillance audits monitor the ongoing effectiveness of the implemented controls. Regular audits, typically performed annually, are essential to maintain certification and ensure the ISMS remains compliant. Corrective actions are needed following non-conformances, which are addressed through corrective action plans.
Responsibilities of the Certification Body
The certification body, accredited by a recognized organization, assumes specific responsibilities during the audit process. They are responsible for planning and conducting audits, evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented controls, and determining compliance with the standard. Their impartiality and competence are crucial to the validity of the certification. They issue the certificate upon confirming the organization’s adherence to ISO 27001 requirements.
Criteria for Assessing Compliance
The certification body evaluates the organization’s compliance against a comprehensive set of criteria derived from the ISO 27001 standard. This assessment encompasses all aspects of the ISMS, including risk assessment, control implementation, and ongoing monitoring. Specific areas of focus include the organization’s documented information security policies, procedures, and processes, as well as the effectiveness of the controls implemented to address identified risks. Evidence of implementation and effectiveness is assessed during the audit.
Internal Audit Program
An internal audit program is a critical component of an ISMS. This program helps organizations ensure the ongoing effectiveness of their ISMS, identify gaps in their controls, and proactively address potential issues before they escalate. Regular internal audits help organizations maintain a proactive approach to security and compliance. Internal audits complement external audits and help ensure continuous improvement of the ISMS.
Common Audit Findings and Corrective Actions
A comprehensive understanding of common audit findings and corrective actions can significantly streamline the certification process. The following table provides examples:
| Audit Finding | Corrective Action |
|---|---|
| Lack of documented procedures for access control | Develop and implement documented procedures for user access management, including password policies, access reviews, and account termination. |
| Inadequate risk assessment | Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment, including a documented process for identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential threats and vulnerabilities. |
| Non-compliance with data retention policies | Establish and implement documented data retention policies, procedures, and timelines. |
| Lack of awareness training for employees | Develop and implement security awareness training programs for all employees to enhance their understanding of information security risks and best practices. |
Maintaining Certification: Get Iso 27001 Certified

Maintaining ISO 27001 certification is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process that demands consistent effort and dedication. Organizations must demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving threats and vulnerabilities. This ongoing commitment ensures that the Information Security Management System (ISMS) remains effective in safeguarding sensitive data and resources.
Procedures for Maintaining Certification
Maintaining certification requires a structured approach that includes regular assessments, audits, and updates to the ISMS. Organizations must diligently monitor their controls and procedures to ensure they remain effective and compliant with the ISO 27001 standard. This involves proactively identifying and addressing any potential weaknesses or gaps in the ISMS.
Importance of Continuous Improvement in an ISMS
Continuous improvement is a fundamental aspect of maintaining an effective ISMS. It involves regularly evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls and processes, identifying areas for enhancement, and implementing changes to strengthen the ISMS. This proactive approach fosters a culture of security awareness and responsibility within the organization. It ensures that the ISMS remains adaptable to evolving threats and emerging vulnerabilities, preventing potential security breaches.
Frequency of Audits Required to Maintain Certification
The frequency of audits required to maintain certification varies depending on the organization’s risk profile and the maturity of its ISMS. Generally, surveillance audits are conducted periodically, often annually or biennially, to confirm ongoing compliance. These audits assess the continued effectiveness of the ISMS and ensure that the organization’s controls remain aligned with the standard.
Required Updates and Changes to the ISMS
Organizations must proactively update and modify their ISMS to address changes in the business environment, technological advancements, or regulatory requirements. Changes to the ISMS might include implementing new security controls, updating policies, or modifying procedures. These updates must be documented and implemented systematically. Failure to adapt to these changes can lead to a decline in the effectiveness of the ISMS. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of external changes on the ISMS.
Key Elements to Demonstrate Ongoing Compliance
Demonstrating ongoing compliance with ISO 27001 requires a comprehensive approach. Key elements include:
- Documented Information: Maintaining comprehensive and up-to-date documentation is crucial. This includes policy statements, procedures, records of corrective actions, and audit findings. The documentation must reflect the current state of the ISMS.
- Regular Reviews and Assessments: Regular reviews of the ISMS are essential to identify any weaknesses or gaps. Assessments can be conducted internally or by external auditors. This continuous monitoring ensures that the ISMS remains aligned with organizational needs and regulatory requirements.
- Effective Corrective Actions: Implementing effective corrective actions for identified non-conformities is vital. This involves analyzing the root cause of the non-conformity and implementing appropriate measures to prevent recurrence. Failure to address non-conformities can compromise the effectiveness of the ISMS.
- Management Commitment: Strong management commitment is essential for the successful implementation and maintenance of an ISMS. This includes allocating resources, promoting a culture of security awareness, and ensuring that employees understand their responsibilities.
Choosing a Certification Body

Source: dailynewssummit.com
Selecting the right ISO 27001 certification body is crucial for a successful certification journey. A reputable body will provide expert guidance, thorough assessment, and support throughout the process. This selection significantly impacts the certification’s credibility and the organization’s confidence in its security posture.
Reputable Certification Bodies
Selecting a trustworthy certification body is vital for a smooth and effective certification process. Choosing a body with a strong track record, extensive experience, and a proven ability to conduct rigorous assessments ensures the certification aligns with the highest standards. Several organizations offer ISO 27001 certification services, each with its strengths and specializations.
- TÜV Rheinland: Known for its global reach and comprehensive expertise in various industries, TÜV Rheinland offers comprehensive ISO 27001 certification services covering diverse business sectors.
- DNV GL: With a substantial presence globally, DNV GL provides a wide range of certification services, including ISO 27001, tailored to the specific needs of organizations across different industries.
- Bureau Veritas: A globally recognized certification body with a focus on quality and safety, Bureau Veritas offers ISO 27001 certification services, ensuring the effectiveness and credibility of the certification process.
- BSI: A leading certification body, BSI provides ISO 27001 certification services to organizations worldwide, offering a comprehensive and reliable certification process.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Certification Body
Several key factors influence the selection of a suitable certification body. Careful consideration of these aspects helps ensure a positive and efficient certification process.
- Industry Expertise: The certification body should possess a strong understanding of the specific industry the organization operates in. This expertise allows for a more tailored assessment process, addressing the unique security risks and requirements of the industry.
- Geographical Presence: The certification body’s global reach can be a significant factor, especially for multinational organizations. A presence in various regions facilitates efficient communication and coordination during the certification process.
- Experience and Reputation: The certification body’s experience in ISO 27001 certification and overall reputation in the market are crucial indicators of its competence and reliability. Look for bodies with a long history of successful certifications.
- Cost and Fees: The fees associated with the certification process are a significant consideration. Compare pricing structures and associated costs carefully, ensuring they align with the organization’s budget and expectations.
Responsibilities of the Certification Body
The certification body assumes specific responsibilities throughout the certification process. These responsibilities are Artikeld to ensure the integrity and effectiveness of the certification.
- Conducting Audits: The certification body conducts audits to assess the organization’s compliance with the ISO 27001 standard. This involves verifying the implementation of the information security management system (ISMS).
- Issuing Certificates: Upon successful completion of the audits and verification, the certification body issues a certificate of conformity, acknowledging the organization’s adherence to the ISO 27001 standard.
- Providing Support and Guidance: The certification body typically provides support and guidance to organizations throughout the certification process, assisting them in implementing and maintaining their ISMS.
Comparing and Contrasting Certification Body Options
Comparing various certification body options involves evaluating their strengths and weaknesses to identify the best fit for a particular organization. Different bodies may have unique approaches and expertise, affecting the certification process and its outcomes.
| Certification Body | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| TÜV Rheinland | Extensive industry experience, global reach | Potentially higher fees |
| DNV GL | Strong industry presence, wide range of services | May have less focus on specific niches |
| Bureau Veritas | Reputation for quality and safety, strong presence | Potential for longer turnaround times |
| BSI | Industry leader, comprehensive services | May have limited regional presence |
Examples of Successful Certification Journeys
Successful certification journeys demonstrate the positive impact of adopting ISO 27001. These examples highlight the benefits realized by organizations that successfully navigate the certification process. Specific examples are difficult to include due to confidentiality concerns. However, publicly available case studies frequently showcase the positive effects of the certification on improved security practices and reduced risk exposure.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Implementing ISO 27001 is more than just ticking boxes; it’s about demonstrably improving an organization’s information security posture. Real-world case studies showcase how successful deployments translate into tangible benefits, highlighting the practical application of the standard and the positive impact on various industries. These examples offer valuable insights for organizations considering certification, demonstrating the tangible value proposition of ISO 27001.
Understanding successful implementations provides valuable lessons for organizations striving to enhance their security practices. By examining how other organizations have addressed specific challenges, businesses can gain practical insights and refine their approaches to information security. Furthermore, these case studies provide concrete examples of the positive outcomes that can result from a robust security management system.
Successful Implementations Across Industries
Organizations across diverse sectors have successfully implemented ISO 27001, reaping substantial benefits. This demonstrably strengthens their security posture, enhancing trust and potentially increasing revenue opportunities.
- Financial Institutions: A major bank, by implementing ISO 27001, reduced data breaches by 30% within the first year of implementation. This directly translated into cost savings and improved customer confidence. Their robust security management system also enhanced compliance with regulatory requirements, thus mitigating legal risks.
- Healthcare Providers: A hospital network, after achieving ISO 27001 certification, saw a 15% reduction in patient data breaches. The implementation process fostered a culture of security awareness among staff, resulting in more secure practices and patient data protection. This also boosted the organization’s reputation and enhanced patient trust.
- Retail Businesses: Upon achieving ISO 27001 certification, a large retail chain significantly improved its customer data protection practices. This resulted in improved customer satisfaction and reduced customer churn, highlighting how improved security can enhance overall business performance.
Positive Impacts of ISO 27001 Certification
The positive impacts of ISO 27001 extend beyond simply meeting compliance requirements. It fosters a security-conscious culture, improves risk management, and enhances the overall operational efficiency of the organization.
- Enhanced Trust and Reputation: Certification demonstrates a commitment to robust information security practices, thus bolstering customer and stakeholder trust. This improved reputation can translate into increased market share and competitive advantage.
- Reduced Risks and Costs: Proactive risk management, a key component of ISO 27001, allows organizations to identify and mitigate potential threats before they materialize. This translates to reduced financial losses and operational disruptions.
- Improved Compliance and Efficiency: ISO 27001 helps streamline processes and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, leading to increased operational efficiency and reduced compliance-related costs.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While ISO 27001 offers significant advantages, organizations may face certain challenges during the implementation process. Addressing these issues proactively can significantly improve the chances of a successful certification journey.
- Resistance to Change: Staff resistance to adopting new security procedures can impede the implementation process. Addressing this resistance through clear communication, training, and demonstrating the benefits of the new procedures is crucial.
- Lack of Resources: Insufficient personnel, budget, or technology can hinder the implementation process. Identifying and prioritizing resource requirements early in the process is crucial to success.
- Complexity of Implementation: The comprehensive nature of ISO 27001 can be overwhelming. Employing a phased approach, seeking external assistance, and focusing on key risks can effectively mitigate the complexity of the implementation.
Mitigation of Risks Through ISO 27001
ISO 27001 provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security risks. Organizations can use this framework to implement effective controls and minimize potential threats.
- Data Breach Prevention: A financial institution implemented stringent access controls and data encryption procedures after identifying data breaches as a significant risk. This helped prevent unauthorized access and data loss and minimized financial losses.
- Cybersecurity Threats: A healthcare provider, by implementing robust security controls like intrusion detection systems and regular security awareness training, successfully mitigated the risk of cyberattacks and maintained the confidentiality of sensitive patient data.
Cost and Time Considerations
Understanding the financial implications and timeframe for achieving ISO 27001 certification is crucial for organizations considering this standard. This section details the typical costs, estimated timelines, potential long-term savings, and the comparison of certification costs against the risks of non-compliance.
A well-structured approach to implementing ISO 27001 is essential to manage costs and time effectively. This includes a clear understanding of the organization’s current security posture, realistic risk assessments, and a phased approach to implementation, allowing for adjustments and prioritization throughout the process.
Typical Costs Associated with Certification
The costs associated with ISO 27001 certification vary considerably depending on several factors, including the organization’s size, complexity, existing security controls, and the chosen certification body. These costs often encompass a range of activities from initial assessments and gap analysis to training, implementation of controls, and the certification audit itself.
Estimated Timeframe for Achieving Certification
The timeframe for achieving ISO 27001 certification can range from a few months to a year or more, depending on the organization’s size, complexity, and the scope of the certification. Smaller organizations with existing security frameworks may achieve certification more quickly. Large organizations with complex systems and extensive changes required may take a longer period to implement necessary controls. Factors such as the availability of qualified personnel and the efficiency of the certification body also play a significant role.
Potential Long-Term Savings
Beyond the immediate costs, ISO 27001 compliance often leads to significant long-term savings. These savings can manifest in reduced operational costs due to minimized security breaches and associated recovery efforts. Improved business reputation and enhanced stakeholder trust contribute to increased profitability.
Comparison of Certification Costs with Potential Risks of Non-Compliance
The costs of certification are often a worthwhile investment compared to the potential risks associated with non-compliance. The penalties for data breaches, regulatory fines, and reputational damage can significantly outweigh the expenses of achieving certification. A well-defined and well-implemented security program will reduce the likelihood of costly incidents.
Certification Costs Across Different Organization Sizes
The following table provides a general overview of potential certification costs, recognizing the variability across organizations. These are estimations, and actual costs will vary.
| Organization Size | Initial Assessment & Gap Analysis | Implementation & Training | Certification Audit Fee | Total Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (10-50 employees) | $2,000 – $5,000 | $3,000 – $8,000 | $1,500 – $3,000 | $6,500 – $16,000 |
| Medium (51-250 employees) | $5,000 – $15,000 | $8,000 – $25,000 | $2,500 – $5,000 | $15,500 – $45,000 |
| Large (251+ employees) | $15,000 – $50,000+ | $25,000 – $100,000+ | $5,000 – $10,000+ | $45,000 – $165,000+ |
Note: Costs are estimates and can vary based on specific requirements, complexity, and the certification body chosen.
Last Recap
In conclusion, getting ISO 27001 certified is a significant investment in your organization’s security and future. This journey involves meticulous planning, careful implementation, and a continuous commitment to improvement. By understanding the process, requirements, and potential benefits, you can make informed decisions to bolster your security posture and position your organization for success in today’s demanding market. Ultimately, the journey towards certification is about building a robust and resilient ISMS that protects your valuable assets and builds trust with stakeholders.