EdTech Assessment Tools A Comprehensive Guide
Edtech assessment tools are revolutionizing education, offering a dynamic approach to evaluating student learning. These powerful platforms provide a wealth of data, enabling educators to gain deeper insights into student progress and tailor instruction to individual needs. From formative assessments that track learning in real time to summative evaluations that measure overall understanding, EdTech tools offer a comprehensive suite of options.
This guide explores the various types of edtech assessment tools, their features, implementation strategies, and integration with learning management systems. We’ll delve into data analysis, ethical considerations, and future trends, offering practical advice for educators seeking to leverage these tools effectively. A crucial element is the ability to tailor assessments to diverse learning styles and needs, optimizing the learning experience for all students.
Introduction to EdTech Assessment Tools

Source: chrmbook.com
Educational technology (EdTech) assessment tools are rapidly transforming how educators evaluate student learning. These tools leverage technology to provide more efficient, comprehensive, and data-driven insights into student progress. They empower educators to tailor instruction to individual needs, fostering a more personalized and effective learning experience.
The purpose of EdTech assessment tools is multifaceted. They aim to measure student understanding, identify learning gaps, track progress over time, and ultimately improve educational outcomes. By automating tasks and providing detailed analytics, these tools allow educators to focus on providing targeted support and interventions, maximizing student engagement and achievement.
Overview of EdTech Assessment Tools
EdTech assessment tools encompass a wide range of applications, from simple quizzes and surveys to complex adaptive learning platforms. They provide a variety of assessment types, catering to different learning objectives and evaluation needs. Understanding the different types of tools and their specific applications is key to choosing the right tools for specific educational contexts.
Types of EdTech Assessment Tools
Different types of EdTech assessment tools serve distinct purposes in the educational process. Formative assessments, conducted throughout the learning process, offer ongoing feedback to both students and educators. Summative assessments, typically administered at the end of a unit or course, provide a comprehensive evaluation of learning outcomes. Diagnostic assessments are designed to identify students’ prior knowledge and skills, guiding educators in creating targeted learning plans.
- Formative Assessments: These assessments are used to monitor student progress and adjust teaching strategies throughout the learning process. They are designed to identify areas where students may be struggling and provide opportunities for timely interventions. Formative assessments are iterative, providing a dynamic feedback loop that improves both teaching and learning. Examples include quick quizzes, in-class discussions, and peer feedback activities.
- Summative Assessments: These assessments are typically administered at the end of a unit or course to evaluate student mastery of learning objectives. They often take the form of tests, projects, or presentations. Summative assessments provide a comprehensive measure of student achievement and are frequently used for grading and reporting purposes. Examples include unit tests, final exams, and research papers.
- Diagnostic Assessments: These assessments are designed to evaluate students’ prior knowledge and skills before the start of a course or unit. They help educators understand where students are in their learning journey and tailor their instruction to meet specific needs. Examples include pre-tests, surveys, and interviews.
Examples of Successful Implementations
Numerous schools and districts have successfully implemented EdTech assessment tools. These implementations have often led to improvements in student performance and engagement. For instance, a school using a learning management system with embedded quizzes saw a significant increase in student participation and a reduction in the number of students falling behind. Another example highlights how a school district using a data-driven platform identified learning gaps in specific areas, leading to targeted interventions that improved student outcomes.
Comparison of EdTech Assessment Tools
| Type of Assessment | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Formative | Provides ongoing feedback, identifies learning gaps early, and allows for immediate adjustments to instruction | Can be time-consuming to develop and administer, may not always reflect overall understanding. |
| Summative | Provides a comprehensive evaluation of learning, often used for grading and reporting | It may not provide detailed insights into specific learning needs and can be stressful for students if not properly managed. |
| Diagnostic | Identifies prior knowledge and skills, allows for targeted instruction, and can help to create personalized learning plans | It may not always accurately predict future performance; it requires careful interpretation of results. |
Features and Functionality
EdTech assessment tools are evolving rapidly, offering a diverse array of features to enhance learning and evaluation. These tools go beyond traditional paper-and-pencil methods, providing a more dynamic and data-driven approach to understanding student progress. The core functionalities are crucial for effective implementation and impactful results.
Key features commonly found in edtech assessment tools include automated grading, real-time feedback, and diverse question types. These features streamline the assessment process, freeing up educators’ time and allowing them to focus on personalized instruction.
Common Features
EdTech assessment tools frequently include a range of features that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the evaluation process. Automated grading saves educators considerable time and reduces the risk of human error, ensuring fairness and consistency in scoring. Real-time feedback provides immediate insights into student understanding, enabling educators to adapt their instruction on the spot. Tools offering diverse question types (multiple choice, short answer, essay, and more) accommodate various learning styles and provide comprehensive assessments.
Data Analysis Capabilities
The ability to analyze assessment data is a critical component of effective edTech tools. These tools provide insightful metrics on student performance, allowing for targeted interventions and adjustments to teaching strategies. Robust data analysis capabilities can identify learning gaps and areas where students are struggling, enabling personalized support. Data visualization is a crucial part of this process, transforming complex data into easily understandable representations. For example, educators can use interactive dashboards to track individual student progress, identify trends in class performance, and compare results across different groups.
Adaptive Learning in Assessments
Adaptive learning in edTech assessments tailors the learning experience to each student’s unique needs and pace. By analyzing student responses in real time, these tools adjust the difficulty and content of subsequent questions, ensuring that students are challenged appropriately. This personalized approach can significantly improve student engagement and comprehension. For instance, a student who consistently answers questions correctly might be presented with more complex material, while a student struggling with a concept might receive more focused support. Adaptive learning can optimize learning outcomes by providing a dynamic and individualized learning pathway.
Usability and Accessibility
The usability and accessibility of edTech assessment tools are crucial factors in their adoption and effectiveness. User-friendly interfaces and intuitive navigation are essential for educators to quickly and easily access and utilize the tools. Accessibility features, such as text-to-speech capabilities and alternative input methods, ensure that the tools are inclusive for all learners. Tools that are designed with both ease of use and accessibility in mind will see greater educator engagement and improved learning outcomes.
Data Visualization Options
Data visualization in edTech assessment tools is critical for transforming raw data into actionable insights. Effective visualization options allow educators to quickly identify trends, patterns, and individual student performance. A range of options for data presentation is crucial for conveying information effectively.
| Visualization Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Charts | Compare different categories of data. | Visualizing the number of students scoring above/below the average in different subjects. |
| Line Graphs | Track changes in data over time. | Monitoring student progress in a particular skill throughout the semester. |
| Pie Charts | Represent proportions of data. | Show the percentage of students who answered each question correctly. |
| Scatter Plots | Show the relationships between two variables. | Correlating student engagement with assessment scores. |
| Interactive Dashboards | Integrate multiple visualizations. | Combine bar charts, line graphs, and other visualizations to provide a holistic view of student performance. |
Implementation Strategies
Integrating EdTech assessment tools effectively into a curriculum requires a strategic approach. This involves careful planning, teacher training, and a focus on clear assessment goals to maximize the tools’ potential for improving student learning outcomes. A well-structured implementation plan will ensure that these tools are used effectively and contribute meaningfully to the educational process.
Effective integration is not just about acquiring the software; it’s about weaving the tools seamlessly into the existing teaching and learning fabric. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the tools’ capabilities and how they can best support the curriculum’s learning objectives. A phased approach, beginning with pilot programs and gradually expanding to wider adoption, is crucial for smooth implementation and minimizes disruption.
Integrating EdTech Assessment Tools into a Curriculum
A systematic approach to integrating EdTech assessment tools into a curriculum ensures a smooth transition. Start by identifying specific learning objectives where these tools can enhance assessment and provide valuable data. Align the tools with existing curriculum content to avoid creating unnecessary work for teachers or students. Pilot the tools with a small group of students and teachers, gathering feedback and making necessary adjustments. Gradually expand the use of the tools to the entire student body and adjust instruction accordingly. Regular evaluation and feedback loops will ensure that the tools remain relevant and useful.
Teacher Training Strategies
Effective teacher training is paramount to successful EdTech assessment tool implementation. A comprehensive training program should encompass not only the technical aspects of the tool but also the pedagogical implications. Demonstrate how the tools can be used to enhance teaching practices, offering practical examples and hands-on activities. Provide opportunities for teachers to experiment with the tools in a supportive environment, fostering a sense of confidence and competence. Offer ongoing support and professional development to address any emerging challenges or questions.
Establishing Assessment Goals and Objectives
Clearly defined assessment goals and objectives are critical for effective EdTech assessment tool implementation. These should be aligned with the overall learning objectives of the curriculum and be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Establish specific criteria for evaluating student performance using the tools, ensuring that the assessment measures the desired learning outcomes. Document these goals and objectives for transparency and consistency.
Creating a Robust Feedback Loop
A robust feedback loop is essential for maximizing the impact of edtech assessment tools. Regularly collect feedback from teachers and students regarding the effectiveness of the tools and make necessary adjustments to improve their usability and impact. Analyze the data generated by the tools to identify areas where students are struggling or excelling, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments to instruction. This feedback should inform instructional practices and ultimately enhance student learning.
Utilizing Reports and Data for Improvement
Analyzing reports and data generated by EdTech assessment tools is critical for continuous improvement. Identify trends in student performance, pinpointing areas where targeted interventions may be needed. Use this data to adjust teaching strategies, modify curriculum content, and tailor instruction to meet the diverse needs of students. Share insights gained from the data with relevant stakeholders, fostering a collaborative approach to improvement.
Teacher Training Methodologies
| Methodology | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interactive Workshops | Hands-on activities, group discussions, and real-world examples. | Engaging promotes collaboration and immediate feedback. | Requires dedicated time and resources, potentially uneven learning experience. |
| Online Tutorials and Courses | Self-paced learning modules, videos, and interactive exercises. | Flexible, accessible anytime, accommodates diverse learning styles. | May lack personalized support, potential for passive learning. |
| Mentorship Programs | Experienced teachers guide newer colleagues, sharing best practices. | Personalized support, transfer of expertise, and practical application. | Requires trained mentors, potentially slow adoption by all teachers. |
| Peer-to-Peer Learning | Teachers collaborate and share experiences, offering support. | Cost-effective, fosters a sense of community, shared responsibility. | It may not be suitable for all teachers, as it involves uneven knowledge transfer. |
Assessment Design and Development
Designing effective assessments using EdTech tools involves a structured process that aligns with learning objectives and employs various formats. Careful consideration of validity and reliability is crucial for producing meaningful and accurate results. This section delves into the practical aspects of assessment design, including the selection of appropriate formats and the importance of aligning assessments with learning objectives.
The process of designing assessments using EdTech tools involves several key steps. First, clear learning objectives must be defined. Next, appropriate assessment formats should be selected to effectively measure student understanding of these objectives. The design process also necessitates careful consideration of the tool’s capabilities and limitations. Finally, the assessment should be piloted and revised based on feedback and data analysis.
Assessment Formats Supported by EdTech Tools
Edtech tools support a wide array of assessment formats to cater to diverse learning objectives and styles. Different formats allow for different types of learning to be evaluated.
- Multiple Choice: This format is widely used for assessing basic knowledge and comprehension. Questions typically present several options, and students select the correct answer. Edtech tools facilitate the creation and grading of multiple-choice questions with ease.
- Short Answer: Short answer questions require students to provide concise responses. These assessments are valuable for evaluating the understanding and application of concepts. Edtech tools often allow for automated scoring based on predefined criteria.
- Essay Questions: Essay questions prompt students to develop a more in-depth understanding of a subject. These questions typically evaluate higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Edtech tools often provide features for grading essays based on rubrics or automated scoring for specific s or phrases.
- Matching: Matching questions require students to pair related terms or concepts. This format is useful for assessing knowledge of relationships between items. Edtech tools can generate and grade matching questions efficiently.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: Fill-in-the-blank questions assess factual recall and comprehension. Edtech tools can automatically grade these assessments based on the correctness of the filled-in words or phrases.
- True/False: True/false questions are simple to construct and can assess basic comprehension. Edtech tools readily support this assessment format, allowing for easy grading and feedback.
Aligning Assessments with Learning Objectives
Effective assessments directly measure the knowledge and skills students acquire. Therefore, it’s critical to align assessments with specific learning objectives. This ensures that the assessment accurately reflects what students are expected to learn. For instance, if the objective is to analyze historical events, an assessment should require students to analyze those events rather than just recall facts.
Validity and Reliability in EdTech Assessment Design
Validity ensures that an assessment measures what it intends to measure. A valid assessment accurately reflects the knowledge and skills of the students being evaluated. Reliability indicates the consistency of an assessment. A reliable assessment yields consistent results across multiple administrations or different versions of the same assessment. Edtech tools can be utilized to improve both validity and reliability through features like automated scoring, random question selection, and feedback mechanisms.
Assessment Formats and Learning Objectives
The suitability of different assessment formats depends on the specific learning objectives. The table below provides a general guideline:
| Assessment Format | Learning Objective Focus | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | Knowledge recall, comprehension | Identifying the capital of France. |
| Short Answer | Comprehension, application | Explain the causes of the French Revolution. |
| Essay | Analysis, evaluation, synthesis | Critically analyze the impact of the French Revolution on European politics. |
| Matching | Knowledge of relationships | Matching historical figures with their accomplishments. |
| Fill-in-the-Blank | Knowledge recall | Filling in the blank in a historical timeline. |
| True/False | Basic comprehension | Determining if a statement about the French Revolution is true or false. |
Integration with Learning Management Systems (LMS)
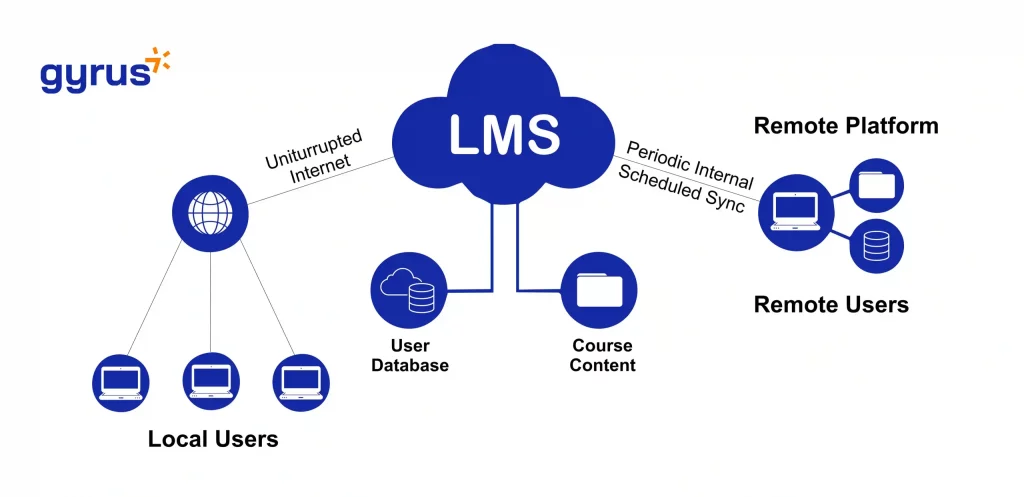
EdTech assessment tools are increasingly integrated with Learning Management Systems (LMS) to enhance the learning experience and streamline administrative tasks. This integration allows for a seamless flow of data, providing valuable insights into student performance and enabling educators to make data-driven decisions. The robust connection between assessment tools and LMS platforms facilitates automated grading, reporting, and personalized learning pathways.
Integration Mechanisms
EdTech assessment tools employ various methods to integrate with LMS platforms. Common methods include Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that facilitate data exchange, allowing for real-time synchronization between the assessment tool and the LMS. Other tools might use direct import/export features, often in CSV or XML formats, enabling users to transfer data manually. The specific integration method depends on the complexity of the assessment tool and the LMS’s capabilities.
Benefits of Seamless Integration
Seamless integration between edTech assessment tools and LMS platforms offers numerous benefits. It reduces manual data entry, streamlining administrative tasks for educators. This automation saves significant time, allowing teachers to focus on instruction and student support. The automated transfer of grades and feedback directly into the LMS streamlines the student record-keeping process. Data synchronization ensures consistency and accuracy across different systems.
Data Transfer and Synchronization
The process of data transfer and synchronization between edTech assessment tools and LMS platforms typically involves the following steps:
- The assessment tool generates data in a specified format (e.g., CSV, XML).
- The LMS imports this data using its import/export functionality or an API.
- The LMS updates the student’s records accordingly, including grades, feedback, and other relevant information.
- Real-time synchronization ensures that data is always current and consistent across both platforms.
Using Assessment Data in the LMS
EdTech assessment data within the LMS can be used to inform various aspects of the learning process. Teachers can utilize student performance data to identify areas where students are struggling and tailor their instruction accordingly. Data can also be used to generate reports on class performance, identify trends, and track student progress over time. This data-driven approach allows for personalized learning paths, adapting to individual student needs and maximizing learning outcomes.
Example Integration Capabilities
The following table illustrates the integration capabilities of some popular edTech assessment tools with common LMS platforms:
| EdTech Assessment Tool | Common LMS Platforms | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Quizizz | Canvas, Moodle, Google Classroom | Automated grading, real-time feedback, data import/export |
| Kahoot! | Canvas, Moodle, Google Classroom | Game-based learning, real-time feedback, data synchronization |
| Google Forms | Google Classroom, Canvas | Data collection, automated grading, integration with Google Workspace |
| MasteryConnect | Canvas, Blackboard | Performance tracking, personalized learning pathways, advanced analytics |
Data Analysis and Reporting: Edtech Assessment Tools
Effective EdTech assessment tools go beyond simply collecting data; they empower educators with insights to improve student learning. Data analysis and reporting are crucial components for maximizing the value of these tools. By understanding how to interpret data, educators can gain actionable information to inform instructional decisions and ultimately enhance student outcomes.
Interpreting data from EdTech assessments requires a systematic approach. First, educators must understand the specific metrics being measured. Next, they should look for patterns and trends in the data, comparing results across different groups of students or learning modules. Finally, they should consider the context of the data, such as the students’ prior knowledge or the specific learning environment.
Interpreting Data Generated by EdTech Assessment Tools
Data interpretation involves more than simply looking at numbers. It’s about understanding what the numbers mean in the context of the learning process. For example, a consistently low score on a specific concept might indicate a need for further instruction or a different teaching approach. Conversely, high scores could suggest areas where students excel and where further enrichment activities could be beneficial. The key is to identify trends, both positive and negative, to gain a comprehensive understanding of student progress and areas for improvement.
Effective Data Visualization Techniques
Visualizing assessment data enhances understanding and allows for easier identification of trends. Visual representations, such as charts and graphs, can transform complex data sets into easily digestible information. For instance, a bar graph can display the performance of different student groups on a particular assessment, while a line graph can track individual student progress over time. Scatter plots can reveal correlations between different variables, helping to pinpoint potential factors influencing student performance.
Importance of Using Data to Inform Decisions
Data-driven decision-making is paramount in education. Assessment data provides valuable insights into student learning, enabling educators to tailor their instruction to meet individual needs. By analyzing student performance, educators can identify gaps in learning and adjust their teaching strategies accordingly. This iterative process of assessment, analysis, and adjustment leads to a more personalized and effective learning experience for all students.
Identifying Areas Needing Improvement Based on Assessment Results
Identifying areas needing improvement involves a careful examination of the assessment results. A significant drop in performance across multiple assessments might indicate a need for a review of instructional materials or strategies. Similarly, a consistent pattern of low performance on particular concepts suggests that those concepts require further emphasis and differentiated instruction. Through careful analysis, educators can pinpoint areas that require additional attention and develop targeted interventions.
Data Visualization Options for Analyzing Assessment Results
| Visualization Type | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Graph | Displays comparisons among categories. | Comparing student performance on different learning modules. |
| Line Graph | Tracks changes over time. | Monitoring individual student progress over a semester. |
| Scatter Plot | Reveals correlations between variables. | Identifying the relationship between study time and test scores. |
| Pie Chart | Shows proportions of different categories. | Illustrating the distribution of student performance levels. |
| Histogram | Displays the frequency distribution of data. | Visualizing the distribution of scores on a particular assessment. |
Ethical Considerations

Source: pinimg.com
EdTech assessment tools offer powerful potential for personalized learning and improved educational outcomes, but their use raises crucial ethical considerations. A responsible approach necessitates careful consideration of data privacy, fairness, and potential biases inherent in these tools. This section explores the ethical implications of EdTech assessment tools, focusing on strategies to ensure responsible use and equitable outcomes for all learners.
Data Privacy and Security
Ensuring the security and privacy of student data is paramount. Data breaches and unauthorized access can compromise sensitive information, leading to serious consequences for students and educators. Robust security measures are essential, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Adherence to relevant data privacy regulations, like FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) in the US, is crucial for safeguarding student information. Clear policies outlining data collection, storage, and usage practices are vital to building trust and transparency.
Fairness and Equity in Assessment
EdTech assessments must strive to be fair and equitable for all learners. Potential biases in algorithms and assessment design can disadvantage certain student groups. Assessment tools should be designed to account for diverse learning styles and backgrounds, ensuring that they measure genuine understanding and skill mastery rather than reinforcing existing inequalities. Regular audits of assessment tools are needed to identify and mitigate any bias in the questions, scoring, and feedback mechanisms.
Ethical Dilemmas in EdTech Assessments
Several ethical dilemmas can arise in the use of EdTech assessment tools. For example, the potential for algorithmic bias leading to inaccurate or unfair evaluations is a significant concern. Another is the lack of transparency in how some assessment tools operate, making it difficult for educators to understand and address potential biases or inaccuracies. The issue of over-reliance on automated assessments and the neglect of human interaction in the assessment process is also a significant challenge. Finally, the potential for the misuse of assessment data for purposes beyond education, such as targeted advertising or profiling, is a growing concern.
Ethical Guidelines for EdTech Assessment Tools
| Ethical Principle | Description and Implementation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Data Privacy and Security | Implement robust security measures, adhere to data privacy regulations (e.g., FERPA), and establish clear data policies. |
| Fairness and Equity | Design assessments to accommodate diverse learning styles and backgrounds, audit tools for bias, and ensure that assessment results reflect true understanding and skill mastery. |
| Transparency and Accountability | Ensure that assessment processes are transparent and understandable, providing clear explanations of how assessments are designed, scored, and interpreted. |
| Informed Consent | Obtain explicit consent from students and parents for data collection and use, providing clear and accessible information about how the data will be used. |
| Teacher Professional Development | Provide ongoing training and support for teachers on ethical considerations in using EdTech assessment tools, emphasizing the importance of human interaction in the learning process. |
Future Trends in EdTech Assessment Tools

EdTech assessment tools are constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and a growing need for more personalized and effective learning experiences. These evolving tools are not merely about automating existing processes; they are about fundamentally reshaping how we measure and understand student learning. The future holds exciting possibilities for innovative assessment methods, leveraging technology to provide richer insights and more dynamic learning pathways.
The increasing integration of artificial intelligence, personalized learning platforms, and gamified elements is poised to transform the landscape of educational assessment. This evolution promises to move beyond traditional methods, providing educators with more comprehensive and nuanced data on student progress, allowing for more targeted interventions and, ultimately, improved learning outcomes.
Emerging Trends in EdTech Assessment Tools
EdTech assessment tools are moving beyond simple multiple-choice tests and quizzes. New tools are being developed to adapt to different learning styles, providing a more comprehensive view of student understanding. These innovations are crucial for tailoring educational experiences to individual needs.
- AI-Powered Assessment: AI is rapidly changing how assessments are designed and administered. AI can analyze student responses in real time, providing instant feedback and adapting the learning path accordingly. This allows for more dynamic and personalized learning experiences, addressing individual learning gaps as they arise.
- Personalized Learning Platforms: These platforms are designed to tailor the learning experience to each student’s unique needs and learning style. Assessments are integrated into these platforms to provide ongoing data that allows for adjustments in the learning path and resources offered. This approach fosters a deeper understanding and mastery of the subject matter.
- Gamification in Assessment Design: Incorporating game mechanics into assessment design makes learning more engaging and motivating for students. Points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges can be incorporated into quizzes and exercises, enhancing motivation and encouraging active participation.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Assessment
AI’s role in assessment extends beyond automating grading. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze student work, identify patterns in performance, and even predict potential learning challenges. This proactive approach enables educators to intervene early and support students effectively.
- Automated Feedback and Personalized Recommendations: AI can provide immediate and detailed feedback on student work, pinpointing specific areas where improvement is needed. It can also suggest tailored learning resources and activities to address individual learning gaps, making the learning process more effective.
- Adaptive Assessments: AI-powered adaptive assessments adjust the difficulty of questions based on student performance in real time. This ensures that assessments accurately reflect the student’s current knowledge level, minimizing frustration and maximizing learning.
Innovative Assessment Methodologies
The focus is shifting from traditional paper-based tests to more dynamic and engaging methods. These methods often integrate technology and allow for a richer understanding of student learning.
- Performance-Based Assessments: These assessments require students to demonstrate their knowledge and skills through projects, presentations, or simulations. They offer a more holistic view of a student’s capabilities than traditional multiple-choice questions.
- Portfolio Assessments: These allow students to showcase their work over time, demonstrating progress and mastery of skills. This provides a more comprehensive picture of student growth than a single assessment.
Impact of Personalized Learning on EdTech Assessment
Personalized learning relies heavily on assessment data to adapt to each student’s unique needs. Tools are being developed to provide ongoing feedback and adjust the learning path dynamically.
- Dynamic Learning Paths: Assessments in personalized learning environments are designed to provide real-time data. This allows the platform to adjust the learning content and pace according to the student’s performance, providing tailored support for individual needs.
- Adaptive Feedback Mechanisms: Assessments provide constant feedback, adjusting content and pacing to meet individual learning styles and progress. This ensures that students receive the appropriate support and resources to succeed.
Potential for Gamification in Assessment Design
Gamification techniques can transform assessments from tedious tasks into engaging challenges. By incorporating elements of games, students become more motivated and actively involved in the learning process.
- Increased Engagement and Motivation: Gamification can increase student engagement and motivation by making learning more fun and interactive. This can lead to higher participation rates and better learning outcomes.
- Improved Knowledge Retention: The interactive and engaging nature of gamified assessments can lead to better knowledge retention and a more profound understanding of the material.
Key Emerging Trends and Their Implications
| Emerging Trend | Implications |
|---|---|
| AI-powered assessment | Personalized feedback, adaptive learning, early intervention |
| Personalized learning platforms | Tailored learning experiences, improved student outcomes |
| Gamification in assessment | Increased engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention |
| Performance-based assessments | Holistic understanding of student skills, deeper learning |
| Portfolio assessments | Comprehensive view of student progress, skill development |
Last Point
By implementing these tools strategically, educators can gain valuable insights, personalize instruction, and ultimately drive student success. The evolving nature of these tools presents exciting opportunities for the future of education, demanding continuous adaptation and innovation.