STEM Education Masters A Deep Dive
A master’s degree in STEM education opens doors to exciting career paths and impactful teaching roles. This program equips educators with advanced knowledge and skills to inspire future generations in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. It delves into the pedagogical approaches and curriculum design essential for fostering a love of STEM subjects. The program structure is carefully crafted to balance theoretical understanding with practical application.
The program typically encompasses specialized tracks like math education, science education, and engineering education, each offering unique course content tailored to specific disciplines. A comprehensive curriculum covering research methods, educational psychology, and curriculum design prepares students for roles in schools, universities, or research institutions. This allows students to specialize in their area of interest while also developing broader STEM educational expertise.
Introduction to STEM Master’s Degrees

A Master’s degree in STEM education equips educators with advanced knowledge and pedagogical skills to teach science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects effectively. These programs go beyond undergraduate coursework, focusing on the specific needs and challenges of teaching STEM disciplines at various levels, from K-12 to higher education. This specialized training fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity within a STEM framework.
The academic structure of a STEM education Master’s program typically involves coursework, research, and practical experience. Students engage in in-depth study of pedagogical theories, learning methodologies, and assessment strategies specific to STEM subjects. Many programs incorporate field experiences, allowing students to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world classroom settings.
Academic Structure and Curriculum
Master’s programs in STEM education emphasize both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Students typically complete core courses in educational psychology, curriculum design, and assessment alongside specialized STEM education courses. The curriculum often includes opportunities for research projects, culminating in a thesis or capstone project, allowing students to delve into a specific area of interest within STEM education. This hands-on experience provides crucial insight into the intricacies of teaching STEM subjects.
Specializations within STEM Education
STEM education Master’s degrees frequently offer specializations in various disciplines. This allows students to focus their studies and tailor their skills to a particular STEM field.
- Mathematics education programs delve into pedagogical approaches for teaching mathematical concepts, often with an emphasis on developing students’ critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
- Science education programs explore effective methods for teaching scientific principles and processes, emphasizing hands-on activities and inquiry-based learning. These programs often include specialized training in specific science disciplines like biology, chemistry, or physics.
- Engineering education programs focus on the development of engineering design thinking and problem-solving skills, preparing students to teach engineering principles engagingly and practically.
Potential Career Paths
Graduates of STEM education Master’s programs are well-positioned for diverse career paths. These include teaching positions at various levels (K-12, community college, university), educational research roles, curriculum development, and educational leadership positions within STEM departments. They may also pursue positions in STEM-related industries or government agencies.
Comparison of Specializations
| Specialization | Key Course Content | Potential Career Paths | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Math Ed | Number theory, algebra, geometry, statistics, pedagogical approaches to teaching math, assessment strategies for mathematical understanding, technology integration in math classrooms | High school math teacher, middle school math teacher, university math instructor, math curriculum developer, and educational researcher specializing in math education | Individuals interested in teaching mathematics at various levels or those seeking to improve their understanding of mathematical concepts and pedagogical practices |
| Sci Ed | Scientific inquiry, research methods, specific science disciplines (biology, chemistry, physics), educational technology, curriculum design for science education, assessment strategies for science understanding | High school science teacher, middle school science teacher, science museum educator, science curriculum developer, science outreach specialist, and educational researcher specializing in science education | Individuals interested in teaching science at various levels, those passionate about scientific principles and processes, or those seeking to develop innovative science curriculum |
| Eng Ed | Engineering design principles, problem-solving strategies, project-based learning, engineering design process, hands-on activities, educational technology, curriculum development for engineering | High school engineering teacher, middle school engineering teacher, university engineering instructor, engineering curriculum developer, STEM outreach coordinator | Individuals interested in teaching engineering, passionate about engineering design, or seeking to create innovative learning environments for engineering |
Benefits and Advantages of Pursuing a STEM Master’s Degree
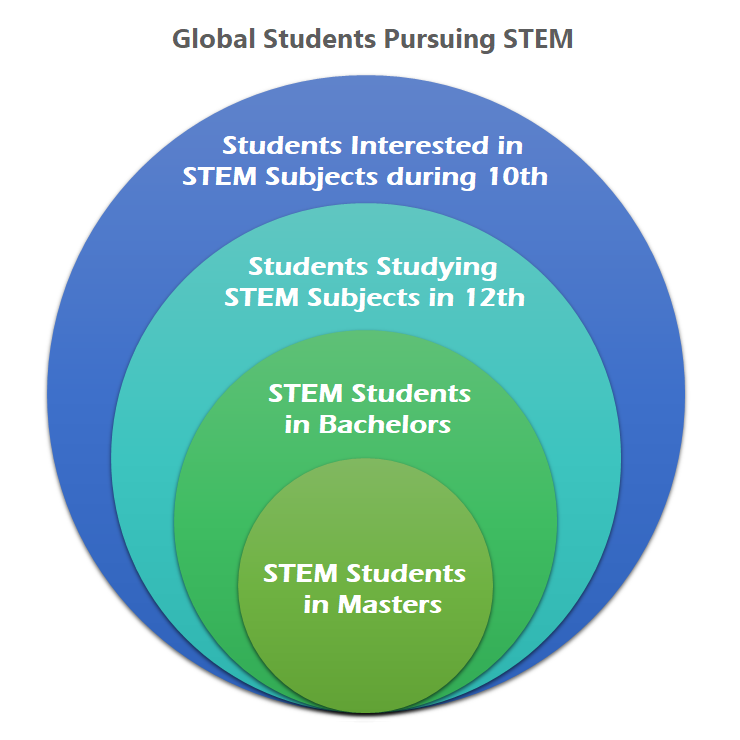
Source: Shiksha.ws
A Master’s degree in STEM education offers significant advantages over a Bachelor’s degree, particularly in terms of career advancement, salary potential, and professional development opportunities. It signifies a deeper commitment to the field and provides a pathway to specialized knowledge and expertise. This enhanced understanding translates into a more impactful contribution to the STEM education community.
Master’s programs in STEM education equip graduates with a robust foundation in pedagogy and curriculum design. This advanced knowledge, coupled with practical experience, enables teachers to create engaging and effective learning environments for students. The focus on research and innovation also allows teachers to stay abreast of the latest advancements in their field, enhancing their ability to prepare students for future challenges and opportunities.
Career Advancement and Salary Increases
A Master’s degree significantly boosts career prospects in STEM education. Graduates often secure leadership roles in schools, colleges, or educational organizations. The enhanced skillset and expertise often translate into higher salaries, potentially exceeding those of individuals with only a Bachelor’s degree. For instance, teachers with Master’s degrees are frequently promoted to positions like department heads, curriculum coordinators, or even university professors. This increased responsibility often comes with higher compensation packages.
Opportunities for Professional Development and Leadership Roles
Master’s programs in STEM education provide numerous opportunities for professional development, fostering leadership capabilities. These programs often integrate workshops, seminars, and mentorship programs that enable graduates to acquire practical skills and knowledge. Participants are given chances to hone their communication, collaboration, and project management skills, which are essential for leadership roles in educational settings. Furthermore, many programs emphasize action research, allowing students to develop practical solutions to real-world educational challenges.
Enhancement of Teaching Skills and Pedagogical Knowledge
Master’s programs in STEM education go beyond theoretical knowledge, focusing on practical application and innovation. Students learn advanced pedagogical approaches, including innovative teaching strategies, curriculum design principles, and assessment methodologies. These programs often incorporate fieldwork and classroom observations, providing students with firsthand experience in applying theoretical concepts to real-world teaching situations. This deep understanding of pedagogy strengthens their ability to craft engaging and effective STEM lessons, leading to enhanced student outcomes.
Professional Development Opportunities for STEM Master’s Students
These programs often offer a variety of professional development opportunities, tailored to enhance skills and knowledge.
- Workshops and Seminars: These events often focus on specific STEM topics, pedagogical approaches, or educational technology tools. They allow students to gain in-depth knowledge and practical skills in a focused environment.
- Mentorship Programs: Experienced educators guide students, providing valuable insights, feedback, and support as they navigate their careers.
- Networking Events: Connecting with peers, professionals, and mentors from the field expands opportunities for collaboration and career advancement.
- Action Research Projects: These projects allow students to identify and address real-world problems in STEM education. The results can lead to published research or innovative teaching practices.
- Field Experience and Classroom Observations: Hands-on experience in diverse educational settings provides a practical understanding of different learning styles and educational contexts. Students develop practical classroom management skills and gain a deeper appreciation of student needs.
Curriculum and Coursework in STEM Education Master’s Programs: Master’s Degree In STEM Education

Source: collegecliffs.com
Master’s programs in STEM education equip aspiring educators with the theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary to effectively teach science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. These programs go beyond undergraduate coursework, delving deeper into the pedagogical strategies and research methodologies that underpin effective STEM instruction. A key focus is on developing educators capable of fostering a love of learning and critical thinking in their students.
The curriculum typically blends theoretical frameworks with practical application, allowing students to synthesize their learning and develop innovative approaches to STEM teaching. Emphasis is placed on fostering a deep understanding of STEM content, not just as a subject matter expert but also as an educator. Students learn to translate complex concepts into accessible and engaging lessons for diverse learners.
Common Coursework
A significant portion of the curriculum is dedicated to foundational coursework in STEM education. Courses often cover various aspects of teaching and learning, encompassing research methodologies, educational psychology, curriculum design, and assessment strategies. A strong understanding of how students learn is vital to creating effective STEM instruction.
Research Methods
Master’s programs frequently include courses on research methodologies specific to education. These courses equip students with the skills to design, conduct, and interpret research studies related to STEM education. Learning to critically evaluate existing research and develop research questions is crucial for informing and improving practice. Examples of research topics include examining the effectiveness of different instructional strategies for teaching specific STEM concepts, investigating the impact of technology integration in STEM classrooms, and studying the factors that influence student engagement in STEM subjects.
Educational Psychology, Master’s degree in STEM education
Understanding how students learn and develop is paramount. Courses in educational psychology provide insight into the cognitive, social, and emotional factors that influence student learning, specifically within the STEM context. This knowledge allows educators to tailor their instruction to meet the diverse needs of their students, fostering an inclusive and supportive learning environment.
Curriculum Design
Master’s programs offer courses focused on the design and development of high-quality STEM curricula. These courses delve into the principles of effective curriculum design, aligning learning objectives with appropriate teaching strategies and creating engaging learning experiences for students. Specific elements often explored include creating standards-aligned lessons, integrating real-world applications, and designing assessments to measure student understanding.
Research Topics and Projects
Students often engage in independent research projects or participate in collaborative research efforts. Possible research topics could include investigating the effectiveness of inquiry-based learning in STEM, analyzing the impact of different assessment methods on student learning outcomes, or examining the influence of culturally responsive teaching practices on student engagement in STEM. These projects allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world contexts and contribute to the existing body of research in STEM education.
Practical Experience and Fieldwork
Practical experience is crucial for developing a deep understanding of the realities of teaching. Master’s programs often incorporate fieldwork components, such as classroom observations, student teaching experiences, and collaborations with practicing STEM educators. These experiences provide students with the opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings and gain valuable insights into effective teaching practices.
Teaching Methodologies and Pedagogical Approaches
Courses dedicated to teaching methodologies explore a range of approaches to STEM instruction. These approaches often include project-based learning, inquiry-based learning, and problem-based learning. Emphasis is placed on developing strategies to engage students actively in their learning and foster critical thinking skills. DA discussion of the benefits and limitations of different approaches is key.
Typical Course Structure
| Semester | Courses | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Fall | Introduction to STEM Education Research, Educational Psychology in STEM, Curriculum Development in STEM | 9-12 |
| Spring | Advanced Research Methods in Education, STEM Pedagogical Strategies, Classroom Management and Discipline | 9-12 |
| Summer | Student Teaching Experience, Research Project, Seminar | 6-9 |
Wrap-Up
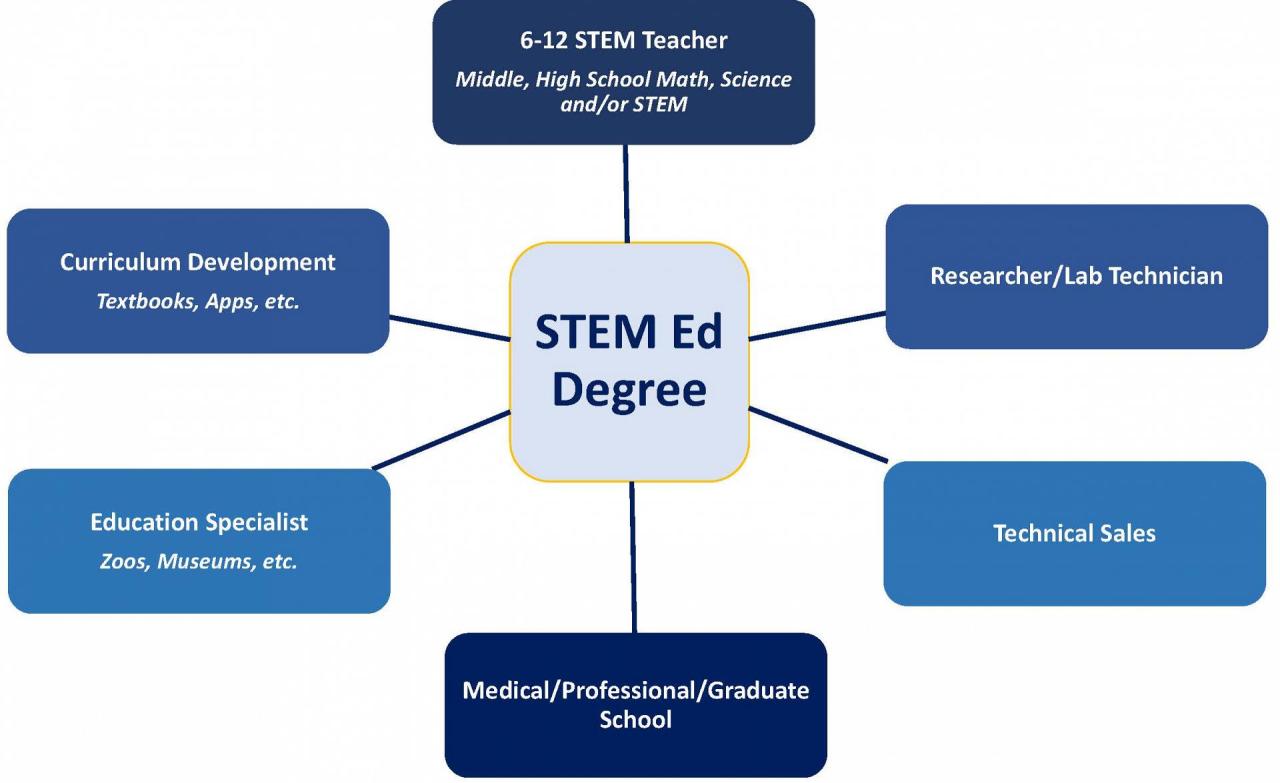
Source: utc.edu
In conclusion, a Master’s degree in STEM education provides a pathway to advanced teaching roles, with the potential for significant career advancement. The curriculum, focused on developing strong pedagogical skills and deep understanding of STEM subjects, sets graduates up for success in a dynamic field. The various specializations within the program allow for tailored learning experiences and career paths, ultimately enriching the teaching profession and shaping the next generation of STEM leaders.





