Drata ISO 27001 A Comprehensive Guide
Drata ISO 27001 sets the stage for a deep dive into information security best practices. This standard provides a structured framework for organizations to manage information security risks effectively. It’s a globally recognized benchmark, outlining key principles and processes for building a robust information security management system (ISMS). This guide will explore the standard’s origins, its key components, and practical implementation strategies, culminating in a discussion of certification and continuous improvement.
The ISO 27001 standard is designed to help organizations of all sizes protect sensitive data and ensure business continuity. It articulates a risk-based approach, emphasizing the importance of understanding potential threats and vulnerabilities. This includes detailed steps for risk assessment, control implementation, and ongoing monitoring. The standard’s comprehensive nature makes it applicable to various industries and organizational structures.
Introduction to ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides a framework for organizations to manage and control information risks, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring business continuity. This framework is highly adaptable to diverse organizational structures and operational environments.
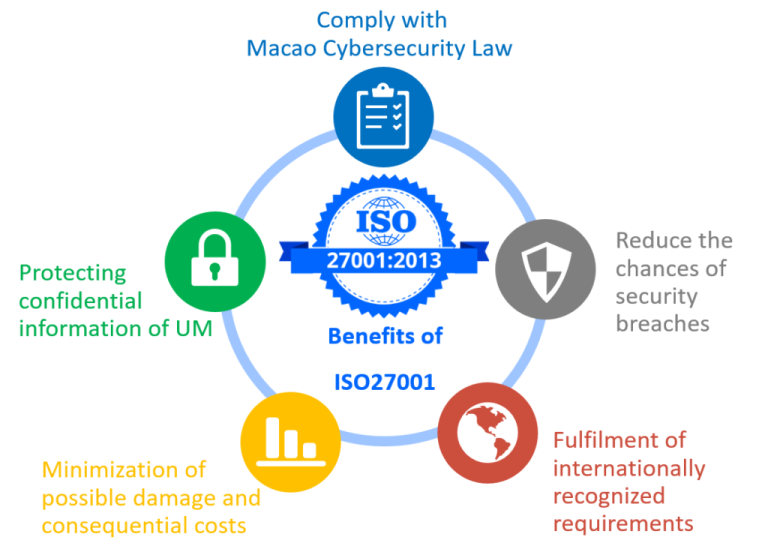
The implementation of ISO 27001 brings several benefits, such as enhanced data security, reduced risk of security breaches, and improved business reputation. It also enables organizations to meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate their commitment to information security to stakeholders. Furthermore, a robust ISMS helps organizations optimize resource allocation, streamline operations, and improve overall efficiency.
Definition of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It articulates the elements necessary for an organization to effectively manage its information risks and enhance its security posture. This standard provides a structured approach to managing information security across the entire organization.
Purpose and Benefits of ISO 27001
The purpose of ISO 27001 is to provide a systematic approach to managing information security risks. It fosters a proactive and preventative mindset towards security threats, minimizing potential damages and disruptions. Organizations benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, reduced security breaches, and improved customer trust. The framework helps organizations demonstrate their commitment to data security to stakeholders, leading to improved brand reputation and potentially attracting new business opportunities.
Key Principles Behind ISO 27001
The key principles behind ISO 27001 are based on a risk-based approach to security. This involves identifying, assessing, and treating information security risks in a systematic manner. Other crucial principles include the continuous improvement of the ISMS, a commitment to stakeholder needs, and a proactive approach to security. These principles ensure a robust and adaptable security framework for the organization.
Historical Overview of the Standard
ISO 27001 evolved from the earlier British Standard BS 7799, which addressed information security management. The standard has undergone several revisions and updates over the years to keep pace with technological advancements and evolving threats. This iterative process ensures that the standard remains relevant and effective in safeguarding information assets.
Types of Organizations Using ISO 27001
ISO 27001 applies to a wide range of organizations, regardless of size or industry. These organizations include financial institutions, healthcare providers, government agencies, educational institutions, and many more. The standard’s adaptability ensures its applicability across various sectors and contexts.
Comparison of ISO 27001 with Other Standards
| Standard | Focus | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | Establishing, implementing, and maintaining an ISMS | Provides a comprehensive framework for managing information security risks, focusing on a risk-based approach. |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Provides a voluntary framework for managing cybersecurity risks | Focuses on identifying and managing cybersecurity risks, offering a more general framework than ISO 27001, and is often used alongside other standards or frameworks. |
This table illustrates the key differences between ISO 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. While both address critical aspects of information security, they have different scopes and objectives. Organizations can leverage both frameworks to achieve a comprehensive approach to information security.
Understanding the ISO 27001 Framework

The ISO 27001 framework provides a structured approach to managing information security risks within an organization. It’s a globally recognized standard, offering a comprehensive set of controls and processes to protect sensitive data and systems. This framework is not merely a checklist, but a dynamic system designed to adapt to evolving threats and organizational needs.
The ISO 27001 framework is based on a cyclical process of risk assessment, control implementation, and ongoing monitoring. It encourages organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities before they cause significant harm. This proactive approach allows organizations to safeguard their reputation, maintain operational continuity, and avoid costly breaches.
Core Components of the ISO 27001 Framework
The framework is built upon several core components, each contributing to a robust information security management system (ISMS). These components include risk assessment, risk treatment, and control implementation. The framework also emphasizes the importance of ongoing monitoring and review, ensuring the effectiveness of the ISMS. Furthermore, it encourages communication and collaboration across different departments to ensure a unified approach to information security.
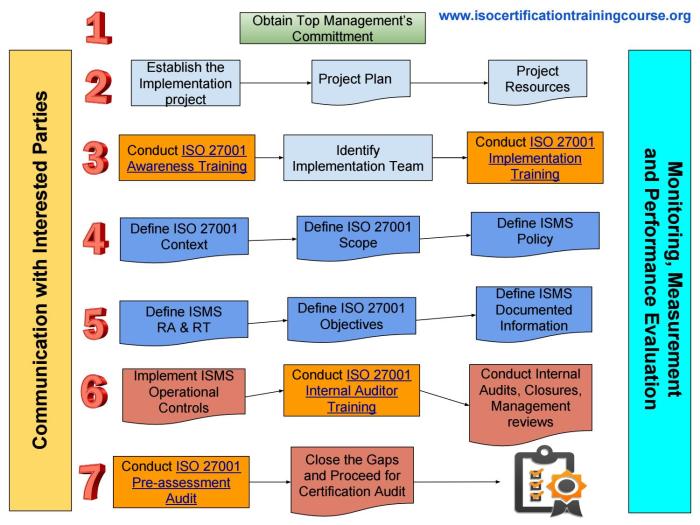
Steps Involved in ISO 27001 Implementation
The implementation process of ISO 27001 is typically a phased approach, allowing organizations to integrate the standard into their existing operations gradually. The initial steps involve establishing the scope of the ISMS, conducting a risk assessment, and defining appropriate controls. Subsequent phases involve implementing these controls, monitoring their effectiveness, and periodically reviewing and updating the ISMS. Organizations often leverage tools and resources to facilitate the process, including templates, checklists, and training materials.
Relationship Between ISO 27001 and Risks
ISO 27001 is inherently linked to risk management. The standard guides organizations in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential information security risks. A strong risk management framework is crucial for compliance with the standard. Understanding the potential consequences of each identified risk is paramount to effective risk treatment.
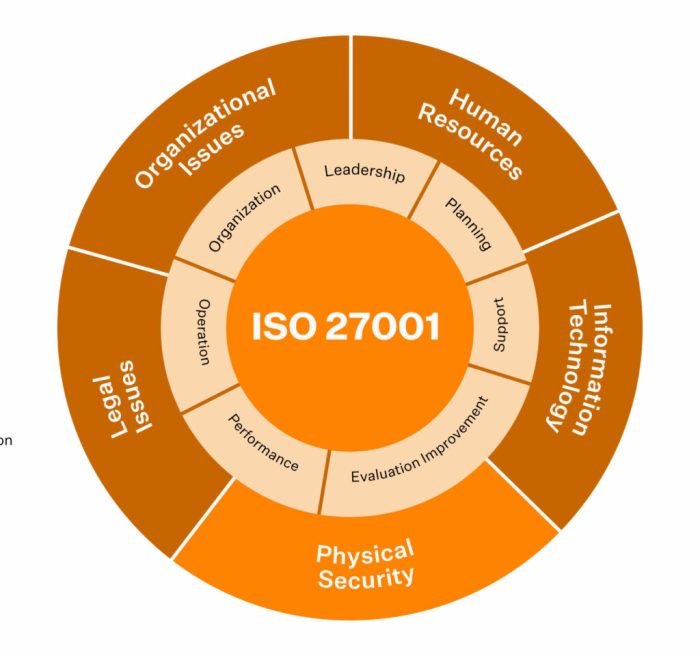
Clauses of ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 standard is structured into distinct clauses, each addressing a specific aspect of information security management. A structured overview of these clauses is presented in the table below:
| Clause | Description |
|---|---|
| 4. Context of the Organization | Understanding the organization’s external and internal environment, including its stakeholders, objectives, and the legal and regulatory framework. |
| 5. Leadership | Establishing the roles, responsibilities, and commitment of leadership towards information security. |
| 6. Planning | Defining the information security objectives and strategies, including risk assessment and treatment plans. |
| 7. Support | Providing the resources, training, and awareness needed for the effective implementation of the ISMS. |
| 8. Operations | Implementing the controls and procedures to ensure the security of information assets. |
| 9. Performance Evaluation | Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the ISMS, identifying areas for improvement. |
| 10. Improvement | Continuously improving the ISMS based on the evaluation results. |
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Process
A comprehensive risk assessment is a critical part of the ISO 27001 implementation. This process involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, analyzing their likelihood and impact, and prioritizing risks for treatment. Organizations should consider various factors, including internal and external threats, the sensitivity of the data, and the potential financial and reputational consequences of a breach. Documented procedures and tools should support the risk assessment process.
Comparison of Risk Management Approaches
Different approaches to information security risk management exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Quantitative methods, relying on numerical data and statistical analysis, provide a precise measure of risk but may struggle with subjective factors. Qualitative methods, focusing on expert judgment and descriptive analysis, offer a flexible approach to risk assessment but can lack objectivity. A combination of both approaches often proves most effective, balancing precision with flexibility. Organizations should choose the approach best suited to their specific context and resources.
Implementing ISO 27001 in Practice

Successfully implementing ISO 27001 requires a systematic approach to building an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). This involves careful planning, meticulous execution, and continuous improvement. A well-structured ISMS will not only meet the standards but also enhance an organization’s overall security posture.
A practical implementation necessitates a deep understanding of the standard’s requirements, coupled with the organization’s specific needs and context. This includes a thorough assessment of existing security controls, identification of vulnerabilities, and development of tailored solutions. A strong ISMS will be adaptable and responsive to evolving threats and changing business needs.
Establishing a Suitable Information Security Management System (ISMS)
Establishing a robust ISMS is crucial for achieving compliance and fostering a security-conscious culture. This involves defining clear roles and responsibilities, establishing processes for risk management, and implementing appropriate controls. The ISMS must be integrated into the organization’s overall operations, ensuring its effectiveness and longevity.
Conducting a Gap Analysis
A gap analysis is a systematic process of identifying the differences between an organization’s current security posture and the requirements of ISO 27001. This process is essential to determine the areas needing improvement and to tailor the implementation to the organization’s specific circumstances. A well-executed gap analysis ensures a focused and efficient implementation strategy. This involves comparing the organization’s current security practices with the clauses and controls Ain rtikeld in ISO 27001. This comparison helps pinpoint any deviations and potential vulnerabilities.
Necessary Documentation for ISO 27001 Implementation
Comprehensive documentation is critical for an effective ISO 27001 implementation. It provides evidence of compliance, aids in training, and supports continuous improvement. Documentation should cover policies, procedures, risk assessments, control implementations, and related activities.
- Policy Documents: These documents Artikel the organization’s commitment to information security and provide a high-level framework for the ISMS.
- Procedures: These detailed instructions guide the implementation and maintenance of security controls. Procedures should address specific actions and responsibilities.
- Risk Assessments: Documented risk assessments are essential to prioritize vulnerabilities and develop appropriate controls. These assessments should consider potential threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts.
- Control Implementations: Records of the implementation of each control, including the chosen method, the responsible personnel, and the completion date, are necessary.
Roles and Responsibilities of Personnel Involved in the Implementation
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure accountability and efficient task allocation during the implementation. This will facilitate a smooth transition and avoid confusion.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Information Security Manager | Overall responsibility for the ISMS, including policy development, risk management, and control implementation. |
| Security Team Members | Specific tasks related to security control implementation and maintenance, such as conducting risk assessments and training employees. |
| Business Units | Understanding and implementing the security controls relevant to their operations. |
| Senior Management | Commitment to the ISMS and providing resources for its successful implementation. |
Developing and Implementing Controls Based on Risk Assessments
Developing and implementing controls based on risk assessments is crucial for mitigating vulnerabilities. Risk assessments should identify potential threats, evaluate their likelihood and impact, and prioritize the controls needed to mitigate the identified risks. This ensures a targeted approach to strengthening security. This involves selecting controls based on the risk assessment results and ensuring the chosen controls are suitable and effective. Implementation includes defining procedures, assigning responsibilities, and monitoring the effectiveness of the controls.
Importance of Employee Training and Awareness Programs, Drata iso 27001
Effective employee training and awareness programs are vital for ensuring that all personnel understand and comply with security policies and procedures. A well-structured program will instill a security-conscious culture and reduce the likelihood of security incidents. These programs help in understanding the importance of their roles in maintaining information security and how their actions impact the overall security posture. They also enhance employee awareness of threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices.
Benefits and Challenges of ISO 27001: Drata Iso 27001

ISO 27001, a globally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS), offers a structured approach to safeguarding sensitive data and assets. Understanding both the advantages and challenges associated with its implementation is crucial for organizations seeking to leverage its benefits effectively.
Implementing ISO 27001 requires a comprehensive understanding of the standard’s principles and practices, coupled with a commitment to continuous improvement. This involves not only establishing controls but also monitoring their effectiveness and adapting them to evolving threats and risks. The process often necessitates significant investment in resources and training, but the potential rewards in terms of enhanced security posture and reputational gains can be substantial.
Key Advantages of Implementing ISO 27001
Implementing ISO 27001 offers numerous advantages that extend beyond simply meeting regulatory requirements. A robust information security management system fosters a culture of security awareness, leading to improved protection of sensitive data and intellectual property.
- Enhanced Customer Trust and Confidence: Demonstrating a commitment to information security through ISO 27001 certification builds trust with customers and stakeholders. This increased trust translates into enhanced brand reputation, increased customer loyalty, and potentially, higher revenue streams.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: A well-defined and implemented information security management system, as guided by ISO 27001, significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks. This protection extends to sensitive customer data, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Implementing ISO 27001 can lead to improved operational efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing redundancies. This can lead to cost savings in the long run, as resources are used more effectively.
- Increased Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have specific regulatory requirements related to information security. Implementing ISO 27001 often helps organizations meet these requirements, reducing the risk of penalties and ensuring continued business operations.
Potential Challenges in ISO 27001 Implementation
While the benefits of ISO 27001 are considerable, the implementation process can present certain challenges. These challenges, however, can be mitigated with careful planning and execution.
- High Initial Investment: Implementing ISO 27001 requires initial investments in resources such as personnel, training, and security tools. This upfront cost can be a barrier for some organizations, especially smaller ones. However, the long-term cost savings from reduced risks and increased operational efficiency can outweigh the initial investment.
- Complexity of the Standard: The standard is comprehensive, and understanding all its aspects and requirements can be challenging. Organizations need to ensure they have the necessary expertise and resources to navigate the standard effectively.
- Maintaining Certification: Maintaining ISO 27001 certification requires ongoing effort and continuous improvement. Organizations need to demonstrate ongoing compliance with the standard and adapt to evolving security threats.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing new processes and procedures can encounter resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing methods. Effective communication and training are essential to address this challenge.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Addressing the challenges associated with ISO 27001 implementation requires a proactive and strategic approach.
- Phased Implementation: A phased approach allows organizations to tackle the standard’s requirements in manageable steps. This ensures a more controlled and less overwhelming implementation process.
- Expert Consultation: Engaging external experts can provide guidance and support throughout the implementation process. They can help organizations navigate the complexities of the standard and tailor it to their specific needs.
- Employee Training: Comprehensive training for employees is crucial for successful implementation. This training should cover the importance of information security, the organization’s policies, and their roles in maintaining security.
- Regular Audits: Regular internal audits help identify gaps and areas for improvement in the security management system. This continuous monitoring is essential for maintaining compliance and improving security posture over time.
Real-World Examples of Successful Implementations
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented ISO 27001, achieving significant improvements in their information security posture. Examples include large corporations, small businesses, and even government entities. These implementations demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of the standard.
- Example 1: [Insert a real-world example of a company successfully implementing ISO 27001. Provide brief details of the company and the positive outcomes they achieved.]
- Example 2: [Insert a second real-world example of a company successfully implementing ISO 27001. Provide brief details of the company and the positive outcomes they achieved.]
Cost-Benefit Analysis of ISO 27001
A cost-benefit analysis of ISO 27001 implementation should consider both the initial costs and the long-term benefits. The benefits often outweigh the costs, but a thorough analysis is crucial.
- Cost Considerations: The cost of implementation encompasses the expenses for training, consultancy, documentation, and security tools. These costs vary based on the size and complexity of the organization.
- Benefit Considerations: Benefits include reduced risk of data breaches, enhanced customer trust, increased operational efficiency, and potential compliance with regulations. These benefits can lead to significant financial savings and improved reputation over time.
Auditing and Certification
The ISO 27001 certification process is crucial for demonstrating an organization’s commitment to information security. This rigorous process validates that the implemented controls are effective and align with international best practices. A successful certification not only enhances the organization’s reputation but also fosters trust with stakeholders.
The certification process involves a structured evaluation of the organization’s information security management system (ISMS) against the requirements of ISO 27001. This evaluation is conducted by a third-party certification body, an independent organization recognized for its competence and impartiality. The process typically comprises several stages, each designed to ensure a thorough assessment of the ISMS.
ISO 27001 Certification Process
The ISO 27001 certification process generally follows these stages: initial assessment, documentation review, on-site audit, management review, and certification award (or non-conformity and corrective actions). The certification body plays a pivotal role in each stage, guiding the organization through the process and ensuring adherence to the standard.
Role of Certification Bodies
Certification bodies act as impartial third parties, assessing an organization’s compliance with ISO 27001. Their role extends beyond mere verification; they also offer guidance and support throughout the certification journey. Certification bodies possess specialized expertise in information security management systems and the requirements of ISO 27001. They ensure a fair and objective assessment of the organization’s ISMS. This independence fosters trust and credibility.
Internal Audit Requirements
Internal audits are vital for maintaining an effective ISMS. They assess the effectiveness of the implemented controls and identify any potential weaknesses. Internal audit programs should be documented and clearly defined. These programs should include regular, scheduled audits covering all critical areas of the ISMS. These audits should be conducted by trained personnel with a thorough understanding of the standard and the organization’s specific controls. Documentation is essential for internal audit findings, actions, and corrective measures.
Importance of Management Reviews
Regular management reviews are integral to an effective ISMS. These reviews allow management to assess the performance of the ISMS, identify areas for improvement, and ensure its ongoing suitability and effectiveness. Management reviews provide a platform for discussing risks and opportunities, and adapting the ISMS accordingly. This proactive approach ensures that the ISMS remains relevant and responsive to evolving business needs.
Types of Audits
| Type of Audit | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Assessment | Evaluates the organization’s readiness for certification and identifies areas for improvement. |
| Internal Audits | Regular assessments of the ISMS against the documented policies and procedures. |
| Certification Audits | Thorough evaluations by a third-party certification body to confirm compliance with ISO 27001. |
| Follow-up Audits | Periodic assessments will be conducted after certification to ensure ongoing compliance. |
Typical Audit Procedures
Typical audit procedures for assessing compliance with ISO 27001 include reviewing documentation, interviewing personnel, examining controls, and testing their effectiveness. The audit process typically follows a structured approach, including planning, execution, and reporting. Documented evidence is meticulously collected and evaluated against the criteria of ISO 27001. A clear audit trail is maintained for traceability and transparency.
Continuous Improvement and Maintenance

Source: sprinto.com
A robust Information Security Management System (ISMS) is not a static entity; it requires ongoing refinement and adaptation to maintain effectiveness. Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle, ensuring that the ISMS remains aligned with evolving business needs and threats. This section details strategies for maintaining and enhancing the ISMS.
Maintaining an effective ISMS necessitates a proactive approach to risk management and a flexible framework for responding to changes. The system should not be viewed as a one-time implementation but rather as a dynamic process requiring continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adjustments.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement within an ISMS
Continuous improvement strategies are essential for maintaining the effectiveness of an ISMS. Proactive identification and mitigation of emerging threats are critical. This requires regular reviews of the security controls and their effectiveness in addressing evolving threats. Regular security awareness training for personnel is also vital.
- Regular audits and assessments: These assessments, performed periodically, provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the ISMS. Results can be used to identify areas needing improvement and to enhance existing controls. For example, an annual penetration test might reveal vulnerabilities in network security, prompting updates to firewalls or intrusion detection systems.
- Employee feedback mechanisms: Gathering feedback from employees on their experiences with security policies and procedures is crucial. This feedback can highlight areas of confusion or frustration, allowing for adjustments to improve user experience and compliance.
- Benchmarking against industry best practices: Staying abreast of industry standards and best practices is crucial. This allows for comparison and identification of areas where the organization can improve its security posture. For instance, benchmarking against the NIST Cybersecurity Framework helps organizations identify gaps and enhance their security controls.
Importance of Ongoing Risk Management
Ongoing risk management is vital for maintaining the effectiveness of an ISMS. The business environment is constantly changing, bringing new risks and vulnerabilities. A static risk assessment is inadequate; a dynamic approach is essential.
- Regular risk assessments: Periodically assessing risks and vulnerabilities ensures that the ISMS remains relevant and effective. This involves identifying potential threats, analyzing their likelihood and impact, and prioritizing mitigation strategies.
- Proactive threat intelligence: Staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities is crucial for adapting security controls. Subscription to threat intelligence feeds allows organizations to proactively address emerging risks.
- Adapting to changing business needs: Changes in business operations or technologies necessitate corresponding adjustments to the ISMS. This might include adding new controls, modifying existing ones, or adjusting security awareness training based on new operational procedures.
Process of Updating and Maintaining the ISMS
Maintaining the ISMS requires a systematic approach to updating and refining the document set. This includes policies, procedures, and the security controls themselves. The process needs to be well-documented to maintain traceability.
- Policy review and updates: Policies should be reviewed at least annually to ensure they remain aligned with current regulations, industry best practices, and business needs. Updating policies when required is essential.
- Procedure reviews and updates: Procedures should be reviewed periodically to ensure their continued relevance and effectiveness. For instance, changes in technology might necessitate modifications to procedures for accessing sensitive data.
- Control testing and improvements: Regular testing of security controls helps to identify vulnerabilities and inefficiencies. This allows for the improvement and optimization of security measures.
Responding to Changes in the Business Environment
An ISMS must adapt to changing business needs and external factors. This includes technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving threat landscapes. Adaptability is crucial for maintaining an effective security posture.
- Identifying changes: Proactively monitoring industry trends, technological advancements, and regulatory updates is essential. For example, the introduction of cloud computing necessitates adjustments to access controls and data security policies.
- Evaluating impact: Evaluating the impact of these changes on the organization’s security posture is crucial. This involves assessing potential vulnerabilities and risks.
- Implementing necessary adjustments: Implementing necessary adjustments to the ISMS to address the identified risks and vulnerabilities is critical. This may include updating policies, procedures, or controls.
Maintaining Compliance with ISO 27001
Maintaining ISO 27001 compliance requires a dedicated plan and a clear understanding of the required documentation and procedures.
- Documentation updates: Document updates to reflect changes in the ISMS should be scheduled and documented.
- Internal audits: Conducting internal audits at regular intervals is essential to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 27001 standards.
- Management review meetings: Regular management reviews of the ISMS are critical to assess its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Frequency of Activities
A well-defined schedule for activities ensures that the ISMS remains current and effective.
| Activity | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Risk assessment | Annually |
| Policy review | Annually |
| Procedure review | Biannually |
| Control testing | Quarterly |
| Internal audit | Semi-annually |
| Management review | Quarterly |
Last Recap
In conclusion, implementing Drata ISO 27001 offers a significant pathway to enhancing information security posture. By adopting the standard’s principles and practices, organizations can strengthen their defenses, mitigate risks, and build trust with stakeholders. While challenges may arise during implementation, a well-defined plan, proper resource allocation, and continuous improvement strategies can lead to a successful outcome. The journey toward ISO 27001 certification ultimately delivers a more secure and resilient organization.