Best EdTech Tools A Comprehensive Guide
The best edtech tools are revolutionizing education, offering innovative approaches to learning and teaching. This guide delves into the world of educational technology, exploring its diverse applications and the key factors to consider when choosing the right tools. We’ll cover everything from defining EdTech tools to evaluating their effectiveness, categorizing them, and showcasing real-world use cases.
The evolution of educational technology has been rapid, with new tools and platforms emerging regularly. From learning management systems to interactive simulations and educational games, these tools are changing how students learn and teachers teach. We’ll explore the various types, their features, and their suitability for different educational contexts.
Defining Educational Technology Tools
Educational technology tools, often abbreviated as edtech tools, are digital resources and platforms designed to enhance learning experiences. They span a wide range of applications, from simple interactive exercises to complex learning management systems. This evolution has profoundly impacted how educators teach and students learn, transforming traditional classrooms into dynamic, technology-integrated environments.
EdTech tools are constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and shifting pedagogical approaches. The past decade has seen a surge in personalized learning experiences, incorporating adaptive learning platforms and AI-powered tools that tailor content to individual student needs. The trend is toward more immersive and engaging learning, moving beyond passive consumption of information toward active participation and exploration.
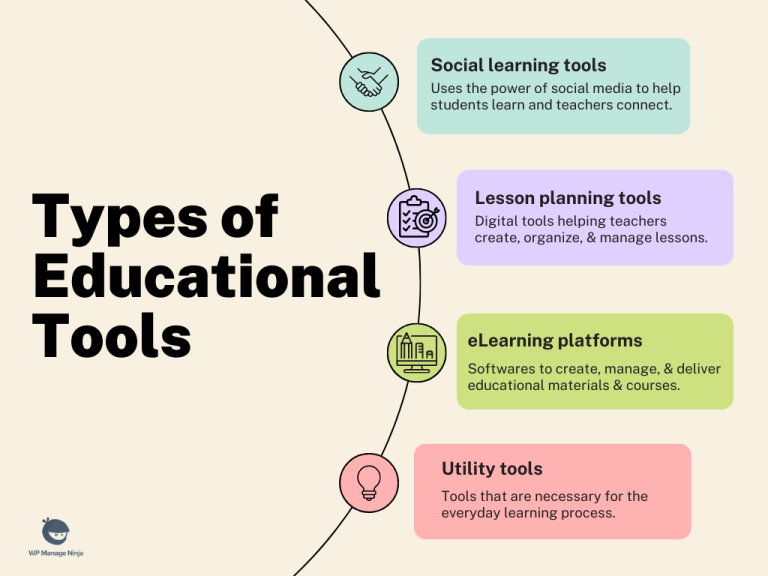
Types of EdTech Tools
EdTech tools encompass a variety of applications, each designed to address specific educational needs. Learning management systems (LMS) are crucial for organizing and delivering course materials, facilitating communication between students and educators, and tracking student progress. Interactive simulations provide hands-on learning opportunities, allowing students to explore complex concepts and processes in a safe and controlled environment. Educational games, often incorporating gamification elements, make learning more engaging and motivating.
Examples of EdTech Tool Use
EdTech tools are used across various educational settings. In K -12 education, interactive simulations can be used to teach complex scientific concepts, like the human circulatory system, more engagingly. In higher education, LMS platforms facilitate the delivery of online courses and support collaboration among students and faculty. Professional development programs leverage EdTech tools to provide educators with opportunities to enhance their teaching skills and learn new methodologies.
Comparison of EdTech Tool Categories
| Tool Category | Key Feature 1 | Key Feature 2 | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Management Systems (LMS) | Course Management | Communication Tools | Students and Educators |
| Interactive Simulations | Hands-on Learning | Visual Representation | Students |
| Educational Games | Engaging Learning | Gamified Experiences | Students |
| Adaptive Learning Platforms | Personalized Learning Paths | Data-Driven Feedback | Students |
The table above provides a basic overview of the different categories of EdTech tools. Each category plays a unique role in the learning process, offering different functionalities and catering to diverse learning styles.
Evaluating Edtech Tools for Effectiveness

Effective educational technology tools are crucial for enhancing student learning experiences. Evaluating these tools requires a systematic approach that considers various factors beyond simple features. This assessment process helps educators choose the most suitable tools to achieve their specific learning objectives.
A comprehensive evaluation process is essential to determine if an EdTech tool truly enhances learning outcomes. This process necessitates a careful examination of the tool’s alignment with pedagogical principles, its practical usability, and its impact on student engagement and performance. Evaluating these elements ensures the tool’s effectiveness and avoids the adoption of tools that may not deliver the desired results.
Criteria for Evaluating Effectiveness
The effective evaluation of EdTech tools hinges on specific criteria. These criteria ensure that the tools chosen truly contribute to improved learning. These criteria include alignment with learning objectives, usability, integration with existing systems, and pedagogical approach. Each criterion plays a crucial role in determining the tool’s suitability for a specific educational context.
Metrics for Assessing Impact on Student Learning Outcomes, Best edtech tools
Assessing the impact of EdTech tools on student learning outcomes necessitates using various metrics. These metrics provide quantifiable data to evaluate the tool’s effectiveness. Examples include student performance on assessments, engagement levels measured through participation rates, and improved understanding as demonstrated by post-implementation knowledge checks. These metrics, when combined, provide a holistic view of the tool’s impact.
Analyzing the Embedded Pedagogical Approach
Analyzing the pedagogical approach embedded within different EdTech tools is critical for evaluating their effectiveness. A tool’s pedagogical approach dictates how it facilitates learning. For example, some tools may focus on active learning strategies, while others might prioritize collaborative learning. Understanding the underlying pedagogy informs the decision of whether the tool aligns with the desired learning environment. This analysis is paramount to selecting a tool that effectively complements the teaching methodology.
Framework for Comparing and Contrasting Edtech Tools
A framework for comparing and contrasting different edtech tools can be structured around their potential benefits. This comparison considers the tool’s features, functionality, and potential impact on student learning. The framework helps educators evaluate the tool’s alignment with learning objectives, ease of use, integration capabilities, and pedagogical approach. A well-structured framework allows for a thorough evaluation, ultimately guiding informed decisions.
Table of Factors to Consider When Selecting an Edtech Tool
This table articulates the key factors to consider when choosing an EdTech tool for a specific educational objective. Carefully considering these factors ensures that the chosen tool is well-suited to the needs of the students and teachers.
| Evaluation Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment with Learning Objectives | Does the tool support the intended learning outcomes? | High |
| User Interface and Usability | Is the tool easy to navigate and use for both students and teachers? | Medium |
| Integration with Existing Systems | Can the tool be seamlessly integrated with other educational platforms, such as learning management systems (LMS)? | High |
| Cost and Accessibility | What are the financial implications and technical requirements for accessing the tool? | Medium |
| Teacher Support and Training | Are adequate resources and support available to assist teachers in using the tool effectively? | High |
Categorizing and Comparing EdTech Tools: Best Edtech Tools

Source: thehansindia.com
Educational technology tools are rapidly evolving, offering a diverse array of options for enhancing learning experiences. Categorizing these tools based on their functionalities and intended audience provides a framework for understanding their strengths and weaknesses. This allows educators to make informed decisions when selecting tools to support their specific instructional goals.
A comprehensive understanding of various EdTech tools enables educators to match the appropriate tools with their students’ learning styles and needs. This approach ensures that the learning experience is engaging and effective, fostering a positive and productive learning environment.
Categorization of EdTech Tools by Function
Different edtech tools serve distinct purposes in the learning process. Classifying them by function offers a clear picture of their intended use. Understanding the specific function of each tool helps educators choose the right tool for the specific task at hand.
- Communication Tools: Platforms like Google Classroom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack facilitate seamless communication between teachers and students. These tools enable the exchange of information, assignments, and feedback, fostering a connected learning environment. These tools also allow for collaborative projects and real-time discussions.
- Assessment Tools: Platforms like Quizizz, Kahoot!, and Google Forms offer interactive assessment methods that engage students and provide valuable feedback. These tools can be tailored to different learning styles, making assessment more comprehensive and dynamic. Tools like these also offer real-time data and insights into student understanding.
- Resource Management Tools: Tools like Canva, Prezi, and Adobe Spark facilitate the creation of engaging multimedia resources for students. These tools can be utilized for creating presentations, infographics, and other learning materials. This allows for diverse and dynamic learning experiences that appeal to visual learners and encourage creative expression.
- Interactive Learning Platforms: Learning Management Systems (LMS) like Moodle and Blackboard provide structured learning environments with a variety of tools for delivering content, facilitating communication, and tracking progress. These platforms often include tools for interactive exercises, simulations, and virtual labs.
Comparison of EdTech Tools within Categories
A detailed comparison of tools within each category highlights their strengths and weaknesses. This comparison allows educators to evaluate the features and functionalities of various tools, leading to the selection of tools that best meet the specific needs of the learners and the educational context.
| Tool Category | Example Tool 1 | Example Tool 2 | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | Google Classroom | Microsoft Teams | Easy-to-use interface; integrated file sharing; streamlined communication | Potential for information overload; may not be suitable for all learning styles |
| Assessment | Quizizz | Kahoot! | Interactive quizzes; gamified learning; real-time feedback | Limited depth of assessment; may not suit all assessment objectives |
| Resource Management | Canva | Prezi | Intuitive design tools; creation of visually engaging content; a variety of templates | May require some technical proficiency; not suitable for all content types |
| Interactive Learning | Moodle | Blackboard | Comprehensive learning management system; diverse features for content delivery and communication; tracking of student progress | Steeper learning curve; potential for complexity in navigation and use |
Supporting Diverse Learning Styles and Needs
Effective EdTech tools should be adaptable to cater to diverse learning styles and needs. This adaptability ensures that all students have the opportunity to learn effectively and efficiently. For example, interactive simulations and gamified activities can engage kinesthetic learners, while visual learners benefit from tools that allow for the creation of multimedia presentations.
Fostering Collaboration and Communication
Edtech tools play a vital role in fostering collaboration and communication. Tools like Google Docs and shared online workspaces enable students to collaborate on projects in real-time. These tools allow for seamless feedback and knowledge sharing.
Creating Engaging and Interactive Learning Experiences
Edtech tools are pivotal in creating engaging and interactive learning experiences. Tools like virtual reality simulations and interactive simulations can make learning more immersive and memorable. These experiences also promote active learning and a deeper understanding of complex concepts.
Illustrating EdTech Tool Use Cases
Educational technology tools are transforming classrooms, offering dynamic and engaging learning experiences. By understanding how these tools are being implemented, we can gain valuable insights into their potential to enhance student learning and teacher effectiveness. Real-world examples illustrate the diverse ways these tools are being used to personalize learning, differentiate instruction, and improve assessment strategies.
Implementing EdTech tools effectively requires a thoughtful approach. Teachers must integrate these tools seamlessly into their existing curriculum, ensuring alignment with learning objectives and student needs. This integration allows teachers to create a more personalized learning environment for all students.
Real-World Examples of EdTech Tool Implementation
Various edtech tools are proving successful in diverse educational settings. Digital platforms are employed to deliver interactive lessons, while simulation software facilitates hands-on learning experiences in fields like science and engineering. For instance, a middle school science teacher might use a virtual dissection tool to explore animal anatomy, enabling students to interact with complex biological structures safely and engagingly.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Edtech tools can significantly enhance student engagement and learning outcomes. Interactive simulations, for example, can make abstract concepts more concrete and tangible, fostering a deeper understanding. Data analysis tools provide students with the opportunity to explore trends and patterns in a way that traditional methods might not allow. A study by the National Center for Education Statistics indicated that students using interactive learning platforms often demonstrated higher levels of engagement and improved academic performance.
Differentiation and Meeting Diverse Needs
Edtech tools facilitate differentiated instruction by providing customized learning pathways. Adaptive learning platforms adjust to each student’s pace and learning style, ensuring that everyone receives the support they need. For example, a language arts teacher might use a digital storytelling tool to help English Language Learners create and share their narratives, catering to diverse communication needs and strengths.
Creating Personalized Learning Experiences
Personalized learning experiences are achievable through the use of EdTech tools. Learning management systems (LMS) allow teachers to track student progress and tailor assignments to individual needs. For example, a high school math teacher might use an adaptive math platform that adjusts the difficulty of problems based on a student’s performance. This customized approach fosters a sense of ownership and empowers students to take control of their learning.
Improving Assessment and Feedback
Edtech tools can improve assessment and feedback by providing immediate and detailed insights into student understanding. Automated grading tools allow teachers to focus on providing valuable feedback instead of tedious grading. For example, a high school history teacher can use a digital essay grading tool to receive immediate feedback on students’ writing and identify areas where they need improvement.
Visual Representation of EdTech Tool Use Across Grade Levels and Subject Areas
| Grade Level | Subject Area | EdTech Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary (Grades K-5) | Reading | Interactive Storybooks | Engage students with interactive stories and activities, fostering vocabulary development and comprehension. |
| Middle School (Grades 6-8) | Science | Virtual Lab Simulations | Allow students to conduct experiments and observe phenomena in a safe and controlled environment, enhancing understanding of complex concepts. |
| High School (Grades 9-12) | History | Digital Timeline Tools | Help students visualize historical events and their connections, promoting critical thinking and historical analysis. |
Addressing Challenges and Limitations

Educational technology tools offer significant potential for enhancing learning experiences, but their effective implementation requires careful consideration of potential challenges. These challenges often stem from issues of access, equity, teacher training, digital literacy, security, and ethical implications. A comprehensive approach that proactively addresses these limitations is crucial for realizing the full benefits of EdTech.
Implementing EdTech tools requires a nuanced understanding of the context within which they will be utilized. Failing to address potential limitations can lead to a less effective or even detrimental impact on the educational process. Understanding and mitigating these challenges is key to maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with EdTech integration.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
A variety of challenges can hinder the successful integration of EdTech tools. These can range from practical difficulties in implementation to more complex issues of equity and accessibility. Insufficient infrastructure, technical glitches, and lack of adequate training can all contribute to less-than-optimal outcomes. Difficulties in teacher training and a lack of ongoing support can also result in subpar utilization of EdTech tools.
Accessibility and Equity Considerations
Ensuring equitable access to EdTech tools is paramount. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds or those with disabilities may face barriers to accessing and effectively using these tools. Schools must actively address these disparities through initiatives that provide necessary hardware, software, and technical support. Tools should be designed and implemented with universal design principles in mind to accommodate diverse learning styles and needs. This includes providing alternative formats, multiple input methods, and assistive technologies.
Teacher Professional Development
Effective EdTech integration relies heavily on teacher preparedness. Ongoing professional development opportunities are crucial to equipping educators with the skills and knowledge necessary to effectively utilize EdTech tools in their classrooms. These professional development programs should not be one-time events but rather ongoing support systems that allow teachers to explore and master new tools and strategies.
Digital Literacy for Students and Educators
Digital literacy is an essential skill for both students and educators in the digital age. Students need to develop the skills to navigate online resources responsibly and critically evaluate information. Educators need to possess the technical skills and knowledge to effectively integrate EdTech tools into their teaching practices. The curriculum should explicitly address digital citizenship and media literacy to foster responsible digital behavior.
Security Concerns
Security is a critical concern when dealing with edtech tools. Protecting student data and ensuring the security of online learning environments is paramount. Schools should implement robust security measures, including strong passwords, encryption protocols, and firewalls. Educators must also teach students about online safety and responsible digital behavior. Regular security audits and updates are essential to maintain a secure learning environment.
Ethical Implications of EdTech Tools
Specific edtech tools may raise ethical concerns, such as issues related to data privacy, algorithmic bias, and potential for misuse. Consideration must be given to the ethical implications of using these tools, and transparent policies and procedures should be established to address any potential ethical dilemmas. Educators should engage in ongoing dialogue about the ethical use of EdTech tools to ensure their use is aligned with the values of the institution and the broader community.
Closure
In conclusion, the best edtech tools empower educators and learners with a wide array of resources and opportunities to enhance the educational experience. By carefully considering the specific needs of the students and teachers, evaluating different tools, and understanding the potential challenges and limitations, educators can make informed decisions to integrate EdTech effectively into their classrooms. Ultimately, the successful integration of EdTech tools hinges on thoughtful planning, ongoing professional development, and a commitment to equitable access for all.