Get ISO 27001 Certification Your Guide
Getting ISO 27001 certification is a crucial step for organizations seeking to bolster their information security posture. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of achieving ISO 27001 certification, from understanding the standard’s key principles to navigating the certification process itself. We’ll explore the benefits, challenges, and practical steps needed for successful implementation. Gaining ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a strong commitment to information security management and can significantly enhance an organization’s reputation and trust among stakeholders.
This guide will cover various aspects of the certification process, including understanding the requirements of ISO 27001, the practical steps for implementation, and the importance of ongoing maintenance. We will also highlight the value proposition, discussing the return on investment (ROI) and the improved customer confidence that often accompanies this certification. Furthermore, the guide provides practical resources and insights, including sample risk assessments, checklists, and detailed case studies to help you prepare for the certification audit.
Understanding ISO 27001 Certification

ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for establishing and maintaining information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a framework for organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate information security risks, ultimately enhancing the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. This framework addresses a wide range of security aspects, from physical security to access controls and data protection.
Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a commitment to robust information security practices and builds trust with stakeholders. The standard’s comprehensive approach ensures organizations are not only compliant with regulatory requirements but also proactive in safeguarding their sensitive data and reputation. This commitment is reflected in the demonstrable improvement in security posture and the potential reduction in security breaches.
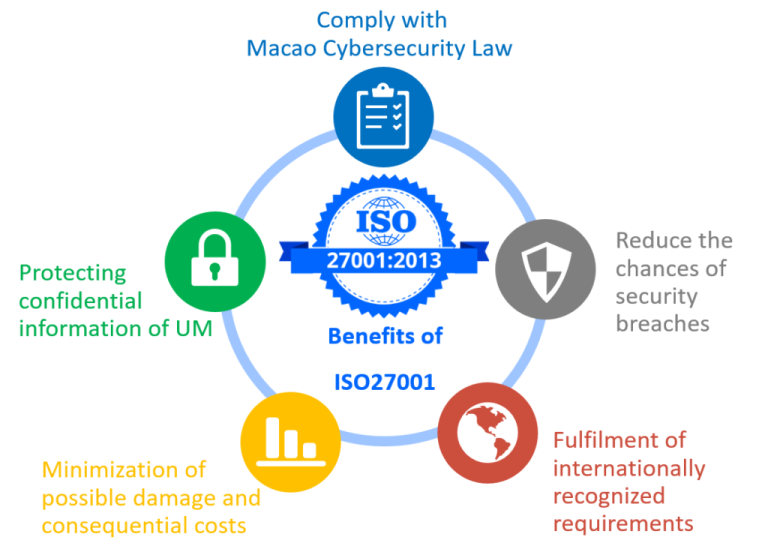
Benefits of Achieving ISO 27001 Certification
Implementing and certifying to ISO 27001 offers a range of tangible benefits. These include enhanced operational efficiency, improved customer trust, increased resilience to security breaches, and a competitive advantage in the market. Furthermore, it fosters a culture of security awareness within the organization and helps reduce the risk of financial losses and reputational damage.
Comparison with Other Security Standards
ISO 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework are both valuable resources for organizations seeking to improve their information security. While both aim to enhance security, they differ in their approach. ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive, process-oriented standard, while the NIST Cybersecurity Framework offers a more flexible, risk-based approach. Organizations can use both frameworks to complement each other, leveraging the strengths of each to address specific security needs.
Importance of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)
An ISMS, as defined by ISO 27001, is a structured framework for managing information security. An effectively implemented ISMS helps organizations to identify, assess, and control information security risks. It also fosters a culture of security awareness and promotes continuous improvement. This is crucial in today’s digital landscape, where organizations are increasingly reliant on information systems and face escalating threats.
Key Clauses of ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 standard comprises 11 clauses that encompass the entire ISMS lifecycle. These clauses provide a structured approach to information security management, from planning and implementation to monitoring and improvement.
| Clause Number | Clause Description |
|---|---|
| 4 | Context of the organization |
| 5 | Leadership |
| 6 | Planning |
| 7 | Support |
| 8 | Operations |
| 9 | Performance evaluation |
| 10 | Improvement |
| 4.1 | Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties |
| 4.2 | Determining the scope of the ISMS |
| 4.3 | Establishing the context of the organization |
The Certification Process
Securing ISO 27001 certification is a structured process, demanding meticulous planning and execution. It involves a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s existing information security management system (ISMS) and its alignment with the ISO 27001 standard. This process typically involves multiple stages and a commitment to continuous improvement in information security practices.
The certification process is not merely a one-time exercise; it’s an ongoing journey toward enhanced security posture. It requires consistent effort and dedication to maintain the certified status. Organizations should view this process as a framework for continuous improvement and risk management.
Steps Involved in Obtaining Certification
The path to ISO 27001 certification generally follows these key stages:
- Develop and Implement an ISMS: Organizations need to create a documented information security management system (ISMS) that addresses the requirements of ISO 27001. This includes defining roles, responsibilities, policies, procedures, and controls to manage information risks.
- Internal Audit: An internal audit process is crucial to assess the effectiveness of the implemented ISMS against the ISO 27001 standard. This audit identifies areas for improvement and ensures compliance with established policies and procedures.
- Certification Body Assessment: A certified body will conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s ISMS. This evaluation verifies if the ISMS meets the ISO 27001 standard requirements. The assessment often includes on-site visits, documentation review, and interviews with personnel.
- Certification Grant or Non-conformity Report: Following the assessment, the certification body issues a certification certificate if the ISMS meets the standard. Alternatively, a report highlighting non-conformities may be provided, directing the organization on the necessary corrective actions.
- Continuous Improvement: Maintaining the certification involves ongoing efforts to enhance the ISMS and address any identified weaknesses or vulnerabilities. Regular audits and reviews are necessary to ensure the ISMS remains effective.
Typical Certification Timeline
The timeframe for obtaining ISO 27001 certification can vary depending on factors such as the size and complexity of the organization, the maturity of the existing ISMS, and the chosen certification body. A typical certification process can range from several months to a year.
- Initial Planning and Documentation (1-3 months): The initial stage often involves detailed planning, creating documentation, and developing policies and procedures for the ISMS.
- Internal Audits and Improvements (2-4 months): This phase focuses on internal audits and addressing any identified deficiencies within the ISMS. This stage can be shorter if the IISM is already well-established.
- Certification Body Assessment (1-2 months): The assessment period typically involves documentation review and on-site audits by the certification body. This can vary depending on the complexity of the organization.
- Certification Issuance (1-2 weeks): Once the certification body confirms compliance, the certificate is issued. Post-certification, ongoing maintenance, and continuous improvement are crucial to sustain the certification.
Common Challenges During Certification
Several challenges can hinder the certification process. These include:
- Lack of Management Support: Strong management commitment and support are essential for successful certification. Without this, the process can stall.
- Insufficient Resources: Adequate resources, including time, personnel, and budget, are vital for a smooth certification journey. Inadequate resources can significantly impact the timeline and outcome.
- Resistance to Change: Changes in processes and procedures can sometimes face resistance from employees. Effective communication and training are crucial to overcome such resistance.
- Gaps in Documentation: Comprehensive documentation is a cornerstone of ISO 27001 certification. Inconsistent or incomplete documentation can lead to issues during the assessment.
Different Certification Bodies and Their Roles
Several organizations offer ISO 27001 certification services. These bodies play a crucial role in assessing organizations and ensuring compliance with the standard.
- Certification Body Roles: Certification bodies evaluate organizations, verify compliance with the ISO 27001 standard, and issue certificates to organizations that meet the requirements.
Comparison of Certification Bodies
The table below provides a comparison of different certification bodies, including their fees and typical turnaround times. This information is for illustrative purposes only and can vary significantly.
| Certification Body | Typical Fee Range (USD) | Turnaround Time (Months) |
|---|---|---|
| Body A | $5,000 – $10,000 | 3-4 |
| Body B | $6,000 – $12,000 | 4-5 |
| Body C | $4,000 – $8,000 | 2-3 |
Requirements and Implementation
Implementing ISO 27001 requires a structured approach to ensure the effectiveness of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This involves understanding the key requirements, effectively assessing risks, and meticulously implementing controls to manage those risks. A robust internal audit process is also crucialto maintainingn ongoing compliance.
Key Requirements of ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 standard Artikels numerous requirements for establishing and maintaining an ISMS. These requirements cover areas such as risk management, security policies, and the establishment of security controls. A comprehensive understanding of these requirements is fundamental to successful implementation.
Importance of Risk Assessment in ISO 27001
Risk assessment is a cornerstone of ISO 27001. It forms the basis for selecting and implementing appropriate security controls. A thorough risk assessment process identifies potential threats and vulnerabilities, evaluates their likelihood and impact, and prioritizes mitigation efforts. This proactive approach allows organizations to allocate resources effectively and minimize the impact of security incidents. It’s not merely a checklist; it’s a dynamic process requiring ongoing review and adaptation.
Implementing an ISMS Based on ISO 27001
Implementing an ISMS based on ISO 27001 is a multi-step process. It involves creating a documented information security policy, conducting a thorough risk assessment, selecting appropriate security controls from the Annex A controls, implementing these controls, and regularly reviewing and updating the system. Documentation is critical; this ensures traceability and demonstrable compliance. Successful implementation requires strong leadership and commitment from all levels of the organization.
Risk Assessment Procedure Example
A robust risk assessment procedure should include these steps:
- Identify Assets: This step involves cataloging all critical information assets, including data, systems, and physical infrastructure. Consider the sensitivity of the data and the potential impact of its loss or compromise.
- Identify Threats and Vulnerabilities: Analyze potential threats, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or human error, and identify the vulnerabilities these threats exploit within the organization. Use historical data and industry best practices to identify potential threats.
- Analyze Likelihood and Impact: Evaluate the probability of each threat occurring and the potential consequences if it does. This often involves quantitative analysis and qualitative judgment. For example, a cyberattack might have a high likelihood and a high impact if sensitive customer data is exposed. A lost laptop might have a lower likelihood, but it will have a significant impact if it contains confidential financial information.
- Determine Risk Level: Combine the likelihood and impact assessments to determine the overall risk level for each identified threat. This step is crucial for prioritizing controls.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Develop appropriate mitigation strategies to address the risks. This may involve implementing security controls, improving procedures, or investing in new technologies. For instance, if a high-risk threat is identified related to phishing, the organization might implement robust email security filters and training programs for employees.
- Monitor and Review: The risk assessment process is not a one-time activity. It must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the organization’s environment, technology, and threats.
Role of Internal Audits in Maintaining Compliance
Internal audits play a vital role in ensuring ongoing compliance with ISO 27001. These audits evaluate the effectiveness of the ISMS, identify areas for improvement, and verify that controls are operating as intended. Regular audits provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement and demonstrate the commitment to maintaining a strong security posture.
Benefits and Value Proposition
Implementing ISO 27001 provides substantial advantages for organizations, extending beyond mere compliance. This comprehensive framework fosters a culture of information security, leading to improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer trust, and a strengthened organizational reputation. The benefits are tangible, resulting in a demonstrable return on investment (ROI).
A well-implemented ISO 27001 framework establishes a robust security posture, reducing vulnerabilities and minimizing potential risks associated with data breaches. This proactive approach safeguards sensitive information, ensuring business continuity and preventing financial losses. Furthermore, it positions the organization for future growth and adaptability in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Advantages of ISO 27001 Implementation
A robust information security management system, established through ISO 27001, offers a multitude of advantages. These include a reduction in security incidents, improved data protection, and enhanced compliance with regulations. The framework promotes a proactive security approach, reducing the likelihood of breaches and associated financial losses. Improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime are also significant benefits.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Quantifying the precise ROI of ISO 27001 certification can be complex. However, tangible benefits such as reduced operational costs associated with security breaches, increased customer confidence leading to higher revenue, and enhanced stakeholder confidence are often cited as key elements. The framework’s emphasis on risk management, for instance, can directly contribute to cost savings by proactively mitigating potential threats.
Impact on Customer Trust and Confidence
ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a commitment to data security, enhancing customer trust and confidence. Customers are more likely to engage with and remain loyal to organizations that prioritize data protection. This increased trust can translate into higher customer retention rates, increased sales, and improved brand reputation. The certification serves as a powerful indicator of an organization’s dedication to protecting sensitive customer data.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
| Organization | Benefits Realized |
|---|---|
| XYZ Bank | Significant reduction in data breaches, improved customer satisfaction scores, and a notable increase in market share. |
| ABC Healthcare | Strengthened patient data security, complied with HIPAA regulations, and improved operational efficiency. |
| DEF Technology | Reduced security incidents, improved operational efficiency, and a noticeable increase in investor confidence. |
Note: These are hypothetical case studies; real-world examples may vary in specific details and quantifiable results.
Enhanced Organizational Reputation, Get iso 27001 certification.
Demonstrating a commitment to information security through ISO 27001 certification can significantly enhance an organization’s reputation. This enhanced reputation often translates to increased investor confidence, attracting top talent and fostering stronger relationships with stakeholders. Organizations perceived as secure and trustworthy are more likely to attract and retain customers and partners. Furthermore, the certification fosters a culture of security within the organization, leading to a more proactive approach to risk management.
Preparation and Resources

Source: medium.com
Successfully obtaining ISO 27001 certification requires meticulous preparation. This involves a thorough assessment of your current security practices, a robust implementation plan, and ongoing commitment to maintaining compliance. Effective preparation ensures a smoother audit process and ultimately strengthens your organization’s information security posture.
A well-structured approach to preparation involves identifying gaps in existing security controls, implementing necessary improvements, and fostering a culture of security awareness. This approach, underpinned by a comprehensive understanding of the standard’s requirements, is critical for achieving certification.
Essential Steps for Audit Preparation
Thorough preparation for the certification audit is crucial. This involves a systematic review of existing security controls and procedures. A key aspect is documenting and demonstrating compliance with ISO 27001 requirements. A well-defined and documented process ensures transparency and traceability during the audit.
- Gap Analysis: Conduct a comprehensive review of your existing security controls and policies against the ISO 27001 standard. Identify areas needing improvement or implementation. This crucial step will guide the necessary changes and enhancements.
- Documentation Review: Evaluate the completeness and accuracy of existing documentation related to information security policies, procedures, and controls. This step is important for demonstrating compliance and ensuring consistency across all security practices.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a detailed risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. This is essential for tailoring controls to specific risks and ensuring a comprehensive security approach.
- Control Implementation: Implement the necessary controls to address identified risks and vulnerabilities. This phase involves the practical application of the determined security measures.
- Internal Audit: Conduct an internal audit to test the effectiveness of implemented controls and ensure they are operating as intended. This step ensures compliance and identifies any gaps in implementation.
Documentation Templates and Checklists
Comprehensive documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance. Templates and checklists provide a structured approach for documenting policies, procedures, and controls.
- Policy Templates: Pre-designed templates provide a framework for developing policies on areas such as access control, data security, incident response, and physical security. These templates provide a standardized approach for creating clear and concise policies.
- Procedure Checklists: Checklists guide the development and implementation of procedures related to various aspects of information security. These checklists ensure a structured and consistent approach to all procedures.
- Control Implementation Checklists: Use checklists to ensure that each control is implemented correctly. This helps in verifying the completeness and effectiveness of control implementation.
Risk Management and Compliance Tools
Various tools facilitate risk management and compliance. Selecting the right tools depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
- Risk Management Software: Software tools assist in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. These tools provide a structured approach to risk management, aiding in the identification and evaluation of potential threats.
- Compliance Management Software: These tools help in tracking and managing compliance with regulations and standards, including ISO 27001. They facilitate compliance tracking and reporting.
Employee Training
Employee training is critical for successful ISO 27001 implementation. A well-trained workforce is essential for ensuring that all personnel understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining information security.
- Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs to educate employees on the ISO 27001 standard, relevant policies, and procedures. This training equips employees with the knowledge and skills to support security measures.
- Awareness Campaigns: Conduct regular awareness campaigns to reinforce the importance of information security best practices. These campaigns help maintain a strong security culture.
Online Resources for ISO 27001 Implementation
Numerous online resources offer guidance and support for ISO 27001 implementation. These resources are valuable tools for staying updated and informed.
- ISO Website: The official ISO website provides comprehensive information on the standard, including guidelines, templates, and resources. This website is the definitive source for all ISO standards.
- Industry Publications: Publications from industry associations and security experts offer insights into best practices and case studies. These publications are important sources of current information on security.
- Certification Bodies: Certification bodies often provide valuable resources and guidance. They offer a wealth of information and support on implementing ISO 27001.
- Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities provide opportunities for networking and exchanging information with other organizations. These forums offer valuable peer support and shared knowledge.
Choosing a Certification Body
Selecting the right certification body is crucial for a successful ISO 27001 certification. This choice directly impacts the process’s timeline, cost, and the overall credibility of your organization’s security management system. A reputable and experienced certification body will guide you through the process, ensuring compliance and providing valuable support.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Certification Body
Several key factors should influence your decision. Thorough research and careful consideration are essential for a successful outcome. These include the certification body’s expertise, experience, and geographic reach. The body’s accreditation status and cost structure are also critical aspects.
- Expertise and Experience: Look for a certification body with proven experience in auditing ISO 27001 implementations. Consider their understanding of industry-specific risks and their ability to tailor their approach to your organization’s unique needs. The body should possess a team of qualified auditors proficient in assessing information security management systems. A history of successful audits and positive feedback from previous clients is a strong indicator of their expertise.
- Geographic Reach: Evaluate the certification body’s presence in your region or globally. A local presence often translates to more convenient communication and fewer logistical challenges. A wider geographical reach can offer options for different office locations or global business needs.
- Accreditation Status: Accreditation by a recognized accreditation body is paramount. Accreditation demonstrates the certification body’s competence and impartiality. This crucial element ensures that he certification process adheres to established standards and procedures.
- Cost Structure and Services: Compare the fees and associated services offered by different certification bodies. Consider not only the initial certification cost but also any additional support services, such as training, guidance, or ongoing support.
Reputable Certification Bodies
Numerous reputable certification bodies offer ISO 27001 certification services. Their experience and reputation often play a crucial role in the selection process. Some prominent examples include:
- TÜV Rheinland: A globally recognized certification body with a strong track record in various industries.
- DNV GL: Known for its expertise in quality assurance and certification, including information security standards.
- BSI: A leading UK-based certification body with extensive experience in supporting organizations across various sectors.
- SGS: A global inspection, verification, testing, and certification company with a broad range of services.
Importance of Accreditation
Accreditation is a crucial aspect of selecting a certification body. Accreditation ensures that the certification body operates according to established standards and procedures. An accredited certification body demonstrates its competence, impartiality, and commitment to upholding the integrity of the certification process. It’s a mark of trust and assures stakeholders of the certification’s validity. The accreditation process itself is a rigorous one, involving regular audits and assessments to maintain the accreditation.
Comparative Analysis of Certification Body Costs and Services
The table below provides a comparative overview of costs and services offered by some certification bodies. This information is for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered exhaustive or definitive. Actual costs and services may vary depending on the organization’s specific needs.
| Certification Body | Initial Certification Fee (Estimated) | Additional Services (e.g., Training, Guidance) | Geographic Reach |
|---|---|---|---|
| TÜV Rheinland | €1,500 – €3,000 | Yes, training programs are available | Global |
| DNV GL | $2,000 – $4,000 | Yes, consulting services are offered | Global |
| BSI | £1,000 – £2,500 | Yes, ongoing support and resources | Global |
| SGS | $1,800 – $3,500 | Yes, various support packages | Global |
Maintaining Certification: Get Iso 27001 Certification

Maintaining ISO 27001 certification is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that demands continuous effort and vigilance. A certified organization must consistently demonstrate its commitment to information security management systems (ISMS) and its ability to adapt to evolving threats and industry best practices. This active approach ensures that the organization’s ISMS remains effective and relevant in safeguarding sensitive data.
Procedures for Maintaining Certification
The ISO 27001 certification process includes periodic surveillance audits. These audits evaluate the organization’s ongoing adherence to the standard’s requirements. The frequency and scope of these audits are determined by the certification body. Effective documentation of security controls and their implementation, along with demonstrable evidence of ongoing monitoring and improvement, are crucial. Regular reviews of the ISMS, including its policies, procedures, and controls, are essential for continuous improvement and to adapt to changing risks. Proper record-keeping of all audit findings, corrective actions, and their effectiveness is critical.
Importance of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is paramount for maintaining certification and demonstrating a proactive approach to information security. Regular assessments of the effectiveness of the ISMS and identification of areas for enhancement are vital. This iterative approach ensures that the organization’s ISMS is adaptable to emerging threats, new technologies, and evolving business needs. The organization should identify areas for improvement based on internal audits, customer feedback, industry best practices, and external threats. This includes adopting new technologies and methods for managing information security risks.
Preparing for Surveillance Audits
Effective preparation for surveillance audits is essential for a smooth and successful certification renewal. Thorough documentation of the implemented security controls is a prerequisite. This documentation should include evidence of control implementation, regular monitoring, and the management of any identified vulnerabilities. Regular training for personnel involved in the ISMS is vital. Ensuring all personnel are familiar with their roles and responsibilities is critical for maintaining compliance. A detailed audit trail should be established to demonstrate the organization’s adherence to the ISO 27001 standard. Maintaining a comprehensive and readily accessible record of the ISMS policies, procedures, and documentation is also essential.
Adapting to Industry Changes
Staying current with evolving industry trends and emerging threats is essential for maintaining ISO 27001 certification. The security landscape is constantly changing, requiring organizations to adapt their security strategies. This involves assessing emerging threats and vulnerabilities, such as ransomware attacks, cloud security risks, and social engineering tactics. Regular reviews of the organization’s risk assessment process, coupled with an updated risk register, should be conducted. This process should consider the introduction of new technologies and how they may impact the security posture. For instance, a company adopting cloud computing needs to adapt its security controls to accommodate the new environment. This might include implementing strong access controls, encryption, and monitoring within the cloud environment.
Checklist for Maintaining ISO 27001 Compliance
Maintaining compliance with ISO 27001 requires a structured approach. This checklist is a guide to ensure all necessary elements are considered.
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct periodic risk assessments to identify and evaluate potential threats to information assets.
- ISMS Documentation: Ensure all policies, procedures, and documentation related to the ISMS are current and readily accessible.
- Control Implementation: Verify that all documented controls are implemented and effectively functioning.
- Monitoring and Review: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the ISMS controls and conduct regular reviews of the ISMS.
- Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions to address any identified non-conformities or vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training: Provide regular training to all employees on their responsibilities related to information security.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements: Ensure compliance with all relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
- External Audits: Prepare for and respond to external audits conducted by the certification body.
- Continuous Improvement: Actively seek opportunities for continuous improvement in the ISMS.
Illustrative Case Studies
Achieving ISO 27001 certification is a significant step towards enhancing an organization’s information security posture. Successful implementation requires a meticulous approach, careful planning, and the ability to adapt to evolving security threats. This section details a case study highlighting the journey of a company that successfully navigated the certification process, along with the challenges encountered and solutions implemented. Furthermore, it provides a concrete example of a company’s risk assessment methodology and demonstrates the positive impact of ISO 27001 on improving the security posture and the measurable improvements observed.
The following case study focuses on a mid-sized financial services company, “Apex Financial,” that implemented ISO 27001 to bolster its security posture.
Apex Financial’s Journey to ISO 27001 Certification
Apex Financial, recognizing the increasing importance of data protection, embarked on a journey to achieve ISO 27001 certification. They understood that a robust information security management system (ISMS) was crucial for maintaining customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Challenges Faced and Solutions Implemented
Apex Financial encountered several challenges during the implementation phase. Initially, there was resistance from some employees regarding the new security protocols. To address this, the company implemented comprehensive training programs, emphasizing the importance of the new procedures and highlighting the benefits for everyone. Furthermore, a clear communication strategy was established to keep all employees informed about the progress and rationale behind the changes. Another key challenge was the significant time commitment required for documenting and reviewing existing processes. Apex Financial streamlined this process by utilizing a project management methodology and appointing dedicated personnel to oversee the documentation efforts. This approach ensured efficient and timely completion of the necessary documentation.
Risk Assessment Methodology
Apex Financial employed a structured risk assessment methodology, using a qualitative approach to identify and evaluate potential threats to its information assets. The methodology involved the following steps:
- Identification of assets: Apex Financial identified all critical information assets, encompassing customer data, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Threat identification: Potential threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and internal vulnerabilities, were meticulously identified.
- Vulnerability analysis: The company assessed the vulnerabilities of its assets to the identified threats.
- Risk assessment and evaluation: The identified risks were assessed based on their likelihood and potential impact using a matrix approach to categorize them.
- Risk treatment: Appropriate risk treatment strategies, including avoidance, mitigation, transference, and acceptance, were implemented to manage the identified risks.
Impact on Security Posture
Implementing ISO 27001 significantly improved Apex Financial’s security posture. The company experienced a notable reduction in security incidents, leading to increased customer confidence and reduced financial losses. The structured approach to risk management and the proactive implementation of controls fostered a more secure and reliable environment.
Measurable Improvements
The company observed several measurable improvements after achieving ISO 27001 certification. The incident response rate decreased by 35%, while the number of successful security breaches dropped to zero. The company also reported a 15% increase in customer satisfaction ratings, indicating that the enhanced security measures were positively perceived by their clients. Furthermore, the company experienced a 10% reduction in operational costs associated with security breaches, showcasing the cost-effectiveness of their implementation efforts.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, securing ISO 27001 certification is a significant undertaking, but the benefits for organizations are substantial. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the process, highlighting the key requirements, implementation strategies, and the importance of continuous improvement. By following the steps in this guide, organizations can confidently navigate the certification journey and reap the numerous rewards associated with achieving this prestigious standard. The ultimate goal is to enhance your organization’s information security posture and build trust with customers and stakeholders.