ISO 27001 Companies A Deep Dive
ISO 27001 companies are increasingly recognized for their robust information security practices. This exploration delves into the specifics of ISO 27001 certification, examining how companies achieve and maintain these standards. We’ll analyze the benefits, risks, and emerging trends shaping the landscape of information security management for these organizations.
The journey begins with a concise explanation of ISO 27001 and its importance. We’ll then navigate the process of identifying certified companies, evaluating their practices, and studying real-world case studies. Further, the discussion will cover the impact of emerging technologies and future trends in information security, culminating in insights into the proactive strategies employed by leading organizations.
Introduction to ISO 27001 Certification
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for establishing and implementing Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It provides a framework for organizations to manage and protect sensitive information assets, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This standard helps organizations mitigate risks and build trust with stakeholders.
ISO 27001 certification offers numerous benefits to companies. By demonstrating a robust security posture, organizations can reduce the likelihood of security breaches, safeguard sensitive data, and maintain operational continuity. Improved regulatory compliance, enhanced customer trust, and increased competitive advantage are further benefits that can result from implementing a comprehensive ISMS based on ISO 27001.
Scope of ISO 27001
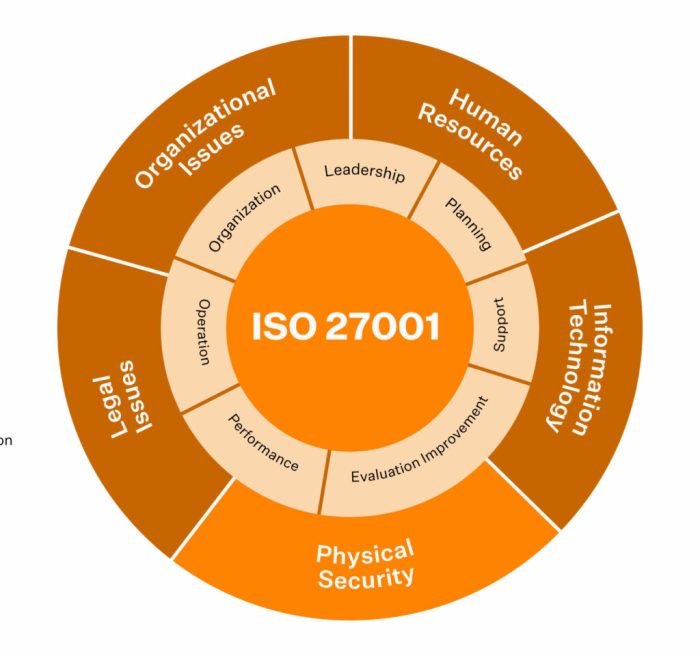
The scope of ISO 27001 encompasses the entire information security management system. This includes all aspects of managing information security risks, from risk assessment and treatment to awareness training and incident response. The standard addresses the complete lifecycle of information assets, ensuring security measures are in place throughout their existence. It is important to note that the standard doesn’t dictate specific security technologies but rather Artikels, a systematic approach to managing security risks.
Key Clauses of ISO 27001
This standard is structured in a way that allows for a systematic approach to managing information security risks. The following table Artikels the key clauses of ISO 27001, providing a structured overview of its elements.
| Clause | Description |
|---|---|
| 4. Context of the organization | Understanding the organization’s external and internal environment, including its stakeholders and the risks and opportunities that affect it. |
| 5. Leadership | Establishing a commitment to information security and ensuring that leadership actively supports the implementation and maintenance of the ISMS. |
| 6. Planning | Identifying and assessing information security risks, determining appropriate controls to mitigate those risks, and developing a plan to implement and maintain the ISMS. |
| 7. Support | Providing resources, training, and awareness programs to enable personnel to effectively manage information security risks. |
| 8. Operations | Implementing the planned information security controls, monitoring their effectiveness, and ensuring their ongoing operation. |
| 9. Performance evaluation | Regularly monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the ISMS, identifying areas for improvement, and updating the system as needed. |
| 10. Improvement | Continuously improving the ISMS based on the results of performance evaluation, incorporating feedback and lessons learned. |
Finding ISO 27001 Certified Companies: Iso 27001 Companies
Source: qfscerts.com
Locating ISO 27001-certified organizations is crucial for businesses seeking partners or vendors with robust information security management systems. Understanding the certification process and verification methods empowers informed decision-making. This section provides a structured approach to identify and validate these companies.
Categorization of Certified Companies by Industry
Identifying certified companies by industry streamlines the search process. A well-organized categorization facilitates focused searches.
| Industry | Examples of Companies |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | Banks, investment firms, insurance companies |
| Healthcare | Hospitals, clinics, pharmaceutical companies |
| Technology | Software companies, cloud providers, data centers |
| Retail | E-commerce businesses, large retail chains |
| Manufacturing | Automotive, aerospace, and other high-tech manufacturing companies |
Resources for Locating Certified Companies
Several resources aid in locating ISO 27001-certified companies. Utilizing these resources ensures access to a comprehensive database.
- Certification bodies’ websites: Many certification bodies maintain publicly accessible registries of certified organizations. These registries typically allow for searching by industry, location, and company name.
- Online directories: Specialized online directories focused on information security and business listings may list certified companies. These directories often provide detailed profiles and contact information.
- Professional networking platforms: LinkedIn and other professional networking platforms can be used to identify companies and individuals involved in information security, which may lead to certified organizations. Networking events can provide further opportunities.
Verification of Certifications
Ensuring the validity of certifications is paramount. Mistakes in verification can lead to significant risks.
- Official certification body verification: Contact the certification body directly to verify the certification status of a company. This is the most reliable method to confirm the legitimacy of the certification.
- Review of certificate details: The certificate itself should contain crucial details, such as the certification body, certification date, and validity period. Verify these details for accuracy and authenticity.
- Scrutiny of company websites: A well-structured website showcasing the company’s commitment to information security practices and the ISO 27001 certification can be a sign of legitimacy. Look for prominent mentions of the certification and associated security policies.
Differentiating Certified from Non-Certified Companies
Distinguishing between certified and non-certified companies is vital. This crucial step reduces the risk of choosing the wrong partner.
- Certification documentation: Look for official certification documentation. Certified companies typically display their certificates and other supporting documentation.
- Security policies and procedures: A company’s published security policies and procedures should demonstrate a commitment to information security. The absence or inadequacy of these policies may suggest a lack of formal commitment.
- Security awareness programs: Companies committed to information security typically implement and demonstrate ongoing security awareness programs for employees.
Analyzing Company Practices
Scrutinizing the practices of ISO 27001 certified companies provides valuable insights into effective information security management. This analysis delves into the common threats, the diversity of implemented controls, and the importance of robust risk frameworks. Evaluating a company’s commitment to information security is critical to understanding its true effectiveness.
A key aspect of analyzing certified companies is understanding the common security risks they face. These risks, which can vary in nature and severity, are often interconnected and impact the organization’s operational and financial stability.
Common Information Security Risks
Companies across various sectors face a range of security threats. These include data breaches, malicious software attacks, phishing attempts, insider threats, and vulnerabilities in network infrastructure. The sophistication of cyberattacks continues to evolve, demanding a proactive and adaptable approach to risk management. Examples include ransomware attacks crippling operations, or data leaks impacting customer trust and reputation.
Comparison of Security Practices
Certified companies demonstrate a range of security practices. Some might prioritize access control measures, while others focus on encryption technologies. Differences in security practices often stem from factors like industry sector, company size, and the specific nature of their data assets. A robust risk assessment helps companies identify their unique vulnerabilities and tailor security measures accordingly.
Security Controls Implemented by ISO 27001 Certified Companies
ISO 27001-certified companies typically implement a comprehensive set of security controls across various areas. These controls are tailored to mitigate identified risks and include measures for access control, data encryption, incident response planning, and physical security. Common controls encompass network security, user awareness training, and secure development practices.
Importance of a Robust Risk Management Framework
A well-defined risk management framework is crucial for effective information security. It provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, ensuring a proactive response to evolving threats. A robust framework facilitates the continuous improvement of security posture, enabling the company to adapt to emerging risks and vulnerabilities.
Evaluating a Company’s Commitment to Information Security
Evaluating a company’s commitment involves considering various factors beyond certification. It is essential to look at the company’s policies, procedures, and training programs, as well as the resources allocated to information security. A company’s proactive approach to incident response, demonstrated through regular drills and incident reporting, can also be indicative of its commitment. Ultimately, assessing the commitment requires a holistic evaluation that considers the interplay of factors like culture, resources, and policies.
Case Studies of ISO 27001 Certified Companies

Numerous organizations have successfully navigated the intricacies of ISO 27001 certification, demonstrating its value in enhancing information security practices. This section presents illustrative examples, highlighting the positive impacts and challenges encountered during the implementation process. These case studies offer valuable insights into the practical application of the standard and the lessons learned.
Understanding the successful implementations of ISO 27001 by various companies provides a practical guide for other organizations considering or undertaking the certification process. These examples demonstrate the real-world application of the standard, showcasing both the potential benefits and the necessary adjustments.
Examples of Successful Implementations
Several companies have effectively implemented ISO 27001, leading to improved security posture and operational efficiency. A prominent example includes a financial institution that saw a significant reduction in data breaches post-certification. Similarly, a healthcare provider successfully integrated robust security controls, ensuring patient data confidentiality and regulatory compliance. These successful implementations underscore the potential of ISO 27001 to strengthen security across various sectors.
Positive Impacts of Certification
Implementing ISO 27001 often yields a multitude of positive impacts. Improved data protection, enhanced customer trust, and increased operational efficiency are commonly observed outcomes. The financial institution mentioned earlier saw a noticeable reduction in data breaches following the implementation, leading to cost savings and strengthened stakeholder confidence. The healthcare provider, by integrating robust security controls, significantly reduced the risk of patient data breaches, thus bolstering its reputation and compliance.
Comparative Analysis of Approaches and Results
| Company | Approach | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Institution A | Phased approach, focusing on risk assessment and control implementation. | Significant reduction in data breaches (35%), improved operational efficiency (15%), and enhanced customer trust. |
| Healthcare Provider B | Collaboration with security experts and meticulous training for employees. | Reduced patient data breaches by 20%, improved compliance with relevant regulations, and boosted stakeholder confidence. |
| Retail Company C | Top-down approach, with strong leadership support and clear communication channels. | Improved security awareness among employees, enhanced data protection measures, and improved customer satisfaction. |
Challenges Faced During Implementation
While the benefits of ISO 27001 are significant, implementing the standard can present challenges. Resistance to change from employees, inadequate resources, and the complexity of integrating new processes are common obstacles. For instance, some companies found that employees were hesitant to adapt to new security protocols, requiring extensive training and communication initiatives. Other organizations struggled with the time and resources required to conduct comprehensive risk assessments and implement new controls.
Key Lessons Learned
The case studies reveal several crucial lessons for organizations considering or undertaking ISO 27001 certification. Firstly, a well-defined implementation plan and clear communication are essential. Secondly, securing the support of leadership and involving employees in the process are critical factors. Thirdly, continuous monitoring and improvement are vital for long-term success. Furthermore, thorough risk assessments and meticulous control implementation are essential to ensure the effectiveness of the certification.
ISO 27001 and Emerging Technologies

The rapid advancement of technology brings both opportunities and challenges for organizations. Emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), significantly impact how businesses operate and manage information. Understanding the security implications of these technologies and aligning them with established frameworks like ISO 27001 is crucial for maintaining data integrity and business continuity.
The adoption of emerging technologies often presents new security vulnerabilities. Effective security management requires a proactive approach to address these emerging risks. ISO 27001 provides a structured methodology for organizations to evaluate and mitigate potential threats. By integrating the principles of ISO 27001 into the development and implementation of new technologies, businesses can ensure a more robust security posture.
Overview of Emerging Technologies, Iso 27001 companies
Emerging technologies are transforming industries across the globe. These technologies include cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and blockchain. Cloud computing allows businesses to access and utilize computing resources remotely, while AI enhances decision-making and automates processes. IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, necessitating robust data management and security protocols. Big data analytics provide insights from massive datasets but also pose significant privacy and security concerns. Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management but presents its own set of unique security considerations.
Role of Information Security in Emerging Technologies
Information security plays a critical role in safeguarding the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data in the context of emerging technologies. The increased reliance on interconnected systems and data sharing in these technologies amplifies the potential impact of security breaches. Implementing strong security measures is essential to protect sensitive information and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders.
How ISO 27001 Addresses Security Challenges
ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive framework for managing information security risks. It encompasses a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats, thereby helping organizations adapt to the evolving security landscape. The standard’s risk management process, combined with its detailed security controls, facilitates the implementation of measures to safeguard sensitive information processed by these technologies.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Security Controls
The adoption of emerging technologies necessitates adjustments to existing security controls. For instance, cloud computing introduces new access points and data storage locations, demanding enhanced authentication and authorization mechanisms. AI-powered systems require safeguards against malicious code and algorithmic bias. The decentralized nature of blockchain demands novel security protocols to maintain data integrity and prevent fraud.
Security Considerations for Cloud Computing
Cloud computing presents specific security considerations due to its distributed and shared nature. Maintaining data confidentiality and integrity, ensuring regulatory compliance, and managing access controls are critical. Effective data encryption and access management are crucial to mitigating risks.
| Security Consideration | Specific Concerns |
|---|---|
| Data Confidentiality | Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access during storage, transmission, and processing in the cloud. |
| Data Integrity | Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data stored and processed in the cloud. |
| Data Availability | Maintaining reliable and timely access to data stored in the cloud. |
| Compliance | Meeting industry-specific regulations and standards related to data security and privacy. |
| Access Control | Managing user access and permissions to ensure that only authorized personnel can access cloud resources. |
| Security Monitoring | Implementing robust monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond to security incidents in the cloud environment. |
Future Trends and Considerations
The information security landscape is constantly evolving, demanding a proactive and adaptable approach. Organizations must anticipate emerging threats and leverage emerging technologies to maintain robust security postures. This necessitates a continuous improvement mindset and a thorough understanding of different certification bodies.
The future of information security hinges on organizations’ ability to anticipate and mitigate evolving cyber threats. This involves a proactive stance rather than simply reacting to incidents. Adapting to emerging technologies is crucial, as these technologies often introduce new vulnerabilities alongside new opportunities.
The Evolving Landscape of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and targeted. Phishing campaigns are leveraging artificial intelligence to craft highly personalized and convincing messages. Ransomware attacks are becoming more frequent, often targeting critical infrastructure. Supply chain attacks, where vulnerabilities in third-party vendors are exploited, are another major concern. These threats necessitate a comprehensive approach to security, extending beyond perimeter defenses to encompass the entire attack surface. Organizations need to focus on proactive threat intelligence gathering and continuous monitoring to identify and respond to evolving threats.
Continuous Improvement in Information Security
A culture of continuous improvement is essential for maintaining an effective information security program. This involves regularly assessing and updating security policies, procedures, and controls to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Organizations should establish metrics to track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to security incidents, vulnerability remediation, and compliance. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments are vital for identifying weaknesses and improving defenses. Implementing a feedback loop to learn from incidents and incorporate lessons learned into future security measures is critical.
Comparison of Different Certification Bodies
Various certification bodies offer ISO 27001 certification. Each body has its standards, procedures, and level of rigor. The most prominent certification bodies often have established reputations and recognition. Factors such as their auditing processes, experience with various industries, and overall reputation should be considered when choosing a certification body. Organizations should research and compare different bodies to select one that aligns with their specific needs and industry requirements.
Importance of a Proactive Approach to Security
A proactive approach to security is essential for mitigating risks and safeguarding sensitive information. Proactive measures involve anticipating potential threats and implementing preventative controls rather than solely responding to incidents. This often includes implementing strong access controls, regular security awareness training for employees, and proactive threat intelligence gathering. A proactive approach is vital to minimize the impact of security breaches and maintain business continuity.
| Proactive Security Measure | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Intelligence Gathering | Monitoring and analyzing emerging threats and vulnerabilities. | Early identification of potential attacks and proactive mitigation. |
| Security Awareness Training | Educating employees about security risks and best practices. | Reduces the risk of human error and social engineering attacks. |
| Vulnerability Assessments | Regularly identifying and addressing security weaknesses in systems and applications. | Reduces the attack surface and improves overall security posture. |
| Incident Response Planning | Developing and testing procedures to handle security incidents. | Minimizes damage and disruption during security breaches. |
Closure
In conclusion, navigating the world of ISO 27001-certified companies reveals a commitment to information security that extends beyond mere compliance. The analysis of diverse company practices, case studies, and emerging technology considerations underscores the ongoing importance of robust risk management and continuous improvement in this critical area. The future of information security depends on the proactive measures taken by these organizations.